Accessibility And Affordability: Examining Over-the-Counter Birth Control In A Post-Roe Landscape

Table of Contents
Increased Accessibility: A Boon for Reproductive Healthcare?
Increased access to over-the-counter (OTC) birth control offers significant potential advantages for reproductive healthcare. The convenience factor alone is transformative. No longer would individuals need doctor's appointments or prescriptions, reducing barriers for many.
- Improved Convenience and Reduced Barriers: OTC birth control offers unparalleled convenience, eliminating the need for appointments, prescriptions, and potentially costly transportation. This is particularly beneficial for individuals in rural areas or those with limited time or mobility.
- Increased Privacy: Obtaining birth control discreetly is crucial for many individuals. OTC access enhances privacy, allowing people to manage their reproductive health without disclosing personal information.
- Potential Reduction in Unintended Pregnancies: Easier access to effective contraception directly contributes to a decrease in unintended pregnancies, a leading factor in maternal mortality and economic strain.
- Empowerment: OTC birth control empowers individuals to take control of their reproductive health, fostering autonomy and self-determination.
However, increased accessibility also presents challenges:
- Potential for Misuse or Incorrect Usage: Without proper guidance, some individuals might misuse hormonal birth control, leading to reduced effectiveness or adverse health consequences. Thorough education is paramount.
- Need for Comprehensive Education and Access to Reliable Information: Providing accurate information about different OTC birth control methods, their effectiveness, and potential side effects is critical to ensure safe and responsible use.
- Ensuring Equitable Access for All Socioeconomic Groups: While OTC access theoretically broadens availability, affordability remains a significant hurdle for many. Ensuring equitable access across all socioeconomic groups is essential.
Affordability Concerns: Is OTC Birth Control Truly Accessible to All?
Even with OTC availability, cost remains a significant barrier for many. The price of various OTC birth control methods, such as condoms, emergency contraception, and potentially future hormonal options, varies considerably.
- Cost Comparison: A thorough cost analysis of various OTC birth control options is necessary to understand their affordability for different income brackets. Condoms, for example, are relatively inexpensive compared to emergency contraceptive pills.
- Insurance Coverage: The role of insurance coverage is critical. Some insurance plans may cover the cost of OTC birth control, while others might not. The variations in cost-sharing among different insurance plans need careful consideration.
- Long-Term Cost Savings: While upfront costs might seem high, the long-term cost savings resulting from reduced unintended pregnancies, and therefore decreased healthcare costs associated with prenatal care, childbirth, and potential abortions, should be factored into the equation.
- Government Subsidies: Government subsidies or financial assistance programs may be necessary to ensure affordability for low-income individuals, making OTC birth control a truly accessible option for all.
Examples of Price Differences:
- Condoms: $10-$30 per pack
- Emergency Contraception: $30-$50 per pill
The Role of Pharmacies and Healthcare Providers in Expanding Access
Pharmacies and healthcare providers play a vital role in expanding access to OTC birth control. Their involvement extends beyond simply stocking shelves.
- Pharmacist Training and Counseling: Pharmacists require extensive training to provide accurate information about different OTC birth control methods, address patient questions, and identify potential contraindications. This includes counseling on proper usage and potential side effects.
- Telehealth Platforms: Telehealth platforms can significantly enhance access to reproductive healthcare services, providing virtual consultations and enabling remote prescription refills, particularly beneficial for individuals in remote areas.
- Partnerships: Collaboration between pharmacies, healthcare providers, and community organizations can create comprehensive programs that address not only access but also education and affordability.
Examples of Successful Initiatives:
- Comprehensive pharmacist training programs developed in conjunction with medical schools and professional organizations.
- Telehealth platforms specifically designed for reproductive health consultations and birth control access.
- Community-based programs providing subsidized birth control and educational resources.
Long-Term Impacts: Assessing the Effects on Public Health
Wider OTC birth control availability will have significant long-term impacts on public health.
- Unintended Pregnancies and Abortion Rates: Increased access to contraception is expected to decrease unintended pregnancies and potentially abortion rates. However, rigorous data collection and analysis will be essential to assess the true impact.
- Maternal and Child Health: A reduction in unintended pregnancies directly improves maternal and child health outcomes. Fewer high-risk pregnancies lead to better health for both mothers and children.
- Sexually Transmitted Infection Rates: The impact on sexually transmitted infection (STI) rates is complex and requires further investigation. While increased contraceptive use might indirectly reduce some STIs through reduced sexual encounters, access to comprehensive sexual health education is crucial.
Potential Long-Term Effects:
- Reduced rates of unintended pregnancies and abortions.
- Improved maternal and child health outcomes.
- Potential impacts (positive or negative) on STI rates require further study.
Securing Accessibility and Affordability of Over-the-Counter Birth Control
In conclusion, increasing the accessibility and affordability of over-the-counter birth control presents both opportunities and challenges. While increased convenience and privacy are significant benefits, addressing affordability concerns and ensuring proper education and access to reliable information are crucial for successful implementation. Equitable access for all socioeconomic groups is paramount. Continued dialogue, policy changes, and further research are essential to guarantee accessible and affordable birth control options for everyone. Learn more about accessing affordable over-the-counter birth control options in your area, and advocate for policies that guarantee accessibility and affordability for all.

Featured Posts
-
 Glastonbury 2025 A Lineup Analysis Charli Xcx Neil Young And Key Artists
May 25, 2025
Glastonbury 2025 A Lineup Analysis Charli Xcx Neil Young And Key Artists
May 25, 2025 -
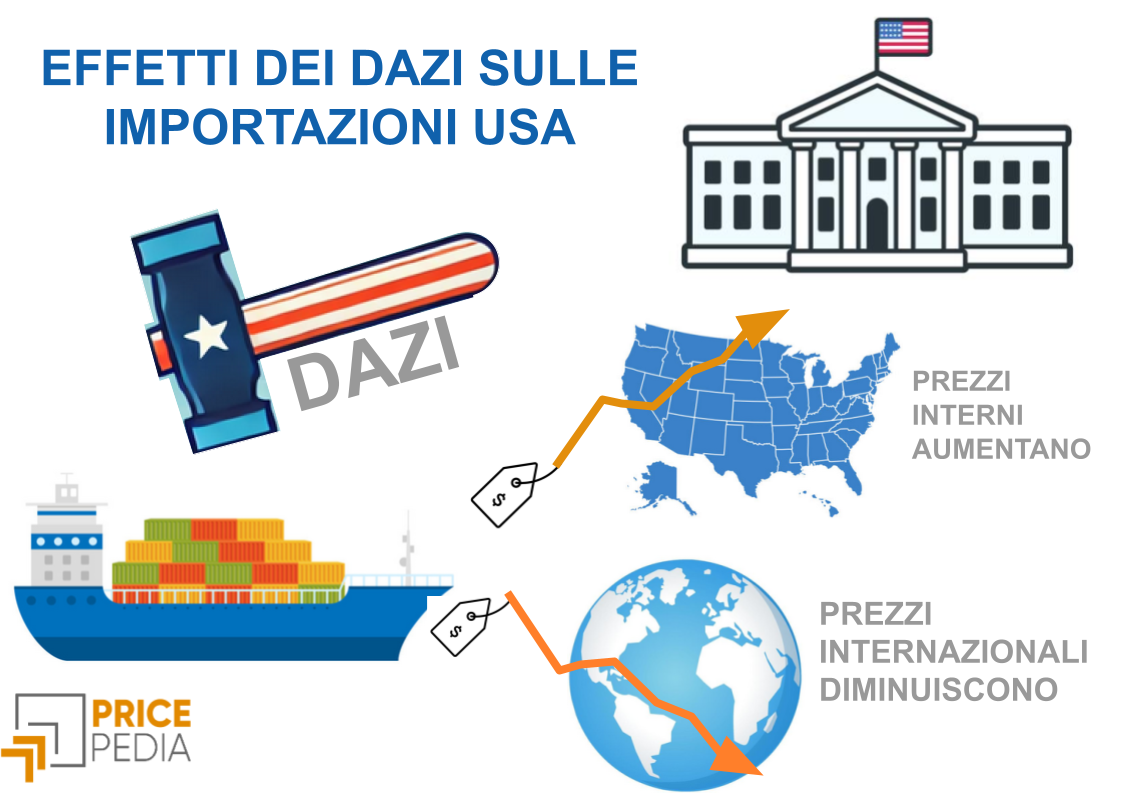 Importazioni Usa Come Influiscono I Dazi Sui Prezzi Dell Abbigliamento
May 25, 2025
Importazioni Usa Come Influiscono I Dazi Sui Prezzi Dell Abbigliamento
May 25, 2025 -
 Obzor Publikatsii Gryozy Lyubvi Ili Ilicha V Gazete Trud
May 25, 2025
Obzor Publikatsii Gryozy Lyubvi Ili Ilicha V Gazete Trud
May 25, 2025 -
 Cenovus Ceo Downplays Merger Speculation Prioritizes Organic Expansion
May 25, 2025
Cenovus Ceo Downplays Merger Speculation Prioritizes Organic Expansion
May 25, 2025 -
 Cassidy Hutchinson Jan 6 Hearing Testimony To Feature In Fall Memoir
May 25, 2025
Cassidy Hutchinson Jan 6 Hearing Testimony To Feature In Fall Memoir
May 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Atletico Madrid In 3 Maclik Durgunlugun Sonu
May 25, 2025
Atletico Madrid In 3 Maclik Durgunlugun Sonu
May 25, 2025 -
 3 Maclik Bekleyisin Ardindan Atletico Madrid In Zafere Ulasmasi
May 25, 2025
3 Maclik Bekleyisin Ardindan Atletico Madrid In Zafere Ulasmasi
May 25, 2025 -
 Atletico Madrid 3 Maclik Kara Seri Sonlandi
May 25, 2025
Atletico Madrid 3 Maclik Kara Seri Sonlandi
May 25, 2025 -
 Atletico Madrid In 3 Maclik Yenilmezlik Serisi
May 25, 2025
Atletico Madrid In 3 Maclik Yenilmezlik Serisi
May 25, 2025 -
 Atletico Madrid In 3 Maclik Hasreti Zaferle Son Buldu
May 25, 2025
Atletico Madrid In 3 Maclik Hasreti Zaferle Son Buldu
May 25, 2025
