U.S. Federal Reserve: Assessing The Likelihood Of A Rate Hike Pause
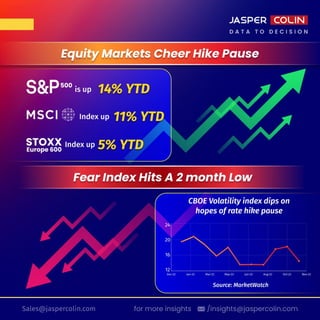
Table of Contents
Inflation as a Primary Determinant of a Rate Hike Pause
Inflation remains a central factor in the Federal Reserve's decision-making process. The Fed's primary mandate is to maintain price stability, aiming for an inflation rate of around 2% as measured by the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index. A rate hike pause is highly dependent on the trajectory of inflation.
Current Inflation Rates and Projections
The latest Consumer Price Index (CPI) and PCE data offer crucial insights into the current inflation landscape. While headline inflation may have cooled slightly, core inflation (excluding volatile food and energy prices) remains stubbornly elevated.
- CPI: [Insert latest CPI data and year-over-year change]. This reflects [brief analysis of CPI data – e.g., a slowing but still elevated rate].
- PCE: [Insert latest PCE data and year-over-year change]. This indicates [brief analysis of PCE data – e.g., a similar trend to CPI, highlighting core PCE].
- Contributing Factors: Persistent supply chain disruptions, robust consumer demand, and elevated energy prices continue to contribute to inflationary pressures.
The Fed's Inflation Target and its Influence on Policy Decisions
The Fed's unwavering commitment to its 2% inflation target dictates its monetary policy approach. Any significant deviation from this target, especially persistent high inflation, necessitates continued rate hikes to cool down the economy. Conversely, a clear and sustained decline towards the target increases the probability of a rate hike pause.
- Fed Statements: Recent statements from Fed officials emphasize the need to bring inflation back to the 2% target. [Cite specific statements and press releases].
- Historical Precedent: Historically, the Fed has responded aggressively to inflationary pressures. [Provide examples of past Fed actions during periods of high inflation].
- Dual Mandate: The Fed's dual mandate requires it to balance price stability with maximum employment. However, currently, high inflation outweighs the employment concerns, making inflation control the top priority.
Potential Scenarios for Inflation and their Impact on a Pause
Several inflation scenarios could play out, each with its own implications for a potential rate hike pause:
- Sustained High Inflation: If inflation remains stubbornly high, the Fed is likely to continue raising interest rates, making a pause unlikely.
- Gradual Decline: A gradual decline in inflation toward the 2% target would increase the likelihood of a rate hike pause in the near future.
- Unexpected Surge: An unexpected surge in inflation could trigger further aggressive rate hikes and push back any possibility of a pause indefinitely.
Labor Market Conditions and Their Role in a Rate Hike Pause Decision
The strength of the labor market plays a crucial role in the Fed's monetary policy decisions. A tight labor market, characterized by low unemployment and strong wage growth, can fuel inflationary pressures. Therefore, the Fed's assessment of labor market conditions significantly influences the probability of a rate hike pause.
Unemployment Rate and Wage Growth
The current unemployment rate remains low, indicating a robust labor market. However, the rate at which wages are increasing is a key indicator for the Fed. Rapid wage growth can accelerate inflation, requiring further action.
- Unemployment Rate: [Insert current unemployment rate and analysis].
- Wage Growth: [Insert current wage growth data and analysis]. High wage growth could indicate that the labor market is overheating.
Fed's Assessment of Employment Situation
The Fed closely monitors various labor market indicators beyond just the headline unemployment rate. They consider factors like labor force participation, job openings, and quit rates to assess the overall health and potential inflationary pressures from the labor market.
- Fed Statements on Employment: [Cite recent statements from Fed officials regarding the labor market].
- Assessment of Labor Market Health: The Fed's assessment of the labor market's health will inform whether a rate hike pause is warranted.
Potential Scenarios for Employment and Their Implications
Different employment scenarios could unfold, impacting the likelihood of a rate hike pause:
- Sustained Low Unemployment: If low unemployment persists along with strong wage growth, the Fed might continue raising rates to control inflation.
- Rising Unemployment: A rise in unemployment, indicating a cooling labor market, might increase the chances of a rate hike pause.
- Unexpected Job Losses: A sharp increase in job losses would likely lead the Fed to pause rate hikes or even consider rate cuts.
Other Factors Influencing the Likelihood of a Rate Hike Pause
Beyond inflation and labor market conditions, other factors influence the Fed’s decision to pause rate hikes.
Global Economic Conditions and their Impact
Geopolitical risks and global economic slowdowns can significantly impact the U.S. economy and influence the Fed's monetary policy.
- Geopolitical Risks: [Discuss current geopolitical events and their potential impact]. Global uncertainty can trigger a rate hike pause.
- Global Recession: The possibility of a global recession could cause the Fed to pause rate hikes to avoid further economic damage.
Financial Market Conditions and their Role
Financial market conditions, including stock market volatility and credit spreads, provide valuable insights into the economy's health and potential risks.
- Stock Market Volatility: High stock market volatility can signal economic uncertainty, potentially prompting a rate hike pause.
- Credit Spreads: Widening credit spreads could reflect increasing credit risk, which might cause the Fed to pause rate hikes.
Upcoming Economic Data Releases and their Significance
Upcoming economic data releases will be crucial in shaping the Fed's outlook and influence the decision regarding a rate hike pause.
- GDP Reports: [Mention upcoming GDP reports and their potential impact].
- Consumer Confidence Indices: [Mention upcoming consumer confidence indices and their potential impact].
Conclusion
The likelihood of a rate hike pause hinges on a complex interplay of factors, primarily inflation and labor market conditions. While a cooling inflation rate and a potential softening of the labor market increase the chances of a pause, the Fed's commitment to its 2% inflation target remains paramount. Global economic uncertainties and upcoming economic data releases also play significant roles in this complex equation. Continuously monitoring these indicators and Fed statements is crucial for accurate predictions. To effectively navigate the evolving economic landscape, stay informed about the latest developments regarding the Fed's monetary policy to understand the implications of potential rate hike pauses and their impact on your investments and financial planning. Continuously assess the likelihood of a rate hike pause and adapt your strategies accordingly.

Featured Posts
-
 Kultoviyat Roman Na Stivn King Skoro Na Netflix
May 10, 2025
Kultoviyat Roman Na Stivn King Skoro Na Netflix
May 10, 2025 -
 How West Ham Can Overcome Their 25m Financial Problem
May 10, 2025
How West Ham Can Overcome Their 25m Financial Problem
May 10, 2025 -
 Putin Announces Victory Day Ceasefire What To Expect
May 10, 2025
Putin Announces Victory Day Ceasefire What To Expect
May 10, 2025 -
 Fentanyl Crisis Record Seizure Announced By Pam Bondi
May 10, 2025
Fentanyl Crisis Record Seizure Announced By Pam Bondi
May 10, 2025 -
 Mariah The Scientist And Young Thug New Music Hints At Committed Relationship
May 10, 2025
Mariah The Scientist And Young Thug New Music Hints At Committed Relationship
May 10, 2025
