Understanding ADHD: A Journey Inside Our ADHD Minds
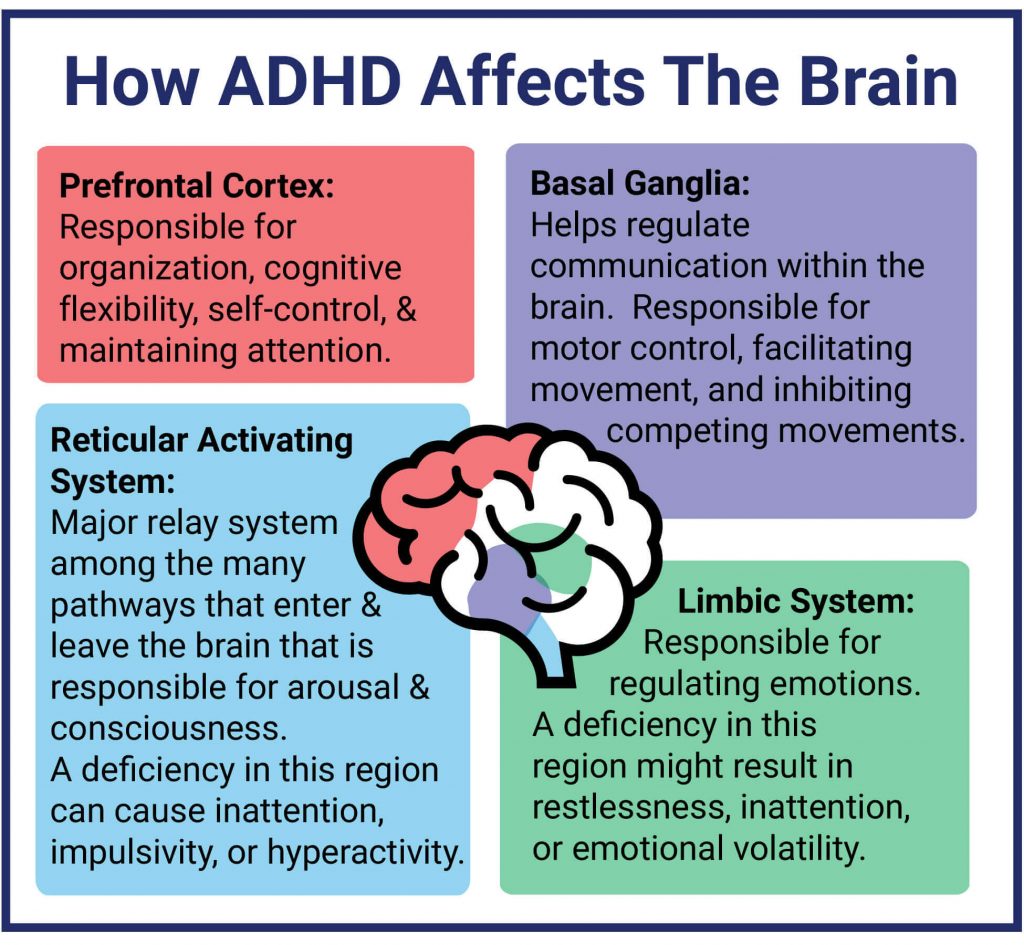
Table of Contents
The Neuroscience of ADHD
The neurobiology of ADHD reveals significant differences in brain structure and function compared to neurotypical individuals. These differences are not simply behavioral issues; they are rooted in the intricate workings of the brain. Neurotransmitter imbalances play a crucial role, particularly concerning dopamine and norepinephrine, which are vital for attention, focus, and reward processing. Brain regions like the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions such as planning and impulse control, and the basal ganglia, involved in motor control and habit formation, are often affected.
- Smaller brain volume: Studies have shown smaller volumes in specific brain areas, including regions crucial for attention and impulse control.
- Delayed maturation: Brain regions involved in executive function may mature more slowly in individuals with ADHD.
- Differences in brain connectivity: There can be altered connectivity between different brain regions, affecting communication and coordination.
These neurological variations contribute to the characteristic symptoms of ADHD, highlighting the disorder's neurological basis rather than simply a matter of willpower or discipline. Understanding the ADHD brain is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and dispelling common myths surrounding this condition. Further research into the neurobiology of ADHD continues to unravel the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors contributing to the disorder.
Common Symptoms and Challenges of ADHD
ADHD manifests differently in individuals, with presentations categorized as predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive, or combined. Symptoms are not static and can fluctuate depending on factors such as stress, environment, and age. The challenges faced in daily life can be significant and far-reaching:
- Difficulty focusing and sustaining attention (attention deficit): This can lead to problems in school, work, and relationships. Examples include struggling to complete tasks, easily getting distracted, and experiencing mind wandering.
- Hyperactivity and restlessness: This manifests as excessive fidgeting, difficulty sitting still, interrupting conversations, and excessive talking. In adults, this can appear as restlessness, an inability to relax, and constant need for activity.
- Impulsivity and poor decision-making: Impulsivity can lead to making hasty decisions without considering consequences, interrupting others frequently, and engaging in risky behaviors.
- Emotional dysregulation: Individuals with ADHD may struggle to regulate their emotions, leading to irritability, frustration, and mood swings.
- Organizational challenges: Planning, time management, and organizing tasks can be extremely difficult, leading to missed deadlines, disorganization, and procrastination.
These symptoms can significantly impact academic performance, professional success, and personal relationships. Understanding these ADHD symptoms in different contexts is key to effective diagnosis and management. For example, a child with ADHD might struggle to sit still during class, while an adult might struggle to manage their workload and meet deadlines. Recognizing the nuances of these challenges is critical for providing tailored support and interventions.
Misconceptions and Stigma Surrounding ADHD
Many misconceptions surround ADHD, perpetuating stigma and hindering proper diagnosis and treatment. It’s crucial to debunk these myths and foster understanding:
- Myth: ADHD is just laziness or a lack of willpower. Reality: ADHD is a neurological condition affecting brain function and impacting attention, focus, and impulse control.
- Myth: ADHD is only a childhood disorder. Reality: While often diagnosed in childhood, ADHD persists into adulthood for many individuals, requiring ongoing management and support.
- Myth: People with ADHD are simply less intelligent. Reality: Intelligence is separate from the challenges posed by ADHD.
The negative impact of stigma can be profound, leading to feelings of shame, isolation, and self-doubt. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to mitigate these effects. Understanding and empathy are vital in creating a supportive environment for individuals with ADHD. By challenging misconceptions and promoting informed dialogue, we can help reduce the stigma and empower those affected to live fulfilling lives.
Strategies for Managing ADHD
Managing ADHD effectively often involves a multi-pronged approach combining medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. Treatment plans are highly individualized, tailored to the specific needs and challenges of each person.
- Medication: Stimulant and non-stimulant medications can help improve focus, reduce impulsivity, and manage hyperactivity.
- Therapy: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and behavioral therapy help individuals develop coping mechanisms and strategies for self-management.
- Lifestyle changes: Improving diet, increasing physical activity, and prioritizing sleep hygiene can significantly impact symptom management.
Developing personalized strategies is key. This could include time management techniques like the Pomodoro Technique, mindfulness exercises to improve focus, and utilizing organizational tools. These ADHD coping mechanisms can dramatically improve daily functioning and quality of life. Seeking professional guidance is crucial to create a tailored treatment plan that addresses individual needs and challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding ADHD involves recognizing its neurological basis, appreciating the diverse ways it manifests, and acknowledging the significant challenges it presents. The journey to understanding and managing ADHD requires empathy, informed support, and early intervention. It's a condition that affects individuals across the lifespan, impacting their lives in many ways. However, with proper treatment and self-management strategies, individuals with ADHD can lead fulfilling and successful lives.
If you suspect you or someone you know may have ADHD, seek professional guidance. Learn more about managing ADHD and advocate for increased understanding of this common neurodevelopmental condition. Understanding ADHD is a crucial step towards building a more supportive and inclusive environment. There are many resources available to help you navigate this journey; don't hesitate to seek them out.

Featured Posts
-
 Istoriya Modeli Merman Broshennaya Beremennaya V Oae Synom Kadyshevoy
May 13, 2025
Istoriya Modeli Merman Broshennaya Beremennaya V Oae Synom Kadyshevoy
May 13, 2025 -
 Gibraltar Blockchain Event Coinsiliums Forza Launch Recap
May 13, 2025
Gibraltar Blockchain Event Coinsiliums Forza Launch Recap
May 13, 2025 -
 Poy Na Deite Agones Serie A Online And Tv
May 13, 2025
Poy Na Deite Agones Serie A Online And Tv
May 13, 2025 -
 I Niki I Fanela Kai O Mpalntok I Istoria Piso Apo Ton Panigyrismo Toy Proponiti Tis Sefilnt Gioynaitent
May 13, 2025
I Niki I Fanela Kai O Mpalntok I Istoria Piso Apo Ton Panigyrismo Toy Proponiti Tis Sefilnt Gioynaitent
May 13, 2025 -
 Prenajatie Nehnutelnosti Romovi Statistika Dovody A Riesenia Diskriminacie
May 13, 2025
Prenajatie Nehnutelnosti Romovi Statistika Dovody A Riesenia Diskriminacie
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Landman Backlash Billy Bob Thorntons Defense Of Ali Larter And Angela Norris
May 13, 2025
Landman Backlash Billy Bob Thorntons Defense Of Ali Larter And Angela Norris
May 13, 2025 -
 7 Budget Return Analyzing Salman Khans Recent Box Office Disappointment
May 13, 2025
7 Budget Return Analyzing Salman Khans Recent Box Office Disappointment
May 13, 2025 -
 Salman Khans Latest Film A Box Office Disaster With Only 4 7 Budget Earned
May 13, 2025
Salman Khans Latest Film A Box Office Disaster With Only 4 7 Budget Earned
May 13, 2025 -
 Salman Khans Biggest Box Office Failure In 25 Years A 4 7 Budget Recovery
May 13, 2025
Salman Khans Biggest Box Office Failure In 25 Years A 4 7 Budget Recovery
May 13, 2025 -
 Renewal Confirmed Demi Moores Drama Series From The Creator Of Yellowstone Returns
May 13, 2025
Renewal Confirmed Demi Moores Drama Series From The Creator Of Yellowstone Returns
May 13, 2025
