Unmasking Private Equity: Four Critical Analyses

Table of Contents
Analyzing Private Equity Investment Strategies
Private equity investment encompasses a range of strategies, each with its own risk profile and return potential. Understanding these strategies is fundamental to navigating the world of private equity. Successful private equity firms adeptly employ various approaches depending on market conditions and investment opportunities. Let's explore some key private equity investment strategies:
-
Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs): LBOs involve acquiring a company using a significant amount of borrowed money (leverage) to finance the purchase. The acquired company's assets often serve as collateral for the loan. A thorough risk assessment, including due diligence on the target company's financials and operations, is crucial before undertaking an LBO. Successful LBOs often involve restructuring the acquired company to improve its profitability and then eventually selling it for a profit.
-
Venture Capital (VC): Venture capital firms invest in early-stage companies with high growth potential. VC investment typically occurs in stages, from seed funding to later-stage financing. Thorough due diligence is paramount, focusing on the management team, market opportunity, and the company's intellectual property. Exit strategies for VC investments often involve an initial public offering (IPO) or a sale to a larger company.
-
Growth Equity: This strategy focuses on investing in established companies that are experiencing rapid growth. Growth equity investments aim to accelerate the company's expansion through strategic partnerships, operational improvements, and expansion into new markets. This approach often involves less operational involvement compared to venture capital.
-
Distressed Debt: This involves investing in the debt of financially troubled companies. Private equity firms may restructure the debt, taking control of the company's operations to improve its financial health and ultimately increase the value of the investment. This strategy demands a deep understanding of financial restructuring and turnaround management.
Evaluating Private Equity Performance and Returns
Assessing private equity performance requires specialized metrics due to the illiquid nature of these investments. Key performance indicators (KPIs) provide valuable insights into the success of private equity investments. Here are some widely used metrics:
-
Internal Rate of Return (IRR): IRR calculates the annualized rate of return on an investment, considering the timing of cash flows. A higher IRR generally indicates a more successful investment. However, interpretation requires careful consideration of the investment timeline and risk profile.
-
Multiple of Invested Capital (MOIC): MOIC measures the multiple of the initial investment that is returned to investors. A MOIC greater than 1 signifies a profitable investment. Benchmarking MOIC against other private equity investments and alternative asset classes provides a valuable context for evaluating performance.
-
Total Value to Paid-In Capital (TVPI): TVPI provides a comprehensive measure of performance by considering both realized and unrealized returns. It's a valuable metric for evaluating the overall success of a private equity fund.
Benchmarking private equity performance against other asset classes, such as publicly traded equities or bonds, is essential for understanding its risk-adjusted returns.
Understanding the Risks Associated with Private Equity
Private equity investments, while potentially highly rewarding, are not without significant risks. Investors should carefully assess and mitigate these risks before committing capital.
-
Illiquidity Risk: Private equity investments are typically illiquid, meaning they cannot be easily sold on a public exchange. This illiquidity can make it difficult to access capital quickly if needed.
-
Market Risk: Private equity investments are susceptible to overall market fluctuations and economic downturns. A decline in market conditions can negatively impact the value of portfolio companies.
-
Operational Risk: Private equity investments involve a degree of operational involvement, particularly in leveraged buyouts and distressed debt situations. Challenges in managing and improving the operations of portfolio companies can lead to underperformance.
-
Management Risk: The success of a private equity investment is significantly dependent on the quality of the management team of the portfolio company. Thorough due diligence on the management team is crucial to minimize this risk. Effective due diligence, including background checks and operational reviews, is crucial in mitigating these risks.
The Regulatory Landscape and Ethical Considerations in Private Equity
The private equity industry operates within a complex regulatory environment, and ethical considerations are increasingly important. Transparency and responsible investment practices are crucial for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the industry.
-
Regulatory Scrutiny: Private equity firms are subject to various regulations, including those related to securities laws, antitrust laws, and corporate governance. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal and reputational risks.
-
Transparency and Disclosure Requirements: Increasing pressure exists for greater transparency in private equity, particularly regarding fee structures and investment performance. Improved disclosure practices are vital for building trust with investors.
-
Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations encompass a wide range of issues, including the treatment of employees of portfolio companies, environmental sustainability (ESG factors in private equity), and the overall social impact of private equity investments.
-
Fee Structures and Alignment of Interests: Private equity firms typically charge management fees and performance fees. Alignment of interests between the general partners (GPs) and the limited partners (LPs) is crucial for ensuring that the interests of all stakeholders are considered.
Conclusion
This article explored four critical analyses of private equity: investment strategies, performance evaluation, inherent risks, and the regulatory landscape. Understanding these aspects is essential for investors, entrepreneurs, and policymakers navigating this complex market. By understanding these four critical analyses, you can navigate the complex world of private equity with greater confidence. Continue your exploration of private equity investing by researching specific firms, investment strategies, and regulatory frameworks. A deeper understanding will allow you to make more informed decisions related to private equity investment opportunities.

Featured Posts
-
 Assassination Records Us To Unseal Key Documents On Robert F Kennedy And Martin Luther King Jr
May 27, 2025
Assassination Records Us To Unseal Key Documents On Robert F Kennedy And Martin Luther King Jr
May 27, 2025 -
 Ftc Probe Into Open Ais Chat Gpt What It Means For Ai Development
May 27, 2025
Ftc Probe Into Open Ais Chat Gpt What It Means For Ai Development
May 27, 2025 -
 Onovlennya Viyskova Dopomoga Ukrayini Vid Nimechchini Spisok Ozbroyennya
May 27, 2025
Onovlennya Viyskova Dopomoga Ukrayini Vid Nimechchini Spisok Ozbroyennya
May 27, 2025 -
 Chi Zavadit Putin Mirotvorchiy Misiyi V Ukrayini Analiz Vplivu Na Frantsiyu Ta Britaniyu
May 27, 2025
Chi Zavadit Putin Mirotvorchiy Misiyi V Ukrayini Analiz Vplivu Na Frantsiyu Ta Britaniyu
May 27, 2025 -
 How To Watch Bad Moms In Hd On Comedy Central
May 27, 2025
How To Watch Bad Moms In Hd On Comedy Central
May 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Epcots Flower And Garden Festival What To Expect
May 30, 2025
Epcots Flower And Garden Festival What To Expect
May 30, 2025 -
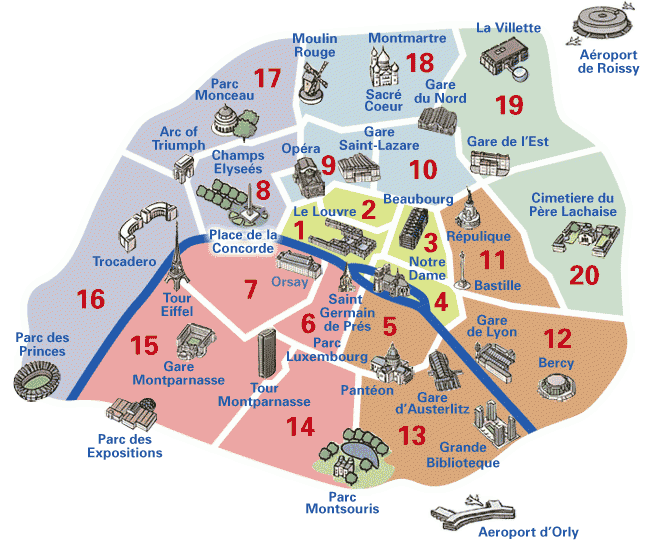 Discover The Best Areas To Stay In Paris A Neighborhood Guide
May 30, 2025
Discover The Best Areas To Stay In Paris A Neighborhood Guide
May 30, 2025 -
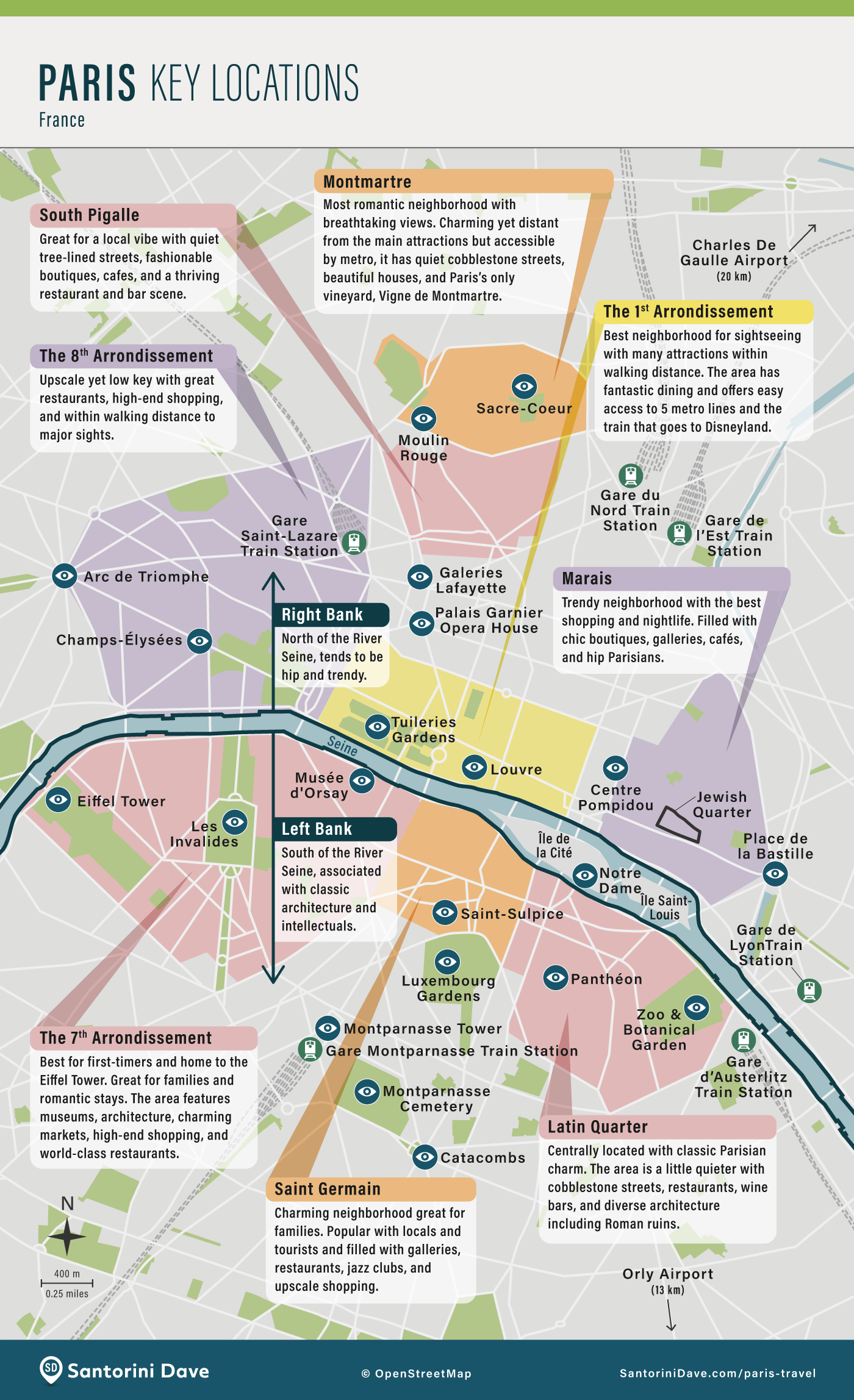 Paris Neighborhood Guide Top Areas To Explore
May 30, 2025
Paris Neighborhood Guide Top Areas To Explore
May 30, 2025 -
 Planning Your Visit To The Epcot Flower And Garden Festival
May 30, 2025
Planning Your Visit To The Epcot Flower And Garden Festival
May 30, 2025 -
 The Best Neighborhoods In Paris A Locals Perspective
May 30, 2025
The Best Neighborhoods In Paris A Locals Perspective
May 30, 2025
