Understanding Your New HMRC Tax Code: Impact Of Savings Income
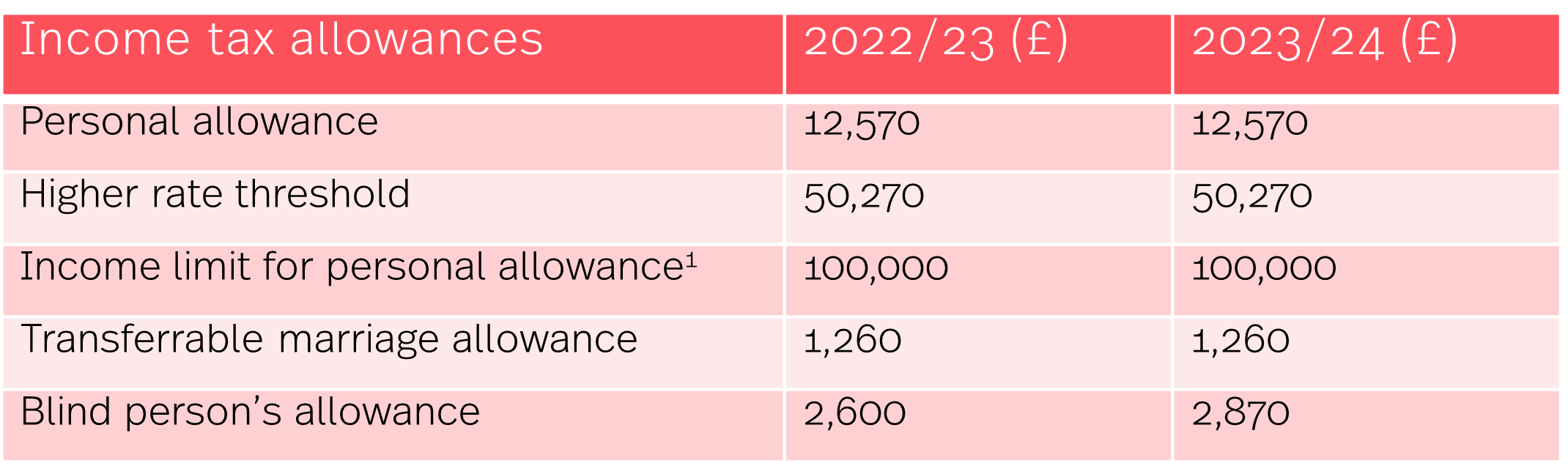
Table of Contents
What is an HMRC Tax Code and How Does it Work?
Your HMRC tax code is a number issued by HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) that dictates how much income tax is deducted from your salary or wages through the PAYE (Pay As You Earn) system. This system ensures you pay tax throughout the tax year, rather than in one large sum at the end. Your tax code reflects your personal tax allowance – the amount you can earn tax-free each tax year. This allowance is currently set at £12,570 (for the 2023/24 tax year, check the latest figures on the HMRC website). Income above this allowance is taxed according to different tax bands, with higher earnings taxed at progressively higher rates.
- Definition of an HMRC tax code: A unique alphanumeric code assigned to each taxpayer.
- How the code determines tax deductions: It calculates the tax-free allowance and applies the relevant tax rates to income above that threshold.
- Tax bands and rates: Income is taxed at different rates (e.g., basic rate, higher rate, additional rate) depending on the level of income.
- Notifying HMRC of changes: It's vital to inform HMRC of any significant changes in your circumstances, such as a change in employment, income, or savings, to ensure your tax code remains accurate.
Understanding the Impact of Savings Income on Your Tax Code
Savings income, such as interest earned from savings accounts, building societies, and even Premium Bonds, is also subject to tax. However, you benefit from a personal savings allowance (PSA). This allowance lets you earn a certain amount of savings interest tax-free each tax year. The PSA amount varies depending on your tax band:
- Basic-rate taxpayers: £1,000
- Higher-rate taxpayers: £500
- Additional-rate taxpayers: £0
Interest earned above your PSA is taxed at your relevant income tax rate. This means that if you are a higher-rate taxpayer and your savings interest exceeds £500, the excess will be taxed at 40%. Investing in a tax-free ISA (Individual Savings Account) can help mitigate the impact of tax on your savings.
- Personal Savings Allowance (PSA): A tax-free allowance for savings interest.
- Taxation above the PSA: Interest earned above your PSA is taxed at your individual income tax rate.
- Higher-rate and additional-rate taxpayers: Face higher tax rates on savings interest exceeding their PSA.
- ISAs and tax efficiency: ISAs offer tax-free growth and withdrawals, making them a popular savings option.
Common Scenarios and Examples of Savings Income Affecting Tax Codes
Let's illustrate how savings income affects your tax bill with some examples:
-
Scenario 1: Basic-rate taxpayer: John earns £25,000 a year and receives £1,500 in savings interest. £500 (£1,500 - £1,000 PSA) will be taxed at 20%, resulting in an additional tax liability of £100.
-
Scenario 2: Higher-rate taxpayer: Sarah earns £55,000 a year and has £800 savings interest. £300 (£800 - £500 PSA) will be taxed at 40%, resulting in an additional tax liability of £120.
-
Scenario 3: ISA impact: David transfers his savings into an ISA. He now avoids paying tax on the interest earned because it’s tax-free within the ISA wrapper.
-
HMRC Tax Calculator: Use the HMRC online tax calculator to estimate your tax liability more accurately.
How to Check Your HMRC Tax Code and Report Changes
Accessing your HMRC tax code is straightforward through the HMRC online service:
- Accessing your tax code online: Log in to your personal HMRC online account to view your current tax code.
- Reporting changes to HMRC: If your circumstances change (e.g., increased savings income), update your details promptly through your online account.
- Importance of accurate information: Keeping your details up-to-date prevents potential tax penalties and ensures accurate tax calculations.
- Contact HMRC: If you encounter difficulties or have questions, contact HMRC directly via their website or helpline.
Conclusion
Understanding your HMRC tax code and its interaction with savings income is essential for responsible tax management. Accurately reporting your savings interest ensures you pay the correct amount of tax and avoid penalties. Review your current HMRC tax code, compare your savings interest against your personal savings allowance, and update your information with HMRC if necessary. Understand your HMRC tax code today, take control of your savings income tax, and ensure your HMRC tax code accurately reflects your savings. Don’t underestimate the impact of your savings income on your HMRC tax code!

Featured Posts
-
 Exploring The Enduring Legacy Of Agatha Christies Hercule Poirot
May 20, 2025
Exploring The Enduring Legacy Of Agatha Christies Hercule Poirot
May 20, 2025 -
 Hmrc Savings Overpayments Are You Missing Out
May 20, 2025
Hmrc Savings Overpayments Are You Missing Out
May 20, 2025 -
 Le Transfert Controverse De Melvyn Jaminet Le Temoignage De Kylian
May 20, 2025
Le Transfert Controverse De Melvyn Jaminet Le Temoignage De Kylian
May 20, 2025 -
 Ia Et Ecriture Une Agatha Christie Virtuelle Revolution Ou Imitation
May 20, 2025
Ia Et Ecriture Une Agatha Christie Virtuelle Revolution Ou Imitation
May 20, 2025 -
 Biarritz Hommage Aux Femmes Parcours De Femmes
May 20, 2025
Biarritz Hommage Aux Femmes Parcours De Femmes
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ecowas Economic Affairs Strategic Planning In Niger
May 20, 2025
Ecowas Economic Affairs Strategic Planning In Niger
May 20, 2025 -
 Eurovision Song Contest 2025 Artist Lineup Announced
May 20, 2025
Eurovision Song Contest 2025 Artist Lineup Announced
May 20, 2025 -
 Niger Retreat Ecowas Charts Economic Development Priorities
May 20, 2025
Niger Retreat Ecowas Charts Economic Development Priorities
May 20, 2025 -
 Enquete Sur Des Allegations De Maltraitance Et D Abus Sexuels A La Fieldview Care Home Maurice
May 20, 2025
Enquete Sur Des Allegations De Maltraitance Et D Abus Sexuels A La Fieldview Care Home Maurice
May 20, 2025 -
 Major Infrastructure Boost 6 Billion Awarded For Coastal Protection Projects
May 20, 2025
Major Infrastructure Boost 6 Billion Awarded For Coastal Protection Projects
May 20, 2025
