Bank Of Canada Interest Rate Outlook: Job Losses And The Potential For Further Cuts
Table of Contents
Recent Job Losses and Their Impact on the Economy
Employment Data and Trends
Statistics Canada's recent employment figures paint a concerning picture. The Canadian economy shed [insert number] jobs in [month, year], pushing the national unemployment rate to [insert percentage]. This marks a [increase/decrease] from the previous month's rate of [insert percentage].
- Specific numbers on job losses: [Insert specific data points, e.g., X number of jobs lost in the manufacturing sector, Y number in retail].
- Sectors most impacted: The manufacturing and retail sectors have been particularly hard hit, reflecting weakening consumer confidence and decreased business investment. The impact has also been regionally varied, with [mention specific regions and their unemployment rates].
- Regional variations in unemployment: Provinces like [mention specific provinces] have experienced disproportionately higher unemployment rates compared to the national average.
These job losses have significant implications. Decreased employment directly translates to reduced consumer spending, a key driver of economic growth. Lower consumer confidence, as reflected in the recent [mention specific index, e.g., Consumer Confidence Index] reading of [insert number], further exacerbates this downward pressure. Businesses, facing reduced demand, are likely to postpone investment plans, leading to a further slowdown in economic activity.
The Ripple Effect on Inflation
Job losses typically exert downward pressure on inflation. The Phillips Curve illustrates the inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation: higher unemployment generally leads to lower inflation.
- Relationship between unemployment and inflation (Phillips Curve): The current rise in unemployment suggests a potential decrease in inflationary pressure.
- Anticipated inflation rates: Economists are currently predicting inflation rates of [insert percentage] for [time period]. This is [higher/lower] than the Bank of Canada's inflation target of [insert percentage].
- The Bank of Canada's inflation target: The Bank of Canada aims to maintain inflation within a target range, typically around 2%. Lower inflation due to job losses might provide the central bank with some room to maneuver on interest rates.
Decreased consumer demand, a direct consequence of job losses, reduces the pressure on prices. This decreased demand might justify lower interest rates to stimulate the economy and prevent a prolonged period of economic stagnation.
The Bank of Canada's Current Monetary Policy Stance
The Current Interest Rate
As of [date of last rate decision], the Bank of Canada's overnight rate stands at [insert percentage]. This is [higher/lower] than the rate of [insert percentage] from [previous date]. The rationale behind the [previous] decision cited [mention the reasons].
- The current overnight rate: [Insert current overnight rate]
- The effective interest rate: [Insert effective interest rate]
- Reasons cited by the Bank of Canada for their last decision: [Summarize the reasons given by the Bank of Canada]
The Bank of Canada Governor, [Governor's name], in their recent statement, [mention key quotes about future expectations, e.g., hinted at the possibility of further rate cuts depending on the economic data].
Factors Influencing the Bank's Decisions
The Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions are not solely determined by domestic employment figures. Several other factors play a crucial role.
- Global economic growth projections: Slowdowns in major global economies can negatively impact Canadian exports and growth, influencing interest rate decisions.
- Commodity prices (oil, etc.): Fluctuations in commodity prices, particularly oil, significantly affect the Canadian economy.
- CAD exchange rate against USD: The exchange rate impacts both inflation and the competitiveness of Canadian exports.
These factors interact dynamically with the job losses situation. For example, a global recession coupled with high unemployment might lead to more aggressive interest rate cuts, while a strengthening Canadian dollar might mitigate the need for such actions.
Predicting Future Bank of Canada Interest Rate Movements
Scenarios for Future Rate Cuts
Several scenarios are possible, depending on the evolution of the economic situation:
- Scenario 1 (continued job losses leading to rate cuts): If job losses continue at the current pace or accelerate, further interest rate cuts are highly likely to stimulate economic activity.
- Scenario 2 (stabilization of the job market, no rate changes): If the job market stabilizes and other economic indicators remain relatively stable, the Bank of Canada might maintain its current interest rate stance.
- Scenario 3 (unexpected economic growth leading to rate hikes): A significant and unexpected surge in economic growth could prompt the Bank of Canada to reverse course and raise interest rates.
Each scenario's likelihood depends on the interplay of numerous economic variables, making precise prediction challenging. Analyzing data from reputable sources like Statistics Canada and the Bank of Canada itself is crucial.
Potential Risks and Uncertainties
Unforeseen events can significantly alter the economic outlook and influence the Bank of Canada's decisions.
- Geopolitical risks: International conflicts or trade wars can significantly disrupt global supply chains and negatively impact the Canadian economy.
- Unexpected changes in commodity prices: Sharp fluctuations in oil prices or other key commodities can significantly affect inflation and economic growth.
- Unexpected shifts in consumer confidence: Sudden shifts in consumer sentiment can lead to changes in spending patterns, affecting economic growth and inflation.
These uncertainties highlight the inherent difficulties in precisely predicting future Bank of Canada interest rate movements.
Conclusion
The outlook for Bank of Canada interest rates remains uncertain, heavily influenced by the ongoing situation with job losses and other macroeconomic factors. While recent job losses suggest a potential for further cuts to stimulate the economy, the Bank of Canada's ultimate decision will hinge on a complex interplay of variables. Staying informed about economic data releases from Statistics Canada and the Bank of Canada's statements is crucial for understanding future interest rate movements. Continue monitoring the Bank of Canada interest rates and stay updated on economic developments to make informed financial decisions.

Featured Posts
-
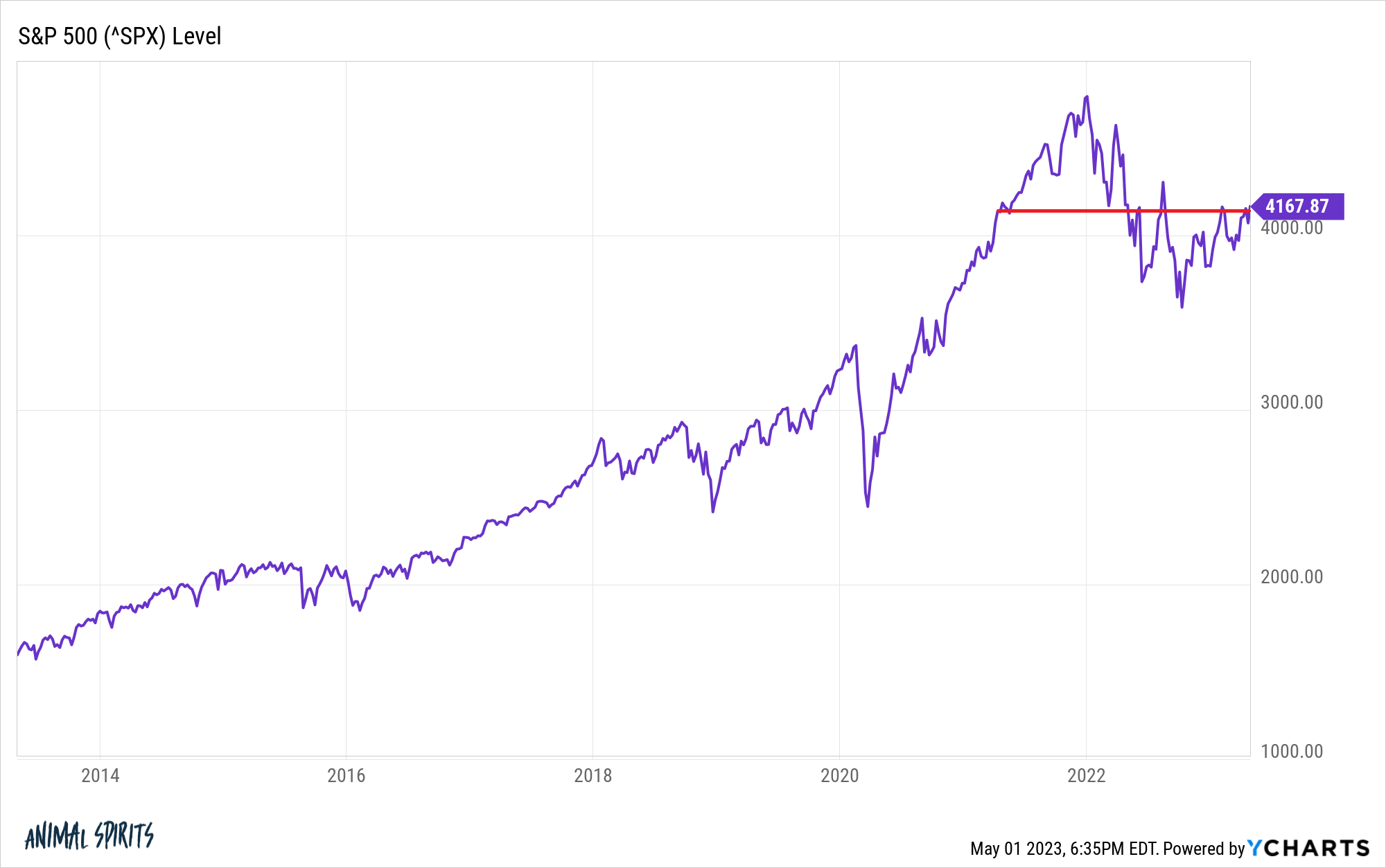 Stock Market Valuations And Investor Confidence A Bof A View
May 11, 2025
Stock Market Valuations And Investor Confidence A Bof A View
May 11, 2025 -
 Is There A Connection Between Michael Kays Remarks And Juan Sotos Bat
May 11, 2025
Is There A Connection Between Michael Kays Remarks And Juan Sotos Bat
May 11, 2025 -
 Bradley Wiggins From Cycling Champion To Drug Addiction And Bankruptcy
May 11, 2025
Bradley Wiggins From Cycling Champion To Drug Addiction And Bankruptcy
May 11, 2025 -
 Addressing Asylum Seeker Issues Netherlands Strategy Of Controlled Detention And Area Restrictions
May 11, 2025
Addressing Asylum Seeker Issues Netherlands Strategy Of Controlled Detention And Area Restrictions
May 11, 2025 -
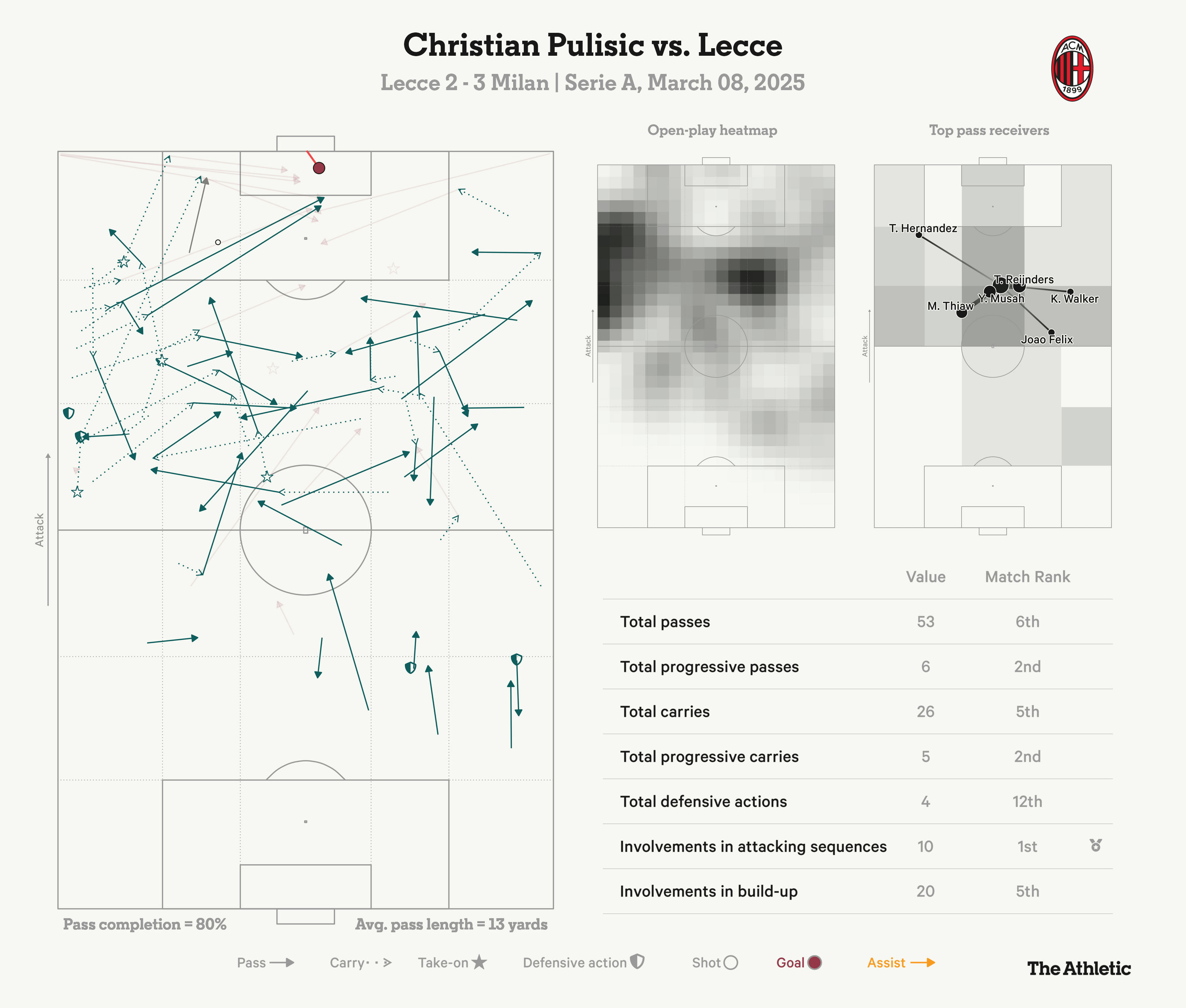 Dest Returns Pulisic Scores Usmnt Weekend Match Review
May 11, 2025
Dest Returns Pulisic Scores Usmnt Weekend Match Review
May 11, 2025
