The Hurdles Of Robotic Nike Shoe Assembly
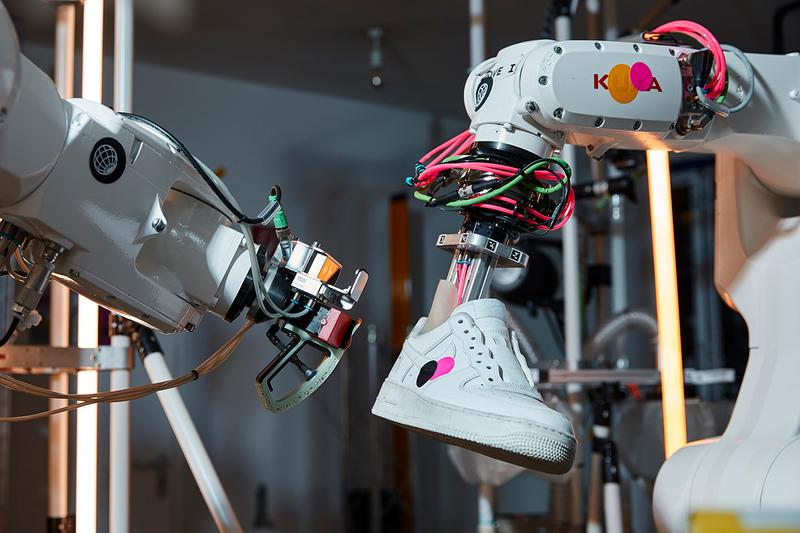
Table of Contents
Technological Limitations in Robotic Shoe Assembly
The intricate nature of shoe assembly presents a formidable challenge for robotic systems. Current technology struggles to match the precision, dexterity, and adaptability required for efficient and high-quality production.
Precision and Dexterity Challenges
Robots face significant difficulties in performing the delicate and complex tasks involved in shoe manufacturing. Achieving the necessary precision and dexterity remains a major technological hurdle.
- Complex stitching patterns: Many Nike shoe designs incorporate intricate stitching patterns that require a high degree of manual skill and fine motor control, currently beyond the capabilities of most robots.
- Delicate material handling: Shoe materials range from supple leather to robust synthetic fabrics, each requiring specific handling techniques to avoid damage. Robots struggle to adapt to this variability.
- Variable shoe sizes and designs: Nike produces shoes in a vast array of sizes and styles, each with unique assembly requirements. Adapting robotic systems to handle this diversity is a significant engineering challenge.
- Accurate adhesive application: Precise application of adhesives is crucial for durability and aesthetics. Current robotic systems often lack the accuracy and control needed for consistent, high-quality bonding.
Advanced sensors, coupled with sophisticated AI algorithms, are crucial for overcoming these precision and dexterity challenges. Further research and development in these areas are critical for advancing robotic footwear production.
Adaptability to Diverse Shoe Models
Nike's diverse product line, featuring numerous styles and materials, presents a significant obstacle to robotic automation. Re-programming robots for each new shoe model is expensive and time-consuming, hindering the scalability of robotic systems.
- Different materials: From leather and suede to textiles and synthetics, the range of materials used in Nike shoes requires specialized handling and processing techniques.
- Varying construction methods: Different shoe designs utilize different construction methods, impacting the assembly process and necessitating re-programming of robotic systems.
- Unique design features: Innovative design features, such as unique lacing systems or complex overlays, further complicate the automation process.
- Frequent product updates: Nike frequently introduces new shoe models and updates existing designs, adding to the re-programming burden and increasing costs.
The need for flexible and adaptable robotic systems capable of handling a wide range of shoe designs without extensive re-programming is paramount. Modular robotic systems and AI-driven learning algorithms could offer solutions to this challenge.
Integration with Existing Manufacturing Processes
Integrating robots into existing Nike factory lines is a complex and costly undertaking. Compatibility issues with legacy equipment, workforce retraining, and workflow redesign pose significant logistical and financial hurdles.
- Compatibility issues with legacy equipment: Existing factory equipment may not be compatible with new robotic systems, requiring significant modifications or replacements.
- Worker retraining: Integrating robots requires retraining existing workers to operate and maintain the new systems, demanding investment in training programs.
- Workflow redesign: Introducing robots often necessitates a complete redesign of the manufacturing workflow to optimize efficiency and integration.
- System integration complexities: Integrating disparate robotic systems and software platforms into a cohesive whole presents significant technical challenges.
The high cost and potential for production downtime associated with integration represent major obstacles to the widespread adoption of robotic shoe assembly.
Economic Factors Hindering Robotic Shoe Assembly
The substantial economic implications of implementing robotic systems in shoe manufacturing represent a significant barrier to widespread adoption.
High Initial Investment Costs
The upfront cost of purchasing, installing, and maintaining advanced robotics systems is substantial, making it a significant barrier, especially for smaller manufacturers.
- Robot cost: The price of advanced industrial robots capable of performing complex tasks is significant.
- Integration costs: Integrating robots into existing production lines requires substantial investment in modifications and infrastructure.
- Specialized software: Developing and implementing specialized software for robotic control and coordination is expensive.
- Maintenance contracts: Maintaining advanced robotic systems requires specialized technicians and ongoing maintenance contracts, adding to the overall cost.
- Skilled technicians: Hiring and training skilled technicians to operate and maintain the robotic systems represents a significant ongoing expense.
A thorough cost-benefit analysis is critical before investing in robotic shoe assembly, as the high initial outlay can be daunting.
Return on Investment (ROI) Uncertainty
Predicting the long-term ROI of robotic shoe assembly is challenging, depending on various factors, and the uncertainty deters investment.
- Predicting production efficiency gains: Accurately estimating the increase in production efficiency resulting from automation is difficult.
- Accounting for downtime and repair costs: Unforeseen downtime and repair costs can significantly impact the overall ROI.
- Calculating long-term maintenance expenses: Accurately predicting long-term maintenance expenses is crucial for a realistic ROI assessment.
The rapid pace of technological change further complicates ROI calculations, making long-term projections inherently uncertain.
Workforce and Societal Implications
The introduction of robotic systems in manufacturing inevitably raises concerns about job displacement and the need for workforce adaptation.
Job Displacement Concerns
Automation in the footwear industry, like in many manufacturing sectors, could lead to job losses for human workers. Addressing this concern requires proactive measures.
- Need for retraining programs: Investing in retraining programs to equip displaced workers with skills relevant to the changing job market is crucial.
- Potential for new job creation: The adoption of robotics creates new jobs in areas such as robotics maintenance, programming, and system integration.
- Societal impact of automation: The societal impact of widespread automation needs careful consideration and mitigation strategies.
The Need for Skilled Labor
Operating and maintaining advanced robotic systems requires specialized skills, leading to a growing demand for skilled technicians and programmers.
- Training programs for existing workers: Companies need to invest in training programs to upskill their existing workforce.
- Collaboration between educational institutions and industry: Close collaboration between educational institutions and industry is needed to develop relevant training curricula.
- Attracting talent in the robotics field: Companies need to develop strategies to attract and retain talent in the rapidly growing field of robotics.
Conclusion
While robotic Nike shoe assembly offers the potential for increased efficiency and lower costs, significant hurdles remain. Technological limitations, high investment costs, and ROI uncertainty pose considerable challenges to widespread adoption. Addressing these issues requires significant technological advancements, careful strategic planning, and a concerted focus on workforce development. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for the future of automated shoe manufacturing and the broader footwear industry.
Call to Action: Further research and development are vital to overcome the hurdles of robotic Nike shoe assembly and unlock the full potential of automation in footwear manufacturing. Let's collaborate to address the challenges and innovate for a more efficient and sustainable future in this critical industry.

Featured Posts
-
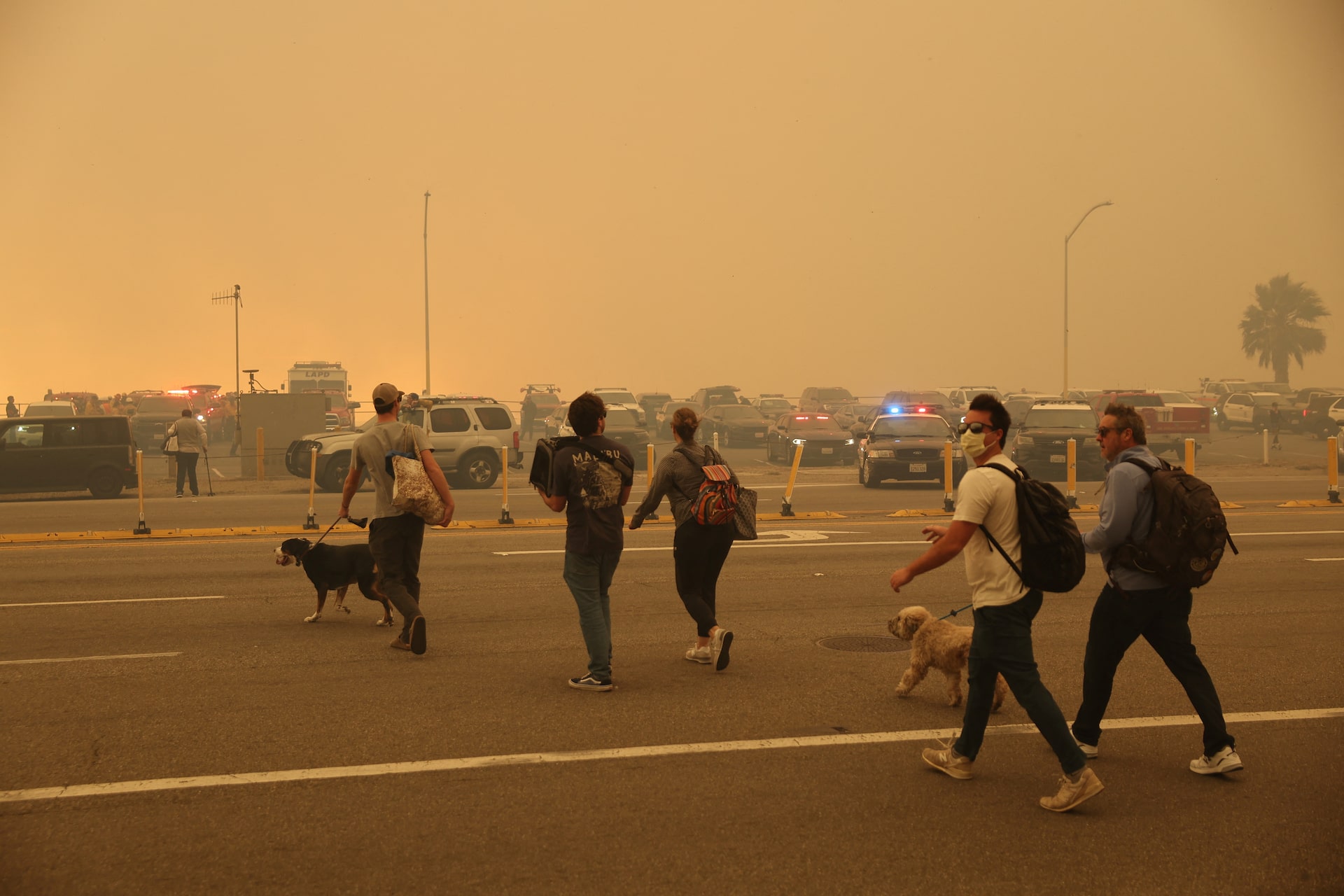 The Los Angeles Wildfires A Reflection Of Our Societal Acceptance Of Disaster Betting
Apr 22, 2025
The Los Angeles Wildfires A Reflection Of Our Societal Acceptance Of Disaster Betting
Apr 22, 2025 -
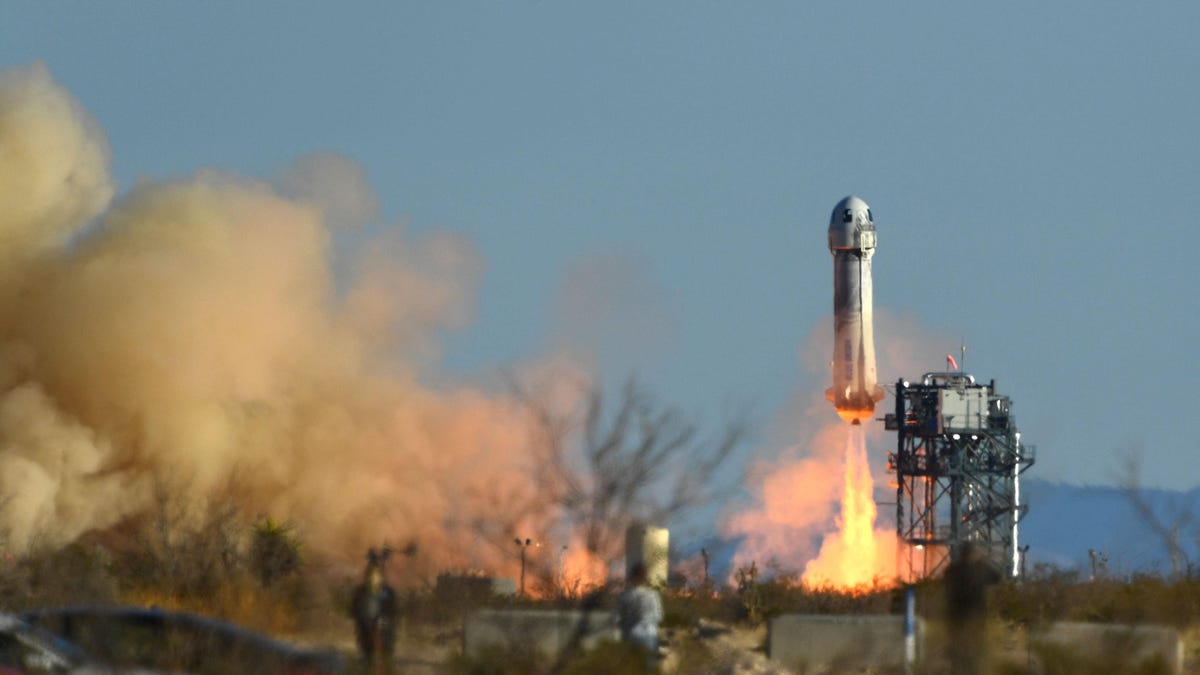 Bezos Blue Origin Vs Katy Perrys Career Comparing Public Perception Of Failure
Apr 22, 2025
Bezos Blue Origin Vs Katy Perrys Career Comparing Public Perception Of Failure
Apr 22, 2025 -
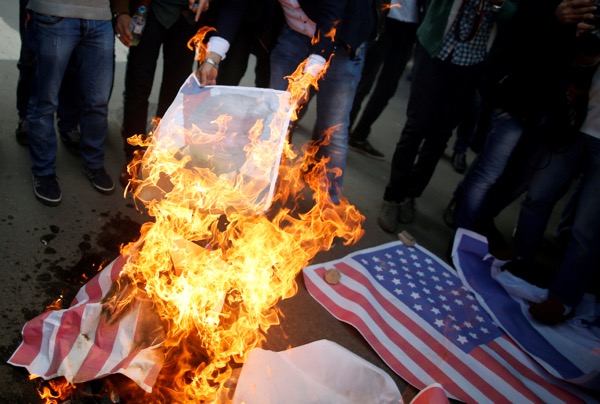 Trump Protests A Nationwide Uprising
Apr 22, 2025
Trump Protests A Nationwide Uprising
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Ftc Launches Investigation Into Open Ai And Chat Gpt
Apr 22, 2025
Ftc Launches Investigation Into Open Ai And Chat Gpt
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Why Current Stock Market Valuations Are Not Cause For Investor Alarm Bof A
Apr 22, 2025
Why Current Stock Market Valuations Are Not Cause For Investor Alarm Bof A
Apr 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Is Conor Mc Gregors Relationship With Fox News Beneficial
May 12, 2025
Is Conor Mc Gregors Relationship With Fox News Beneficial
May 12, 2025 -
 Recent Conor Mc Gregor Fox News Segment Sparks Debate
May 12, 2025
Recent Conor Mc Gregor Fox News Segment Sparks Debate
May 12, 2025 -
 Conor Mc Gregors Media Strategy A Case Study Of His Fox News Appearances
May 12, 2025
Conor Mc Gregors Media Strategy A Case Study Of His Fox News Appearances
May 12, 2025 -
 Nba Playoffs Prediction Cavaliers Vs Knicks Odds And Expert Picks Feb 21
May 12, 2025
Nba Playoffs Prediction Cavaliers Vs Knicks Odds And Expert Picks Feb 21
May 12, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Conor Mc Gregors Fox News Interviews
May 12, 2025
The Impact Of Conor Mc Gregors Fox News Interviews
May 12, 2025
