Analyzing The Great Decoupling: Trends And Future Predictions

Table of Contents
Geopolitical Factors Driving the Great Decoupling
Several significant geopolitical factors are fueling the Great Decoupling and reshaping the global economic order. These factors represent a move away from the previously dominant narrative of unrestricted globalization and increased economic interdependence.
The Rise of Protectionism and Trade Wars
Protectionist policies, characterized by tariffs, trade barriers, and sanctions, are significantly impacting global trade and economic interdependence. The rise of protectionism is a key driver of the Great Decoupling.
- Impact on Global Trade: Tariffs increase the cost of goods, reducing trade volume and hindering economic growth. This is exemplified by the ongoing trade tensions between various countries.
- Examples of Trade Wars: The US-China trade war, initiated in 2018, serves as a prime example. The imposition of tariffs on billions of dollars worth of goods led to disruptions in global supply chains and increased costs for consumers. Similar trade disputes have occurred between other nations, further contributing to economic decoupling.
- Sanctions and Embargoes: Sanctions, such as those imposed on Russia following its invasion of Ukraine, highlight the use of geopolitical tools to disrupt economic relations and foster decoupling. These measures often have far-reaching consequences, impacting global energy markets and supply chains.
The US-China Tech Cold War
The escalating technological rivalry between the US and China is another major contributor to the Great Decoupling. This "tech cold war" involves competition for technological dominance, impacting various sectors, from semiconductors to artificial intelligence.
- Impact on Supply Chains: The decoupling of technological supply chains is forcing companies to diversify their sourcing and manufacturing locations, leading to increased costs and complexity. This necessitates a reassessment of supply chain resilience.
- Technological Innovation: The tech cold war is incentivizing both countries to invest heavily in research and development, potentially accelerating technological innovation but also creating a more fragmented technological landscape.
- Intellectual Property and Data Security: Concerns over intellectual property theft and data security are driving nations to limit technology transfer and collaboration, further exacerbating the decoupling.
Shifting Geopolitical Alliances
The Great Decoupling is also causing a realignment of geopolitical alliances and partnerships. Nations are increasingly forming regional blocs and trade agreements to reduce their reliance on global supply chains.
- New Alliances: The formation of new alliances, such as the AUKUS pact between Australia, the UK, and the US, reflects a strategic shift toward regional cooperation and security partnerships.
- Regional Trade Agreements: The rise of regional trade agreements, like the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), illustrates a move toward regional economic integration and a reduced reliance on global trade.
- Multilateral Institutions: The effectiveness of multilateral institutions like the World Trade Organization (WTO) in navigating the changing global landscape is being tested as nations increasingly prioritize bilateral and regional agreements over multilateral cooperation.
Economic Consequences of the Great Decoupling
The Great Decoupling carries significant economic consequences, affecting global supply chains, inflation, and economic stability.
Impact on Global Supply Chains
The decoupling of global supply chains is leading to significant disruptions. Companies are increasingly focusing on regionalization, “friend-shoring” (prioritizing trade with trusted allies) and “near-shoring” (relocating production closer to home).
- Supply Chain Disruption: The pandemic underscored the fragility of globally integrated supply chains. Disruptions caused by geopolitical events and natural disasters highlight the need for greater resilience.
- Regionalization: Companies are increasingly diversifying their supply chains, moving away from reliance on single sourcing and geographically concentrated manufacturing.
- Reshoring and Nearshoring: The trend towards reshoring (bringing manufacturing back to the home country) and near-shoring (moving production to nearby countries) is gaining momentum, driven by concerns over geopolitical risk and supply chain vulnerability.
Inflationary Pressures and Economic Volatility
The Great Decoupling is contributing to inflationary pressures and increased economic volatility. Disruptions in global supply chains, protectionist policies, and geopolitical uncertainty all contribute to this instability.
- Inflation: Disruptions to supply chains, coupled with increased transportation costs and trade barriers, contribute to inflationary pressures.
- Economic Volatility: Geopolitical risks and uncertainty create increased economic volatility, making it harder for businesses to plan and invest.
- Risk Management: Companies and governments need to develop effective risk management strategies to mitigate the economic risks associated with the Great Decoupling.
Impact on Developing Economies
Developing economies are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of the Great Decoupling. Their reliance on global trade and foreign investment makes them susceptible to disruptions in global supply chains and reduced demand for their exports.
- Challenges for Emerging Markets: Emerging markets face challenges related to reduced export demand, increased competition, and difficulty accessing financing.
- Opportunities: Some developing economies may benefit from the shift towards regionalization, attracting investment and becoming part of new regional value chains.
- Economic Resilience: Developing economies need to foster economic resilience by diversifying their economies, strengthening their institutions, and building more resilient supply chains.
Technological Advancements and the Future of Decoupling
Technological advancements are likely to play a crucial role in shaping the future of the Great Decoupling.
The Role of Automation and AI
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) could both accelerate and mitigate the effects of decoupling.
- Automation: Automation can help reduce reliance on global supply chains by enabling domestic production and reshoring.
- AI: AI can enhance supply chain visibility and resilience, optimizing logistics and reducing disruptions.
- Labor Markets: The impact on labor markets needs careful consideration, as automation may lead to job displacement in some sectors while creating new opportunities in others.
The Rise of Digital Currencies and Fintech
Digital currencies and fintech innovations have the potential to reshape international finance and potentially mitigate some aspects of financial decoupling.
- Cross-border Payments: Digital currencies could streamline cross-border transactions, reducing reliance on traditional banking systems and potentially fostering greater economic integration despite geopolitical tensions.
- Financial Decoupling: While digital currencies might facilitate transactions, they also present risks related to regulation, stability, and potential for misuse. The impact on international finance and monetary policy is still evolving.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and security in cross-border payments, reducing risks associated with fraud and illicit activities.
Analyzing the Great Decoupling: Key Takeaways and Future Outlook
The Great Decoupling is a multifaceted phenomenon with far-reaching implications for the global economy, geopolitics, and technology. Understanding its drivers and consequences is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of the 21st century. The shift towards regionalization, increased protectionism, and technological rivalry are reshaping global supply chains and international relations. Developing economies face specific challenges, requiring adaptation and resilience-building strategies. Technological advancements offer both opportunities and challenges, impacting labor markets and international finance.
To prepare for the future, it's essential to continue researching the Great Decoupling and its implications for your industry and region. Stay informed about ongoing developments by exploring resources such as academic journals, industry reports, and government publications. Analyzing the Great Decoupling and its evolving dynamics is not just an academic exercise; it's a critical aspect of navigating the changing global landscape. Understanding this complex phenomenon will be essential for success in the years to come.

Featured Posts
-
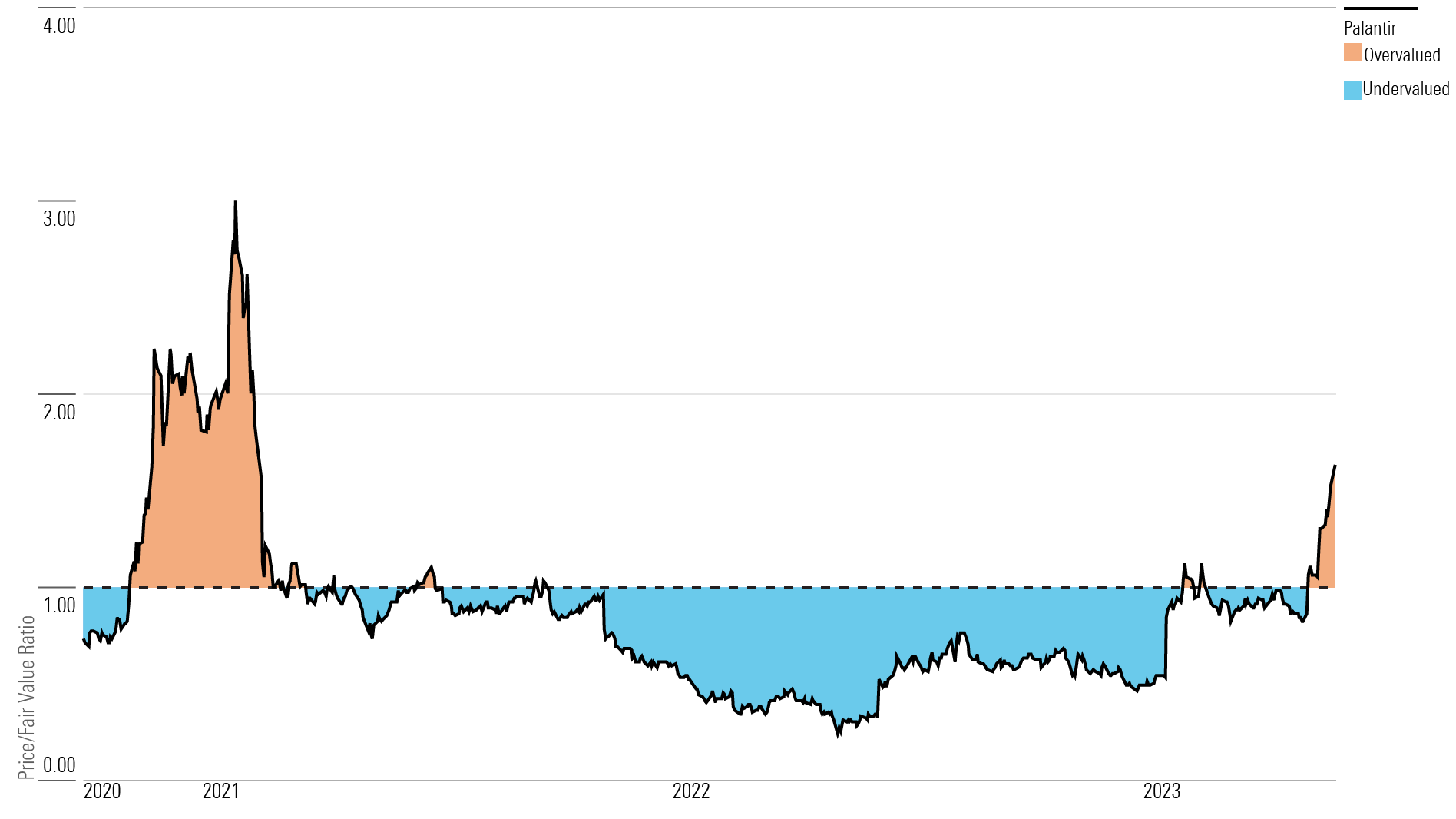 Should You Buy Palantir Stock Before May 5th Wall Streets Surprising Consensus
May 09, 2025
Should You Buy Palantir Stock Before May 5th Wall Streets Surprising Consensus
May 09, 2025 -
 Bitcoin Madenciliginde Azalan Karlilik Ve Gelecegin Senaryolari
May 09, 2025
Bitcoin Madenciliginde Azalan Karlilik Ve Gelecegin Senaryolari
May 09, 2025 -
 White Houses Last Minute Pivot Maha Influencer Replaces Nominee For Surgeon General
May 09, 2025
White Houses Last Minute Pivot Maha Influencer Replaces Nominee For Surgeon General
May 09, 2025 -
 Pam Bondis Response To Congressman Comers Epstein Files Accusations
May 09, 2025
Pam Bondis Response To Congressman Comers Epstein Files Accusations
May 09, 2025 -
 Montoya Claims Doohans F1 Future Already Decided
May 09, 2025
Montoya Claims Doohans F1 Future Already Decided
May 09, 2025
