Understanding The Recent 20-Cent Gas Price Increase
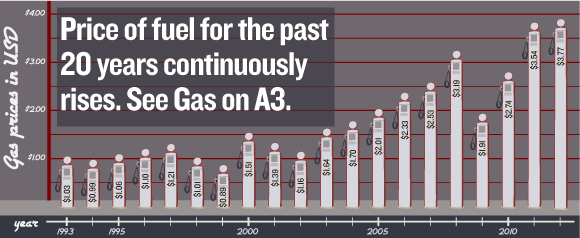
Table of Contents
Global Crude Oil Prices and Their Impact
The price of gasoline at the pump is intrinsically linked to global crude oil prices. Crude oil is the primary raw material used in gasoline production; therefore, fluctuations in its price directly translate into changes at the gas station. Recent events significantly impacting global oil supply have contributed to the 20-cent increase.
- Increased demand from recovering economies: As global economies recover from the pandemic, demand for oil has surged, outpacing supply and driving prices higher. This increased consumption puts upward pressure on crude oil prices, directly impacting the final price of gasoline.
- Supply chain disruptions: Ongoing supply chain issues, exacerbated by geopolitical events and logistical challenges, have hampered the efficient delivery of crude oil to refineries. These bottlenecks restrict supply and contribute to higher prices.
- Geopolitical tensions impacting oil production: Geopolitical instability in various oil-producing regions creates uncertainty and can lead to production cuts or disruptions, further limiting supply and boosting prices. Sanctions and conflicts often have a significant effect on global oil markets.
- Seasonal fluctuations in demand: Demand for gasoline typically increases during warmer months due to increased travel and outdoor activities. This seasonal surge in demand can put upward pressure on prices, especially when coupled with other contributing factors.
Refining Capacity and Distribution Costs
The cost of refining crude oil into gasoline and distributing it to gas stations also plays a crucial role in determining the final price. Refining capacity and operational efficiency directly influence the cost of gasoline production.
- Maintenance shutdowns at refineries: Planned and unplanned maintenance shutdowns at refineries can temporarily reduce refining capacity, leading to tighter supplies and higher prices. These shutdowns are necessary for safety and upkeep but can impact the immediate availability of gasoline.
- Increased transportation costs due to fuel prices: The cost of transporting gasoline from refineries to distribution centers and then to gas stations is influenced by fuel prices themselves, creating a feedback loop where higher fuel prices increase transportation costs and, consequently, the final price of gasoline.
- Labor shortages in the refining and distribution sectors: Labor shortages within the refining and distribution industries can constrain the efficient operation of refineries and the timely delivery of gasoline, impacting supply and prices.
- Infrastructure limitations impacting efficient distribution: Outdated or insufficient infrastructure, such as pipelines and storage facilities, can create bottlenecks in the distribution process, contributing to higher transportation costs and ultimately higher gas prices.
Seasonal Demand and its Effect on Prices
Seasonal changes significantly impact gasoline demand and, consequently, price fluctuations. Summer months typically see a peak in demand due to increased travel.
- Increased driving during summer vacation months: The summer driving season, with increased road trips and vacations, significantly increases gasoline demand, leading to higher prices. This is a recurring seasonal pattern.
- Shift in demand for specific gasoline blends: The type of gasoline blended for different seasons (e.g., summer blends versus winter blends) can also impact prices due to varying production costs and demand.
- Impact of weather events on supply and distribution: Severe weather events, such as hurricanes or blizzards, can disrupt supply chains and distribution networks, leading to temporary shortages and price spikes.
Government Regulations and Taxes
Government regulations and taxes also contribute to the final price of gasoline. These policies can impact various stages of the production and distribution process.
- Federal and state gasoline taxes: Taxes levied by federal and state governments directly add to the price consumers pay at the pump. These taxes fund various infrastructure projects and government programs.
- Environmental regulations impacting refining processes: Environmental regulations designed to reduce emissions from refineries can increase production costs, which can be passed on to consumers in the form of higher gas prices. These regulations are designed to protect the environment but can have economic consequences.
- Government subsidies or incentives related to fuel production: Government subsidies or incentives aimed at promoting specific types of fuel production (e.g., biofuels) can influence gasoline prices by affecting the overall supply and demand dynamics.
What Consumers Can Do
While the factors influencing gas prices are largely beyond individual control, consumers can still take steps to mitigate the impact on their budgets.
- Driving efficiently to improve gas mileage: Adopting fuel-efficient driving habits, such as maintaining a steady speed, avoiding aggressive acceleration and braking, and properly inflating tires, can significantly improve gas mileage and reduce fuel consumption.
- Comparing gas prices across different stations: Using gas price comparison apps or websites allows you to identify the cheapest gas stations in your area, helping you save money on each fill-up.
- Using fuel-efficient vehicles: Choosing fuel-efficient vehicles, such as hybrids or electric cars, can substantially reduce your long-term fuel costs.
- Considering alternative transportation options: Exploring alternative transportation options, such as public transit, biking, or walking, can reduce your reliance on gasoline and decrease fuel expenses.
Conclusion
The recent 20-cent gas price increase is a multifaceted issue resulting from a combination of global and domestic factors, including rising crude oil prices, refining capacity constraints, seasonal demand shifts, and government regulations. Understanding these contributing factors is crucial for navigating the fluctuating gas market. Stay informed about the latest developments affecting gas prices by regularly checking reliable news sources and utilizing price comparison tools. Understanding the factors behind gas price increases, like this recent 20-cent jump, empowers you to make informed decisions and manage your fuel costs effectively. Keep learning about the dynamics of gas price changes so you can better manage your budget and understand future fluctuations in the price of gas.

Featured Posts
-
 Racial Hatred Tweet Ex Tory Councillors Wife Seeks To Overturn Sentence
May 22, 2025
Racial Hatred Tweet Ex Tory Councillors Wife Seeks To Overturn Sentence
May 22, 2025 -
 Nvidias Huang Us Export Controls Failed Trump Praised
May 22, 2025
Nvidias Huang Us Export Controls Failed Trump Praised
May 22, 2025 -
 Grem Ta Inshi Senatori Konfiskatsiya Rosiyskikh Aktiviv Neobkhidniy Krok
May 22, 2025
Grem Ta Inshi Senatori Konfiskatsiya Rosiyskikh Aktiviv Neobkhidniy Krok
May 22, 2025 -
 Significant Zebra Mussel Infestation Detected On Casper Boat Lift
May 22, 2025
Significant Zebra Mussel Infestation Detected On Casper Boat Lift
May 22, 2025 -
 Blake Lively Addressing The Recent Allegations And Rumors
May 22, 2025
Blake Lively Addressing The Recent Allegations And Rumors
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Israeli Diplomat Shooting In Washington A Developing Story
May 22, 2025
The Israeli Diplomat Shooting In Washington A Developing Story
May 22, 2025 -
 Understanding The Israeli Diplomat Shooting Incident In Washington
May 22, 2025
Understanding The Israeli Diplomat Shooting Incident In Washington
May 22, 2025 -
 Two Israeli Embassy Staff Members Killed In Washington Dc Shooting Ap Images
May 22, 2025
Two Israeli Embassy Staff Members Killed In Washington Dc Shooting Ap Images
May 22, 2025 -
 Ap Photos Deadly Shooting Near Dc Jewish Museum Israeli Embassy Staff Victims
May 22, 2025
Ap Photos Deadly Shooting Near Dc Jewish Museum Israeli Embassy Staff Victims
May 22, 2025 -
 Merzs Condemnation Of Washington Attack Full Statement And Reaction
May 22, 2025
Merzs Condemnation Of Washington Attack Full Statement And Reaction
May 22, 2025
