Dangerous Climate Whiplash: A Global Urban Crisis

Table of Contents
Infrastructure Vulnerability to Dangerous Climate Whiplash
Urban infrastructure, designed for relatively predictable weather patterns, is increasingly ill-equipped to handle the volatile extremes of dangerous climate whiplash.
Overburdened Drainage Systems & Flooding
Many cities struggle with outdated drainage systems unable to cope with intense rainfall following periods of drought. The ground, parched from prolonged dryness, absorbs less water, leading to rapid surface runoff and devastating flash floods. This waterlogging overwhelms existing infrastructure, causing widespread damage to property, transportation networks, and vital services.
- Examples: Jakarta regularly experiences severe flooding, as does Mumbai during monsoon season. These events highlight the inadequacy of current urban drainage systems.
- Costs: The economic cost of flood damage is substantial, including repair costs, business interruption, and loss of life. For example, the 2017 Houston floods caused billions of dollars in damage.
- Solutions: Investing in green infrastructure, such as permeable pavements and bioswales, can significantly improve water management. Upgrading existing drainage systems and implementing early warning systems for flash floods are also crucial. Keywords: Flash floods, waterlogging, urban drainage, infrastructure investment.
Heat Island Effect & Extreme Heat
Urban areas, with their dense concrete and asphalt surfaces, trap heat, creating the urban heat island effect. This intensifies heatwaves, posing significant risks to public health. The rapid swings between extreme heat and potentially heavy rainfall further exacerbate the problem.
- Mitigation: Strategies to mitigate the urban heat island effect include increasing green spaces (urban tree planting), installing green roofs, and using lighter-colored pavements.
- Health Impacts: Extreme heat leads to heatstroke, respiratory illnesses, and cardiovascular problems. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and those with pre-existing conditions, are particularly at risk.
- Vulnerable Communities: Marginalized communities often lack access to cooling resources and are disproportionately affected by extreme heat. Keywords: Urban heat island, heatwave preparedness, heat stress, public health.
Transportation Disruptions & Emergency Response
Extreme weather events frequently disrupt transportation networks, hindering access to essential services and impacting emergency response capabilities. Roads may be flooded, public transportation may be suspended, and supply chains may be disrupted.
- Transportation Challenges: Flash floods can render roads impassable, while extreme heat can damage railway lines and cause power outages affecting public transportation.
- Improved Preparedness: Investing in resilient transportation infrastructure, developing robust emergency response plans, and improving communication networks are essential for mitigating these challenges.
- Critical Infrastructure: Ensuring the resilience of critical infrastructure, such as hospitals and emergency services, is paramount during extreme weather events. Keywords: Transportation resilience, emergency management, disaster preparedness, supply chain disruptions.
Socioeconomic Impacts of Dangerous Climate Whiplash
The consequences of dangerous climate whiplash extend far beyond infrastructure damage, profoundly impacting the social and economic fabric of cities.
Economic Losses & Displacement
Extreme weather events cause significant economic losses through damage to property, businesses, and infrastructure. The costs of recovery and reconstruction can be immense, placing a strain on local and national economies.
- Economic Costs: The economic damage from extreme weather events is escalating globally, impacting insurance markets and placing a burden on taxpayers.
- Insurance Implications: Increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events are driving up insurance premiums and making insurance unavailable in some high-risk areas.
- Displacement & Migration: Climate-related disasters often lead to displacement and migration, as people are forced to leave their homes due to damage or unlivable conditions. Keywords: Economic damage, climate migration, insurance costs, economic vulnerability.
Public Health Challenges & Inequalities
Dangerous climate whiplash poses substantial public health challenges, particularly for vulnerable populations. Heatwaves lead to heat-related illnesses, while flooding can increase the risk of waterborne diseases and respiratory problems.
- Health Risks: Extreme heat, flooding, and air pollution exacerbate existing health conditions and create new health risks.
- Health Disparities: Vulnerable populations often lack access to adequate healthcare and are disproportionately impacted by these health challenges.
- Access to Healthcare: Disruptions to transportation and infrastructure during extreme weather events can hinder access to essential healthcare services. Keywords: Climate change health impacts, health equity, environmental justice, public health emergency.
Social Instability & Conflict
Resource scarcity, displacement, and inequality exacerbated by dangerous climate whiplash can increase social tensions and even lead to conflict. Competition for dwindling resources can create social unrest.
- Competition for Resources: Climate-related disasters can lead to shortages of food, water, and other essential resources, increasing competition and potential conflict.
- Social Tensions: Displacement and migration can strain resources and lead to social tensions between different communities.
- Conflict Resolution: Effective conflict resolution mechanisms and community-based resilience building are crucial for mitigating these risks. Keywords: Social vulnerability, climate security, conflict mitigation, community resilience.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Dangerous Climate Whiplash
Addressing the challenges of dangerous climate whiplash requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Improving Urban Planning & Design
Sustainable urban planning and design are crucial for building resilient cities. This involves incorporating green infrastructure, improving drainage systems, and implementing climate-resilient building codes.
- Sustainable Urban Development: Prioritizing sustainable urban development practices that minimize environmental impact and enhance resilience is essential.
- Green Infrastructure: Investing in green infrastructure, such as green roofs, urban forests, and permeable pavements, can significantly improve urban resilience.
- Climate-Resilient Design: Buildings and infrastructure should be designed to withstand extreme weather events, minimizing damage and ensuring continued functionality. Keywords: Sustainable urban planning, green infrastructure, resilient cities, urban design.
Investing in Early Warning Systems & Emergency Preparedness
Effective early warning systems, coupled with comprehensive emergency preparedness plans, are vital for minimizing the impact of extreme weather events.
- Early Warning Systems: Investing in advanced meteorological monitoring and early warning systems allows for timely evacuation and preparedness measures.
- Community Education: Educating communities about the risks of dangerous climate whiplash and promoting preparedness is crucial.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: Implementing disaster risk reduction strategies, including land-use planning and building codes, can significantly reduce vulnerability. Keywords: Early warning systems, disaster preparedness, emergency response, risk reduction.
Strengthening International Collaboration & Policy
Addressing dangerous climate whiplash requires strong international collaboration and effective climate policies. This includes increasing climate finance and implementing ambitious emission reduction targets.
- International Agreements: Strengthening international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, is essential for collective action on climate change.
- Climate Finance: Increased climate finance is needed to support developing countries in building resilience to climate change.
- Policy Recommendations: Implementing effective climate policies at national and local levels is crucial for driving change. Keywords: Climate policy, international cooperation, climate finance, sustainable development.
Conclusion
Dangerous climate whiplash poses a significant and multifaceted threat to global urban areas, impacting infrastructure, economies, and public health. The interconnectedness of infrastructure vulnerability and socioeconomic impacts underscores the urgency of action. Key takeaways include investing in resilient infrastructure, implementing early warning systems, and improving urban planning. Strengthening international collaboration and adopting robust climate policies are equally essential. Understanding and addressing dangerous climate whiplash is not merely an environmental concern; it is a fundamental challenge to the safety, well-being, and future of our global cities. Let's work together to build a more resilient tomorrow by actively mitigating and adapting to dangerous climate whiplash and its cascading consequences.

Featured Posts
-
 Abd Tueketici Kredileri Mart Ayinda Artti Detayli Analiz
May 28, 2025
Abd Tueketici Kredileri Mart Ayinda Artti Detayli Analiz
May 28, 2025 -
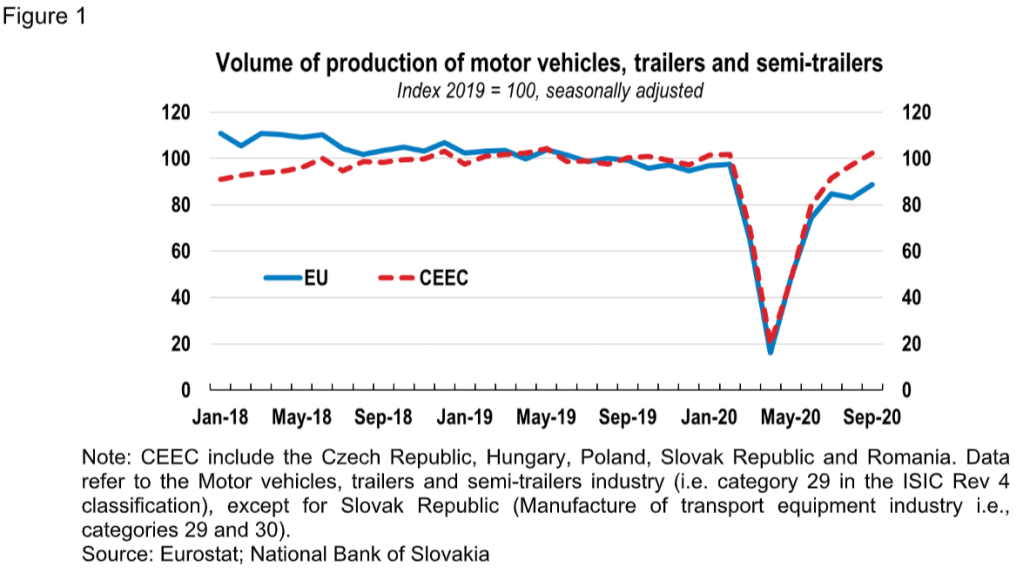 Europes Car Industry Faces Headwinds Amidst Economic Crisis
May 28, 2025
Europes Car Industry Faces Headwinds Amidst Economic Crisis
May 28, 2025 -
 Latest On Alejandro Garnacho Chelsea Pursuit And Manchester Uniteds Response
May 28, 2025
Latest On Alejandro Garnacho Chelsea Pursuit And Manchester Uniteds Response
May 28, 2025 -
 Angels Losing Streak Continues With Marlins Shutout
May 28, 2025
Angels Losing Streak Continues With Marlins Shutout
May 28, 2025 -
 Injury Report Pacers Vs Hawks Will Key Players Suit Up On March 8th
May 28, 2025
Injury Report Pacers Vs Hawks Will Key Players Suit Up On March 8th
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Vaervarsel For Bading Finn De Beste Temperaturene For Et Forfriskende Bad
May 29, 2025
Vaervarsel For Bading Finn De Beste Temperaturene For Et Forfriskende Bad
May 29, 2025 -
 Planlegg Sjobad Vaermeldingen Og Perfekte Badetemperaturer
May 29, 2025
Planlegg Sjobad Vaermeldingen Og Perfekte Badetemperaturer
May 29, 2025 -
 Amanda Holdens Dog Grooming Practices Spark Outrage On Heart Radio
May 29, 2025
Amanda Holdens Dog Grooming Practices Spark Outrage On Heart Radio
May 29, 2025 -
 Sjobading Guide Til Beste Badetemperaturer Og Vaerforhold
May 29, 2025
Sjobading Guide Til Beste Badetemperaturer Og Vaerforhold
May 29, 2025 -
 Lush Nyc 30 Minute Bubble Bath Experience For 75
May 29, 2025
Lush Nyc 30 Minute Bubble Bath Experience For 75
May 29, 2025
