Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Derailment: Months-Long Building Contamination
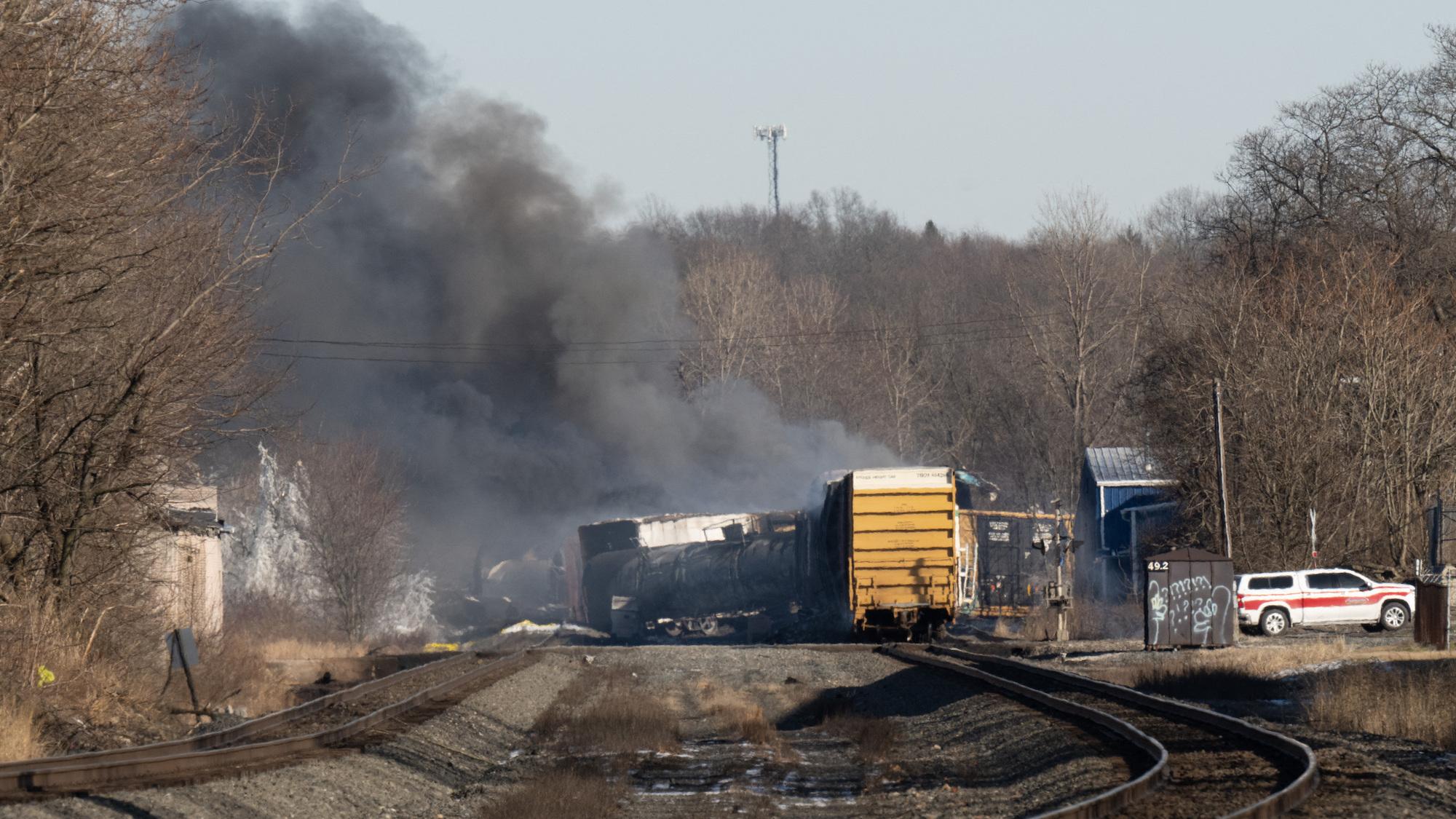

Table of Contents
Types of Toxic Chemicals and Their Impact on Buildings
The Ohio derailment released a cocktail of hazardous substances, including vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether. These chemicals, known for their volatility and toxicity, pose a significant threat to building integrity and indoor air quality.
- Vinyl chloride: A known carcinogen, vinyl chloride is easily absorbed by porous building materials like wood, drywall, and insulation. It can leach out slowly over time, leading to persistent indoor air contamination.
- Butyl acrylate: This chemical irritates the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Its presence in building materials can lead to ongoing health problems for occupants.
- Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether: This solvent can also penetrate building materials and contaminate indoor air and water sources. Long-term exposure can result in various health issues.
The ability of these chemicals to penetrate building materials presents a significant challenge. The contamination levels vary depending on the proximity to the derailment site and the porosity of the building materials. The long-term leaching and off-gassing from contaminated materials are a primary concern, impacting indoor air quality and potentially contaminating water sources within affected buildings. Detecting and remediating these chemicals within building structures is extremely difficult, adding to the complexity of the situation.
Assessing the Extent of Building Contamination
Accurately assessing the extent of building contamination following the Ohio derailment is a complex and ongoing process. Challenges include the variety of chemicals involved, the difficulty of sampling porous materials, and the potential for contamination to spread beyond initially affected areas.
- Environmental testing: Various testing methods are being employed, including air sampling to detect airborne chemicals, water testing to assess contamination of drinking water sources, and soil testing to determine the extent of ground contamination around buildings.
- Testing methodologies: While these methods provide valuable data, the accuracy and limitations of current testing methodologies are significant. Detecting low levels of contamination in porous materials remains a challenge.
- Ongoing monitoring: The effectiveness of ongoing monitoring efforts is crucial for understanding the long-term impacts and informing remediation strategies. More comprehensive and long-term testing programs are urgently needed. The accuracy of testing also needs further scrutiny and improvement.
The Role of Porous Building Materials
Porous building materials such as wood, brick, and concrete readily absorb and retain toxic chemicals. This poses a significant challenge for remediation efforts. The absorption rates vary depending on the material's porosity and the chemical's properties.
- Remediation challenges: Removing contaminants from these materials is extremely difficult and often requires extensive and costly remediation techniques, including potentially complete demolition and reconstruction of affected buildings.
- Long-term risks: Even after initial cleanup, these materials can continue to release chemicals over time, leading to prolonged exposure risks for occupants.
- Building materials testing: More research is needed on the long-term behavior of various building materials when exposed to these specific chemicals to inform better remediation strategies.
Health Risks Associated with Long-Term Exposure
Exposure to the toxic chemicals released in the Ohio derailment poses significant health risks. Both short-term and long-term health effects are a serious concern for residents.
- Respiratory problems: Exposure to vinyl chloride and other chemicals can lead to respiratory issues, including asthma and bronchitis.
- Cancer risk: Vinyl chloride is a known carcinogen, increasing the risk of various cancers.
- Neurological damage: Some of the chemicals may cause neurological damage, leading to cognitive impairment and other neurological problems.
- Reproductive effects: Exposure to certain chemicals may also impact reproductive health.
- Public health concerns: Ongoing medical monitoring of residents in affected areas is crucial to understand the full extent of health consequences and provide necessary medical care. The psychological impact on residents living with the threat of long-term contamination must also be addressed.
Cleanup and Remediation Efforts
The cleanup and remediation efforts following the Ohio derailment are complex and require a multifaceted approach. Current strategies involve removing contaminated soil, cleaning affected water sources, and decontaminating buildings.
- Cleanup strategies: The effectiveness of these methods varies depending on the type of contamination and the affected materials.
- Cost of remediation: Large-scale remediation is extremely expensive, requiring significant financial resources and logistical planning.
- Government response: The government's role in overseeing and funding the cleanup efforts is paramount to ensure effective and comprehensive remediation.
- Community involvement: Community involvement is crucial for successful remediation and to address the concerns of affected residents.
- Long-term cleanup plan: A comprehensive long-term cleanup plan is essential to address the ongoing challenges and mitigate long-term risks.
Conclusion:
The Ohio train derailment’s toxic chemical residue presents a significant and ongoing challenge, with months-long building contamination posing substantial health and environmental risks. The extent of the damage is still being assessed, and thorough, long-term testing and remediation are crucial. Understanding the long-term effects of this toxic chemical residue from the Ohio derailment is paramount. Demand increased transparency and accountability from authorities, and advocate for comprehensive and sustained building contamination cleanup efforts to protect the health and safety of affected communities. Stay informed and continue to demand effective action to address this ongoing crisis.

Featured Posts
-
 Rising Phone Repair Costs The Legacy Of Trumps Tariffs
May 17, 2025
Rising Phone Repair Costs The Legacy Of Trumps Tariffs
May 17, 2025 -
 Liverpools Angelo Stiller Interest German Medias Update And Arne Slot Implications
May 17, 2025
Liverpools Angelo Stiller Interest German Medias Update And Arne Slot Implications
May 17, 2025 -
 Close Call For Knicks Overtime Loss Raises Concerns
May 17, 2025
Close Call For Knicks Overtime Loss Raises Concerns
May 17, 2025 -
 New York Knicks Success Despite Brunsons Absence
May 17, 2025
New York Knicks Success Despite Brunsons Absence
May 17, 2025 -
 Trump Family Tree Exploring The Extensive Lineage Of The Former President
May 17, 2025
Trump Family Tree Exploring The Extensive Lineage Of The Former President
May 17, 2025
