The Great Decoupling: Economic Implications And Global Shifts
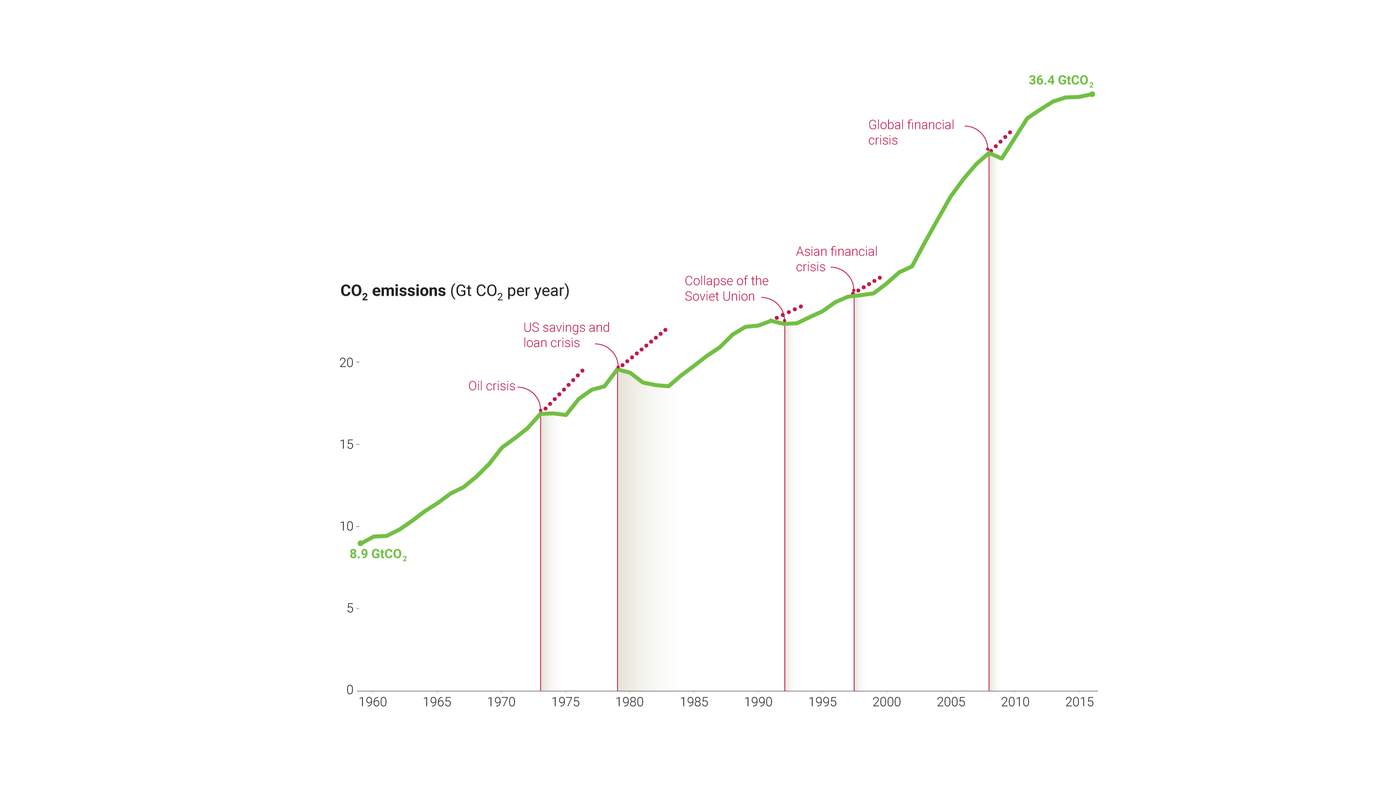
Table of Contents
Defining "The Great Decoupling" and its Drivers
The Great Decoupling refers to the diminishing interdependence of major economies, most notably the decoupling of the US and Chinese economies. This isn't a sudden break but rather a gradual process driven by a confluence of factors that are reshaping global economic relationships. Key drivers include:
-
Geopolitical tensions and the rise of technological nationalism: The increasing rivalry between the US and China, encompassing trade disputes, technological competition (particularly in areas like 5G and artificial intelligence), and differing geopolitical ambitions, is a primary driver of economic decoupling. This rivalry fuels policies aimed at protecting national interests, even at the expense of global economic efficiency.
-
Trade wars and protectionist policies: The imposition of tariffs, trade restrictions, and sanctions by various countries reflects a growing trend towards protectionism. This undermines the principles of free trade and fosters a more fragmented global market. The US-China trade war serves as a prime example of this trend impacting economic decoupling.
-
Diversification of supply chains: Businesses are increasingly seeking to diversify their supply chains to reduce their reliance on single countries or regions. This "de-risking" strategy aims to enhance supply chain resilience and mitigate the impact of geopolitical instability, leading to a reduction in interdependence. Nearshoring and friend-shoring are becoming increasingly popular strategies.
-
Differing economic and political systems: The fundamental differences in economic and political systems between major powers, particularly between democratic and authoritarian states, contribute to growing mistrust and a decreased willingness to cooperate on global economic issues. This divergence in ideologies further fuels economic decoupling.
Economic Implications of The Great Decoupling
The Great Decoupling carries significant economic implications, impacting global trade, investment, and overall growth.
-
Impacts on global trade and investment: We are witnessing an increased regionalization of trade, with countries prioritizing partnerships and trade agreements within their respective spheres of influence. This trend is further fueled by a shift in investment patterns toward "friend-shoring" (investing in countries with aligned political and security interests) and "near-shoring" (relocating production closer to home markets). This regionalization of trade potentially leads to trade fragmentation and reduced global efficiency.
-
Effects on global growth and stability: The decoupling process could lead to slower overall economic growth compared to a scenario of continued globalization. Increased regionalization increases the risk of economic instability and volatility, as economies become less interconnected and less able to absorb shocks. Furthermore, the decoupling process is contributing to significant shifts in inflation and commodity prices, impacting economies worldwide.
Global Shifts and Power Dynamics in the Age of Decoupling
The Great Decoupling is reshaping global power dynamics in several crucial ways.
-
Reshaping of global power dynamics: We are witnessing the rise of new economic and geopolitical players, challenging the established order. The formation of new economic blocs and alliances reflects this shift, as countries seek to align themselves with like-minded partners. Competition for resources and technological dominance is intensifying, leading to increased geopolitical tensions.
-
Impact on developing economies: Developing economies face both opportunities and challenges. While some may benefit from increased investment and trade within regional blocs, others may be negatively impacted by reduced access to global markets and resources. This process could exacerbate global inequality, necessitating diversified economic strategies for developing nations to navigate the changing landscape.
The Role of Technology in The Great Decoupling
Technological advancements play a crucial role in shaping the Great Decoupling.
- The race for technological dominance, particularly in areas like AI, 5G, and semiconductors, is fueling technological nationalism. Countries are increasingly implementing restrictions on technology transfer, driven by national security concerns. This limits global collaboration and innovation, driving further fragmentation.
Conclusion
The Great Decoupling represents a profound shift in the global economic order, driven by geopolitical tensions and technological rivalry. It presents both opportunities and risks. Understanding its implications is crucial for businesses, governments, and individuals. The increased regionalization of trade, shifting investment patterns, and the rise of technological nationalism are reshaping global power dynamics and impacting global growth and stability. To effectively navigate this evolving landscape, further research into economic decoupling trends, managing decoupling risks, and understanding the great decoupling's implications for your sector is essential. Proactive adaptation and strategic planning are crucial for success in this new era of global economics.

Featured Posts
-
 Brekelmans India Strategie Maximalisatie Van De Samenwerking
May 09, 2025
Brekelmans India Strategie Maximalisatie Van De Samenwerking
May 09, 2025 -
 Elizabeth Line Strikes February And March Service Disruptions
May 09, 2025
Elizabeth Line Strikes February And March Service Disruptions
May 09, 2025 -
 North Idaho Event Conservative Commentator Jeanine Pirro To Appear
May 09, 2025
North Idaho Event Conservative Commentator Jeanine Pirro To Appear
May 09, 2025 -
 Doohans Future At Williams Addressing The Colapinto Replacement Rumors
May 09, 2025
Doohans Future At Williams Addressing The Colapinto Replacement Rumors
May 09, 2025 -
 Adin Hills Strong Goaltending Propels Golden Knights Past Blue Jackets
May 09, 2025
Adin Hills Strong Goaltending Propels Golden Knights Past Blue Jackets
May 09, 2025
