Trump's Trade War With China: Winners And Losers In The US Economy
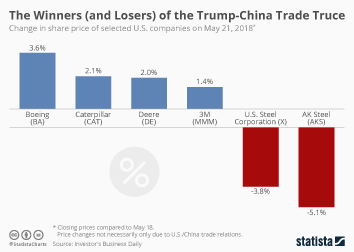
Table of Contents
Agricultural Sector: A Major Loser
The agricultural sector emerged as a significant loser in Trump's trade war with China. China, a major importer of US agricultural products, retaliated against US tariffs by imposing its own tariffs on key American exports.
Declining Exports and Increased Prices:
Tariffs imposed by China led to a sharp decrease in US agricultural exports, particularly soybeans and pork. This resulted in lower farm incomes and increased domestic prices for consumers. The impact was felt across the farming community, from large-scale operations to family farms.
- Reduced demand from China for US soybeans: Soybean exports to China plummeted, forcing farmers to seek alternative markets or accept lower prices.
- Increased reliance on government subsidies for farmers: The US government implemented various subsidy programs to help farmers cope with the loss of export revenue, adding to the national debt.
- Higher food costs for American consumers: Reduced supply and increased import costs translated into higher food prices at the grocery store, impacting household budgets.
- Loss of market share to other agricultural exporters: Competitors like Brazil and Argentina benefited from increased demand from China, gaining market share previously held by US farmers. This shift in the global agricultural landscape had lasting consequences for US competitiveness.
Manufacturing: A Mixed Bag of Winners and Losers
The impact of Trump's Trade War with China on the manufacturing sector was far from uniform, creating a complex picture of winners and losers.
Winners: Some Domestic Manufacturers:
Certain US manufacturing sectors, particularly those producing goods that directly competed with Chinese imports, saw a temporary boost. This was due to increased demand as consumers shifted to domestically produced alternatives, benefiting from the reduced competition.
- Growth in domestic steel and aluminum production: Increased tariffs on imported steel and aluminum provided a temporary boost to domestic producers.
- Increased employment in some manufacturing sectors: The shift in consumer demand and increased domestic production led to some job creation in specific manufacturing sectors. However, this increase was often temporary and didn't offset losses in other areas.
- Reduced reliance on Chinese-made components: Some companies began to diversify their supply chains, reducing reliance on Chinese-made components, although this often came at a higher cost.
Losers: Manufacturers Relying on Chinese Components:
Many US manufacturers who relied on Chinese components or intermediate goods experienced increased costs and disruptions to their supply chains due to the tariffs. This had a significant negative impact on profitability and competitiveness.
- Increased production costs due to higher import tariffs: Tariffs increased the cost of raw materials and components, squeezing profit margins and reducing competitiveness.
- Supply chain disruptions and delays: Tariffs and trade restrictions led to delays and disruptions in the supply chain, impacting production schedules and increasing uncertainty.
- Reduced competitiveness in global markets: Higher production costs due to tariffs made US manufacturers less competitive in global markets, hindering export opportunities.
Technology Sector: Navigating Complex Challenges
The technology sector faced unique challenges during Trump's trade war with China. The conflict intensified existing geopolitical tensions and accelerated efforts to decouple the US and Chinese economies.
Increased Tensions and Decoupling:
The trade war heightened tensions between the US and China in the technology sector, leading to efforts to decouple the two economies. This involved restrictions on technology transfer and increased investment in domestic semiconductor production.
- Restrictions on Chinese companies' access to US technology: The US government implemented restrictions on the sale of advanced technologies to Chinese companies, citing national security concerns.
- Increased investment in domestic semiconductor production: The trade war spurred increased investment in domestic semiconductor manufacturing to reduce reliance on Chinese production.
- Challenges for US tech companies operating in China: US tech companies operating in China faced increased regulatory scrutiny and challenges in accessing the Chinese market.
Consumers: The Broad Impact of Higher Prices
The ultimate impact of Trump's trade war with China was felt by consumers through increased prices on a wide range of goods.
Increased Costs and Reduced Purchasing Power:
Tariffs ultimately led to higher prices for many consumer goods, impacting consumers' purchasing power and reducing overall economic growth. This inflationary pressure affected households across different income levels.
- Increased costs for electronics, clothing, and other imported goods: Tariffs on imported goods were passed onto consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Reduced consumer spending and economic growth: Higher prices led to reduced consumer spending, impacting overall economic growth.
- Potential for inflationary pressures: The widespread increase in prices contributed to inflationary pressures within the US economy.
Conclusion:
Trump's Trade War with China had a complex and multifaceted impact on the US economy. While some domestic manufacturers experienced short-term gains, many sectors, including agriculture and those reliant on Chinese supply chains, faced significant losses. Consumers bore the brunt of increased prices on various goods. Understanding the winners and losers of this trade conflict provides valuable lessons for navigating future economic relations with China and formulating effective trade policies. Further research into the long-term effects of Trump's Trade War with China is crucial for informed decision-making regarding future trade strategies and mitigating the negative consequences of such trade disputes. Avoiding future escalations similar to Trump's Trade War with China requires careful consideration of potential economic ramifications.

Featured Posts
-
 Elite Universities Form Secret Group To Oppose Trump Administration
Apr 29, 2025
Elite Universities Form Secret Group To Oppose Trump Administration
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Papst Tod Flaggen Auf Halbmast In Deutschen Ministerien
Apr 29, 2025
Papst Tod Flaggen Auf Halbmast In Deutschen Ministerien
Apr 29, 2025 -
 How To Secure Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets A Comprehensive Guide
Apr 29, 2025
How To Secure Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets A Comprehensive Guide
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Strong Q Quarter Number Earnings Send Reliance Shares To 10 Month Peak
Apr 29, 2025
Strong Q Quarter Number Earnings Send Reliance Shares To 10 Month Peak
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nfl International Series 2025 Packers Chances For A Global Game
Apr 29, 2025
Nfl International Series 2025 Packers Chances For A Global Game
Apr 29, 2025
