Understanding The Record High In Global Forest Loss: Wildfire's Contribution
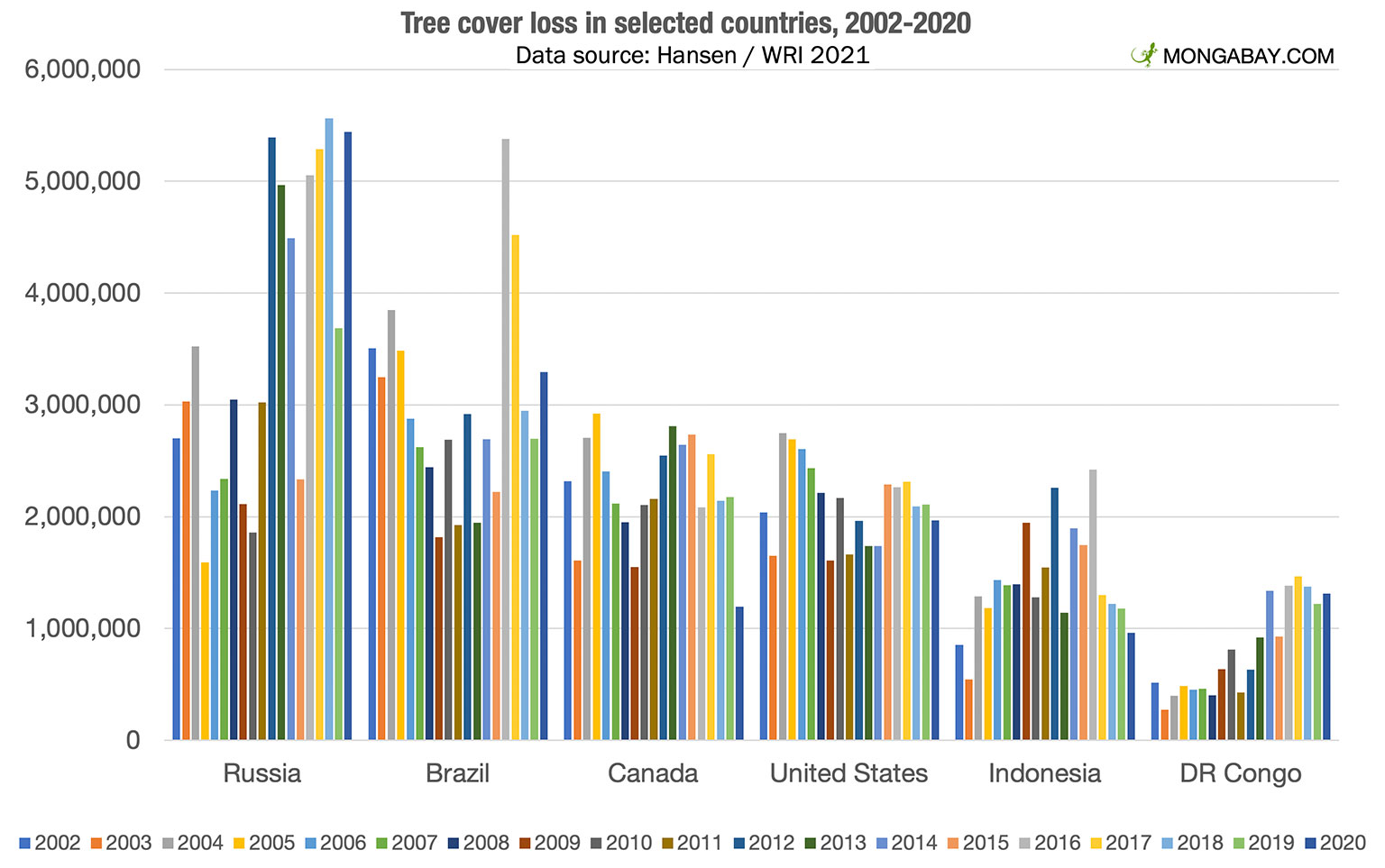
Table of Contents
The Alarming Statistics of Wildfire-Driven Forest Loss
The frequency and intensity of wildfires globally are increasing at an alarming rate. Data reveals a stark picture of escalating forest loss due to these devastating events. Recent years have witnessed unprecedented hectares lost annually, far surpassing historical averages. The impact is geographically widespread, with significant consequences observed in regions such as the Amazon rainforest, Siberia, and Australia.
- Specific data points: A recent report indicates a percentage increase of X% in wildfire-related forest loss over the last decade, highlighting the accelerating nature of the problem. (Note: Replace "X%" with actual data from reputable sources like the Global Forest Watch or FAO).
- Examples of devastating wildfires: The 2019-2020 Australian bushfires destroyed an estimated X million hectares of forest, impacting countless species and releasing massive amounts of carbon into the atmosphere. (Note: Replace "X million" with actual data). Similarly, the Siberian wildfires of 2021 released unprecedented levels of greenhouse gases.
- Geographical distribution: While regions like the Amazon and boreal forests are particularly vulnerable, wildfire-related forest loss is a global concern, impacting diverse ecosystems worldwide. Mediterranean regions are also experiencing a sharp increase in wildfire frequency and intensity.
Underlying Causes of Increased Wildfire Activity
The rise in wildfire activity is a complex issue with interconnected causes. Climate change plays a dominant role, creating conditions highly favorable to fire ignition and spread. Prolonged droughts, higher temperatures, and altered wind patterns all contribute to increased wildfire risk and intensity. However, human factors also significantly exacerbate the problem.
- The feedback loop between deforestation and increased wildfire risk: Deforestation reduces forest density and creates drier conditions, making remaining forests more susceptible to fire. This creates a dangerous feedback loop, where deforestation leads to more wildfires, which further contribute to deforestation.
- Examples of human activities increasing wildfire risk: Improper disposal of cigarettes, faulty power lines, and accidental ignitions from agricultural activities all contribute to wildfire outbreaks. In some cases, deliberate arson also plays a significant role.
- The role of climate change: Climate change is not just increasing the frequency and intensity of wildfires; it is also extending the wildfire season in many regions, giving fires more time to spread and cause greater damage.
The Impact of Wildfires Beyond Forest Loss
The consequences of wildfires extend far beyond the immediate loss of forested areas. The ecological damage is profound, impacting biodiversity, air quality, and carbon cycles.
- Biodiversity loss: Wildfires destroy habitats, leading to the extinction or endangerment of countless plant and animal species. The loss of keystone species can have cascading effects on entire ecosystems. For example, the Australian bushfires led to significant declines in koala populations.
- Air pollution and human health: Wildfire smoke contains harmful pollutants that pose serious health risks to humans, particularly those with respiratory problems. The smoke can travel vast distances, impacting air quality in areas far from the fire itself.
- Economic costs: The costs associated with wildfire suppression, recovery efforts, and the economic losses due to damaged infrastructure and disrupted livelihoods are substantial, placing significant burdens on governments and communities.
Strategies for Mitigating Wildfire-Driven Forest Loss
Combating wildfire-driven forest loss requires a multi-pronged approach that addresses both the underlying causes and the immediate consequences.
- Climate change mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to mitigating the long-term drivers of increased wildfire risk. Transitioning to renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and protecting existing forests are all vital steps.
- Improved forest management practices: Implementing controlled burns under carefully managed conditions can reduce fuel loads and prevent larger, more destructive wildfires. Active forest management techniques, such as thinning dense forests and creating firebreaks, are also essential.
- Technology's role: Early warning systems, improved firefighting techniques (e.g., drones, aerial water bombing), and advanced satellite monitoring can significantly improve our ability to detect, respond to, and suppress wildfires.
- International cooperation and community engagement: Addressing global forest loss requires international collaboration on research, data sharing, and the implementation of effective policies. Engaging local communities in wildfire prevention and management is also critical for long-term success.
Specific examples: Successful forest management strategies in various regions demonstrate the effectiveness of proactive approaches. Technological advancements, such as AI-powered wildfire detection systems, are improving early warning capabilities. Community-based programs for fuel reduction and fire prevention education have proven successful in reducing wildfire risk in several areas.
Conclusion
The scale of global forest loss due to wildfires is alarming and demands urgent action. The interconnected nature of climate change, unsustainable land management practices, and increasing wildfire activity necessitates a concerted global effort. We must address the root causes of this crisis through climate change mitigation, improved forest management techniques, technological advancements, and strong international cooperation. Understanding the devastating impact of wildfires on global forest loss is crucial. We must act now to protect our planet’s vital forests and prevent further devastating losses due to wildfires and global forest loss. Let's work together to combat this critical environmental challenge.

Featured Posts
-
 Understanding The Impact Of Hamiltons Input On F1 Rule Changes
May 26, 2025
Understanding The Impact Of Hamiltons Input On F1 Rule Changes
May 26, 2025 -
 Did Claire Williams Wrong George Russell Examining The Evidence
May 26, 2025
Did Claire Williams Wrong George Russell Examining The Evidence
May 26, 2025 -
 Jrymt Mrwet Fy Frnsa Tfasyl Jdydt Fy Qdyt Dfn Afrad Alasrt
May 26, 2025
Jrymt Mrwet Fy Frnsa Tfasyl Jdydt Fy Qdyt Dfn Afrad Alasrt
May 26, 2025 -
 2025 Monaco Grand Prix The Ultimate Guide To Live Streaming And Tv Schedules
May 26, 2025
2025 Monaco Grand Prix The Ultimate Guide To Live Streaming And Tv Schedules
May 26, 2025 -
 Jonathan Peretz A Year Of Loss A Fathers Love
May 26, 2025
Jonathan Peretz A Year Of Loss A Fathers Love
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Jawa Barat Peringatan Hujan Lebat Besok 7 Mei
May 28, 2025
Jawa Barat Peringatan Hujan Lebat Besok 7 Mei
May 28, 2025 -
 Update Prakiraan Cuaca Sumatra Utara Medan Karo Nias Toba
May 28, 2025
Update Prakiraan Cuaca Sumatra Utara Medan Karo Nias Toba
May 28, 2025 -
 Prakiraan Cuaca Jabar Besok 7 5 Antisipasi Curah Hujan Tinggi
May 28, 2025
Prakiraan Cuaca Jabar Besok 7 5 Antisipasi Curah Hujan Tinggi
May 28, 2025 -
 Dangerous Climate Whiplash A Comprehensive Report On Global Urban Impacts
May 28, 2025
Dangerous Climate Whiplash A Comprehensive Report On Global Urban Impacts
May 28, 2025 -
 Ramalan Cuaca Akurat Sumatra Utara Medan Karo Nias Toba Dan Sekitarnya
May 28, 2025
Ramalan Cuaca Akurat Sumatra Utara Medan Karo Nias Toba Dan Sekitarnya
May 28, 2025
