Wildfires Drive Unprecedented Global Forest Loss: A Critical Analysis
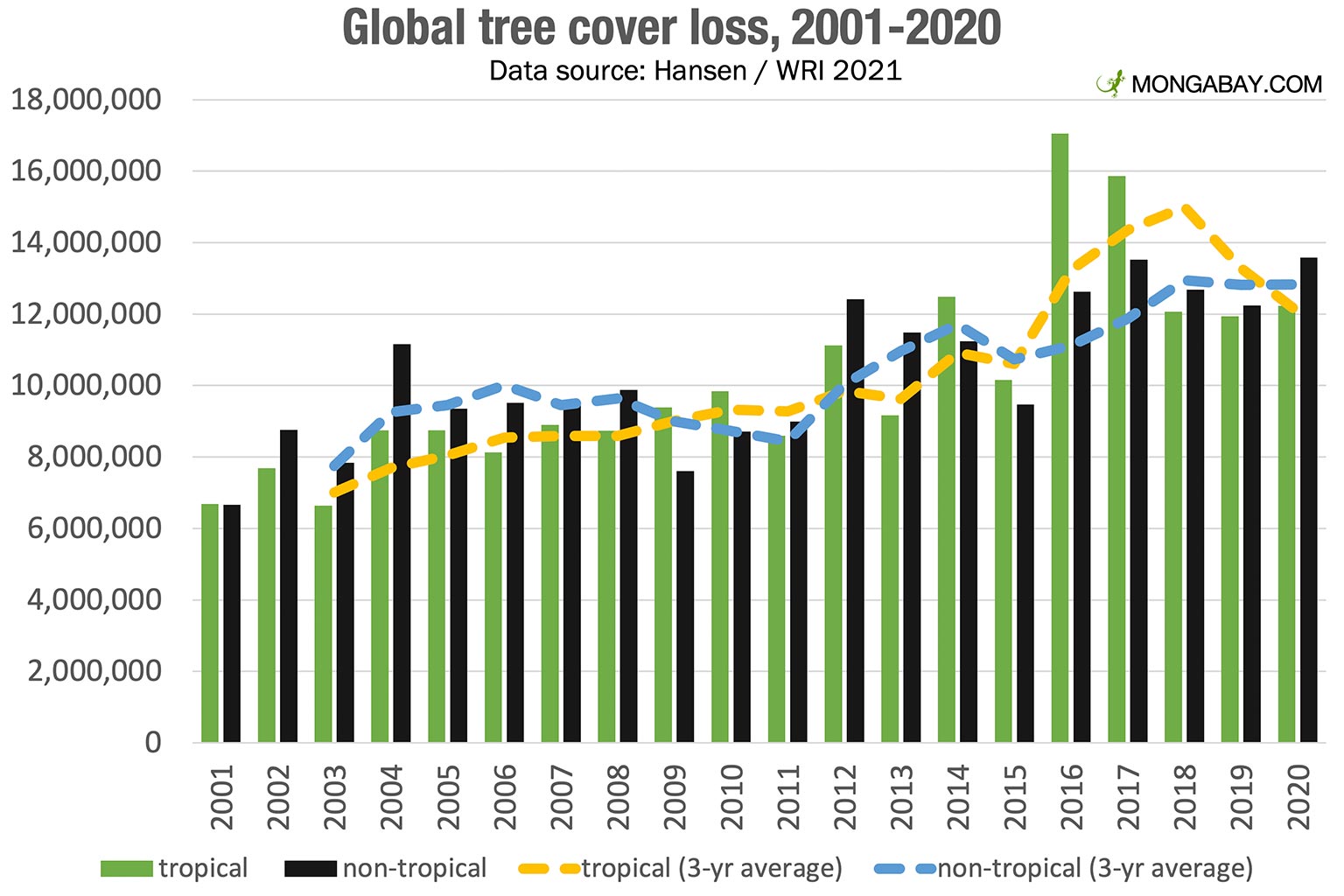
Table of Contents
The Escalating Threat of Wildfires
The frequency and intensity of wildfires are dramatically increasing worldwide, driven largely by the effects of climate change. This escalating threat presents a significant challenge to global forest conservation efforts and exacerbates existing environmental issues.
Increased Frequency and Intensity
The rising global temperatures and increasingly dry conditions create a perfect storm for wildfire ignition and spread. We are witnessing a disturbing trend of larger, more intense, and more frequent wildfires across the globe.
- Amazon Rainforest: The Amazon, once considered the "lungs of the planet," has experienced record-breaking deforestation and wildfire outbreaks in recent years, significantly impacting biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- Australia: The devastating 2019-2020 bushfire season in Australia burned an area larger than the size of some European countries, resulting in catastrophic wildlife loss and significant environmental damage.
- California: The western United States, particularly California, faces increasingly frequent and severe wildfires fueled by prolonged drought and extreme heat.
Data from the Global Forest Watch indicates a significant upward trend in the total area burned by wildfires over the past three decades. This alarming statistic underscores the urgency of addressing this critical issue.
Expanding Wildfire Seasons
Climate change is not only intensifying wildfires but also extending their seasons. Early snowmelt and prolonged droughts create longer periods of dry, flammable vegetation, providing ample opportunity for fires to start and spread uncontrollably.
- Mediterranean Region: The Mediterranean basin experiences increasingly longer and hotter summers, leading to extended wildfire seasons and an elevated risk of large-scale forest fires.
- Siberia: The boreal forests of Siberia are experiencing longer periods of drought, making them highly susceptible to intense and widespread wildfires.
- Canadian Forests: Canada's vast boreal forests are also witnessing longer wildfire seasons, contributing significantly to national and global carbon emissions.
The extended fire seasons further exacerbate the already significant environmental damage caused by wildfires, placing immense pressure on ecosystems and communities.
Devastating Consequences of Wildfire-Driven Forest Loss
The consequences of wildfire-driven forest loss extend far beyond the immediate destruction of trees. The impacts ripple through the environment, economy, and society, creating a complex web of interconnected challenges.
Biodiversity Loss
Wildfires are a major driver of biodiversity loss. The intense heat and flames destroy habitats, leading to the displacement and extinction of countless plant and animal species.
- Koalas in Australia: The 2019-2020 bushfires decimated koala populations, highlighting the devastating impact of wildfires on vulnerable species.
- Amazonian Birds: The loss of rainforest habitat due to wildfires in the Amazon threatens a wide array of bird species.
- Endemic Plants: Many plant species found only in specific regions are at severe risk of extinction due to wildfire-driven habitat loss.
The destruction of habitats disrupts delicate ecological balances, causing cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
Climate Change Exacerbation
Forest loss due to wildfires significantly exacerbates climate change. Trees act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. When forests burn, they release vast amounts of stored carbon back into the atmosphere, further accelerating global warming.
- Carbon Emissions: Wildfires are a substantial source of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to the overall increase in atmospheric CO2 levels.
- Reduced Carbon Sequestration: The loss of forests reduces the planet's capacity to absorb CO2, creating a dangerous positive feedback loop.
- Albedo Effect: The blackened landscapes left by wildfires reduce the Earth's albedo (reflectivity), leading to increased absorption of solar radiation and further warming.
The interconnectedness of wildfires and climate change necessitates a holistic approach to address both issues simultaneously.
Economic and Social Impacts
The economic and social costs associated with wildfires are substantial. Wildfire suppression efforts are expensive, and the damage to property and infrastructure can be devastating. Communities dependent on forests for their livelihoods often suffer significant economic losses.
- Property Damage: Wildfires cause billions of dollars in damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure each year.
- Loss of Livelihoods: Forestry, tourism, and other industries dependent on healthy forests suffer significant economic losses due to wildfires.
- Displacement and Health Impacts: Wildfires displace communities, cause respiratory problems, and create other health challenges.
The devastating impact of wildfires requires a multi-faceted response that addresses both the immediate crisis and the long-term consequences.
Addressing the Crisis: Mitigation and Conservation Strategies
Combating the devastating effects of wildfires requires a comprehensive strategy that incorporates several key elements. Effective mitigation and conservation strategies are essential to reduce the risk and impact of future wildfires.
Improved Forest Management Practices
Sustainable forest management plays a crucial role in reducing wildfire risk. Practices such as controlled burns, fuel reduction, and the prevention of human-caused fires can significantly minimize the impact of wildfires.
- Controlled Burns: Carefully planned and controlled burns can reduce the accumulation of flammable materials, lessening the intensity and spread of future wildfires.
- Fuel Reduction: Thinning forests and removing underbrush can reduce the amount of fuel available for wildfires.
- Public Education and Awareness: Educating the public about wildfire prevention and responsible land management is essential.
Implementing effective forest management strategies requires collaborative efforts between governments, landowners, and communities.
Climate Change Mitigation
Addressing climate change is crucial to reducing the frequency and intensity of wildfires. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is essential to slow the rate of global warming and lessen the conditions that fuel wildfires.
- Renewable Energy Transition: Shifting towards renewable energy sources is crucial for reducing carbon emissions.
- Sustainable Transportation: Promoting sustainable transportation options can significantly reduce emissions from the transportation sector.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation and agreements are vital for coordinated action on climate change.
Aggressive climate change mitigation is paramount for preventing future wildfire disasters.
Community Engagement and Preparedness
Engaging communities in wildfire prevention and preparedness is crucial. Effective early warning systems, evacuation plans, and community-based wildfire prevention programs can save lives and minimize damage.
- Early Warning Systems: Robust early warning systems are vital for alerting communities to impending wildfire threats.
- Evacuation Plans: Well-defined and regularly practiced evacuation plans can ensure the safe evacuation of communities in the event of a wildfire.
- Community-Based Fire Prevention: Community-based programs can promote responsible land management and educate residents about wildfire risks.
A concerted effort to educate and engage communities is a cornerstone of effective wildfire management.
Conclusion
Wildfires are a major driver of unprecedented global forest loss, with devastating consequences for biodiversity, climate change, and human societies. The escalating frequency and intensity of wildfires, exacerbated by climate change, demand immediate and concerted action. The economic and social impacts are severe, highlighting the need for comprehensive strategies that incorporate improved forest management practices, aggressive climate change mitigation, and community engagement and preparedness. Combating the devastating effects of wildfires and preventing further global forest loss requires immediate and concerted action from individuals, communities, and governments alike. Let's work together to protect our forests and safeguard the planet's future.

Featured Posts
-
 March 6 2025 Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers
May 24, 2025
March 6 2025 Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers
May 24, 2025 -
 Zekanin Sirri Burclar Ve Entelektueel Yetenekler
May 24, 2025
Zekanin Sirri Burclar Ve Entelektueel Yetenekler
May 24, 2025 -
 Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend 2025 Tickets How To Get Yours Now
May 24, 2025
Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend 2025 Tickets How To Get Yours Now
May 24, 2025 -
 Znaete Li Vy Vse Roli Olega Basilashvili Proydite Nash Test
May 24, 2025
Znaete Li Vy Vse Roli Olega Basilashvili Proydite Nash Test
May 24, 2025 -
 Huge Diamond Ring Annie Kilners Public Display After Walker Spotting
May 24, 2025
Huge Diamond Ring Annie Kilners Public Display After Walker Spotting
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Porsche 956 Nin Tavan Sergisinin Sirri
May 25, 2025
Porsche 956 Nin Tavan Sergisinin Sirri
May 25, 2025 -
 Porsche 956 Muezede Tavan Sergisi Neden
May 25, 2025
Porsche 956 Muezede Tavan Sergisi Neden
May 25, 2025 -
 Porsche Now
May 25, 2025
Porsche Now
May 25, 2025 -
 Porsche Macan Rafbill Skodadu Taeknithrounina
May 25, 2025
Porsche Macan Rafbill Skodadu Taeknithrounina
May 25, 2025 -
 Fyrsta 100 Rafutgafa Porsche Macan Upplysingar Og Eiginleikar
May 25, 2025
Fyrsta 100 Rafutgafa Porsche Macan Upplysingar Og Eiginleikar
May 25, 2025
