U.S. Economy And The Implications Of Reduced Tariffs With China
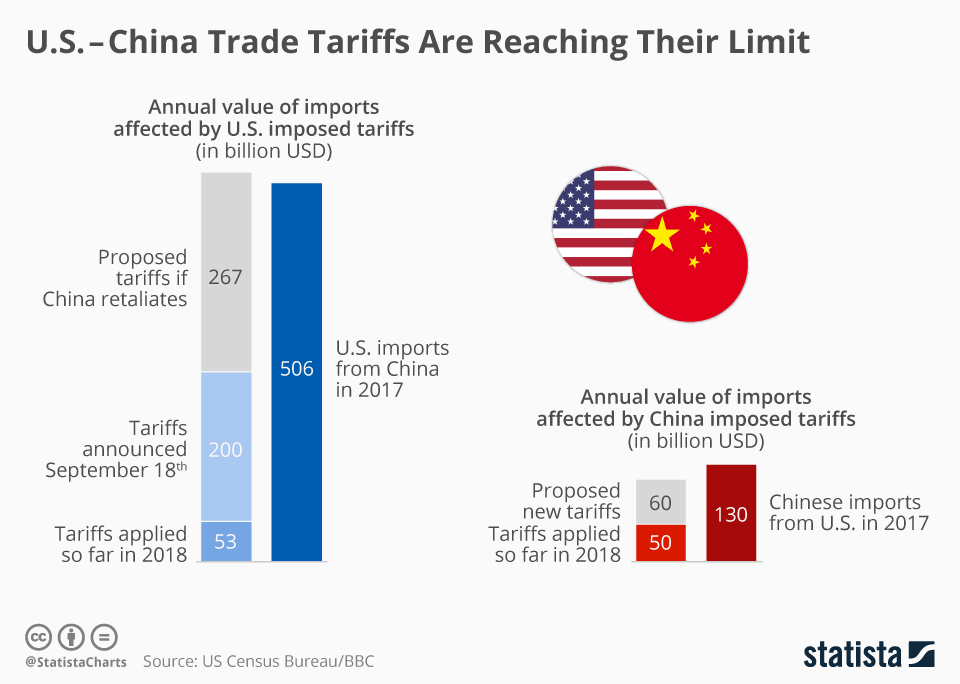
Table of Contents
Impact on Consumer Prices and Inflation
Reduced tariffs directly impact consumer prices and the inflation rate. Lower import costs from China translate to lower prices for consumers, potentially easing inflationary pressures. This is because tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, directly increase the price consumers pay. The reduction of these tariffs should, in theory, lead to a decrease in prices.
-
Lower Import Prices: Reduced tariffs lower the cost of imported goods, impacting everything from electronics and clothing to furniture and toys.
-
Easing Inflationary Pressures: By reducing the cost of goods, reduced tariffs can help to curb inflation, boosting consumer purchasing power. The Consumer Price Index (CPI), a key measure of inflation, should reflect this change, showing a decreased rate of inflation, or at least a slower rate of increase.
-
Elasticity of Demand and Pass-Through: The extent to which these price reductions are passed on to consumers depends on several factors. The elasticity of demand for specific goods plays a crucial role; if demand is inelastic (consumers will buy regardless of price changes), companies might not fully pass on the tariff savings. Similarly, the extent to which companies absorb the cost reduction themselves or increase their profit margins also influences consumer pricing.
-
CPI Data Analysis: A thorough analysis of CPI data before and after tariff changes is crucial for accurately assessing the real impact of reduced tariffs on consumer prices. This analysis needs to account for other economic factors influencing inflation.
For example, the reduction of tariffs on certain types of clothing might lead to noticeable price drops at retail level, offering consumers greater affordability. However, increased transportation costs due to global supply chain issues could partially offset these savings.
Effects on U.S. Manufacturing and Supply Chains
The impact of reduced tariffs on U.S. manufacturing and supply chains is multifaceted. While lower input costs could benefit some U.S. manufacturers who rely on Chinese components, increased imports of cheaper Chinese goods could harm domestic producers.
-
Increased Imports: Reduced tariffs could lead to a surge in imports of cheaper Chinese goods, potentially undercutting domestic manufacturers and leading to job losses in certain sectors.
-
Lower Input Costs: On the other hand, U.S. manufacturers using Chinese components in their production processes could benefit from lower input costs, improving their competitiveness.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: The impact on supply chains will vary significantly across industries depending on their reliance on Chinese imports. While some might experience benefits, others might face further disruption.
-
Reshoring and Nearshoring: The reduced tariff advantage for Chinese goods might incentivize some companies to consider reshoring (bringing manufacturing back to the U.S.) or nearshoring (moving production to nearby countries) to mitigate risks and reduce dependence on long and potentially volatile supply chains.
Industries like textiles, electronics, and furniture are particularly sensitive to changes in tariffs. However, technological advancements and automation in U.S. manufacturing could help mitigate some of the negative impacts by increasing productivity and efficiency, thus potentially offsetting lower labor costs in China.
Implications for U.S. Trade Balance and Economic Growth
Reduced tariffs could significantly impact the U.S. trade balance and overall economic growth. While lower consumer prices and increased consumer spending can boost economic activity, an increase in imports from China could widen the U.S. trade deficit.
-
Widening Trade Deficit: An increase in imports from China due to reduced tariffs could lead to a larger trade deficit, potentially increasing concerns about the long-term health of the U.S. economy.
-
Stimulating Economic Growth: Lower consumer prices and increased consumer purchasing power resulting from tariff reductions could stimulate economic growth by boosting aggregate demand and increasing overall spending.
-
Complex Impact on GDP Growth: The overall impact on Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth is complex and depends on the interplay between increased consumer spending, decreased domestic production, and changes in investment.
-
Increased Exports: Improved trade relations, potentially fostered by reduced tariffs, could also lead to an increase in U.S. exports to China, partially offsetting the impact of increased imports.
Analyzing historical data on the U.S.-China trade balance in relation to past tariff changes can provide valuable insights into the potential consequences of current tariff reductions. This analysis should consider not only the direct impact on the trade balance but also the broader effects on employment, investment, and overall economic output.
Conclusion
Reduced tariffs with China present a complex and nuanced picture for the U.S. economy. While lower consumer prices and potentially increased consumer spending offer clear benefits, there are legitimate concerns about the impact on U.S. manufacturing and the trade deficit. The overall effect will depend on a multitude of intertwined economic factors and is likely to vary considerably across different sectors. Understanding the implications of U.S. and China reduced tariffs is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. Further research and analysis are needed to fully comprehend the long-term consequences of these changes on the U.S. economy. Stay informed about the evolving U.S.-China trade relationship and the impact of fluctuating tariff policies on the U.S. economy and its various sectors.

Featured Posts
-
 The Pay Gap Between Colin Jost And Scarlett Johansson A Discussion On Gender And Earnings In Hollywood
May 13, 2025
The Pay Gap Between Colin Jost And Scarlett Johansson A Discussion On Gender And Earnings In Hollywood
May 13, 2025 -
 Scarlett Johansson Clarifies Black Widows Potential Mcu Return
May 13, 2025
Scarlett Johansson Clarifies Black Widows Potential Mcu Return
May 13, 2025 -
 Pretstavuvanje Na Prvata Kniga So Romski Narodni Prikazni
May 13, 2025
Pretstavuvanje Na Prvata Kniga So Romski Narodni Prikazni
May 13, 2025 -
 Eva Longoria 50 Evesen Bikinifotok Es A Titka
May 13, 2025
Eva Longoria 50 Evesen Bikinifotok Es A Titka
May 13, 2025 -
 Nba Draft Lottery 2024 Espns New Coverage Strategy
May 13, 2025
Nba Draft Lottery 2024 Espns New Coverage Strategy
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Watch Captain America Brave New World Best Pvod Streaming Services
May 14, 2025
Watch Captain America Brave New World Best Pvod Streaming Services
May 14, 2025 -
 Where To Stream Captain America Brave New World Digital And Disney Release Dates
May 14, 2025
Where To Stream Captain America Brave New World Digital And Disney Release Dates
May 14, 2025 -
 When Can I Stream Captain America Brave New World On Disney
May 14, 2025
When Can I Stream Captain America Brave New World On Disney
May 14, 2025 -
 Where To Stream Captain America Brave New World Online Via Pvod
May 14, 2025
Where To Stream Captain America Brave New World Online Via Pvod
May 14, 2025 -
 Scotty Mc Creerys Son Honors George Strait A Must See Video
May 14, 2025
Scotty Mc Creerys Son Honors George Strait A Must See Video
May 14, 2025
