End Of School Desegregation Order: Implications And Future Of School Integration

Table of Contents
Legal Implications of Ending School Desegregation Orders
Ending school desegregation orders carries substantial legal ramifications, potentially altering the landscape of educational equity.
Challenges to the Brown v. Board of Education Ruling
The dismantling of desegregation orders could face legal challenges, questioning the very foundation of Brown v. Board of Education. These challenges could:
- Reignite debates over the interpretation of the 14th Amendment's Equal Protection Clause. Arguments might center on whether separate but equal educational opportunities are truly possible.
- Lead to lawsuits arguing for the reinstatement of desegregation orders in specific districts. Cases could cite continued racial and socioeconomic disparities as evidence of ongoing segregation.
- Challenge the precedents set by decades of court decisions upholding and interpreting school desegregation mandates. These challenges could create uncertainty and legal battles for years to come.
The ongoing debate highlights the complexities of interpreting Brown v. Board of Education in the 21st century and its continued relevance in addressing systemic inequalities. The ruling's core principle—that separate educational facilities are inherently unequal—remains a cornerstone of the fight for educational justice.
Impact on Federal and State Laws
The termination of desegregation orders would significantly shift the balance of power and responsibility regarding school integration.
- Federal oversight and funding related to school desegregation could diminish. This shift could disproportionately affect districts with a history of significant segregation.
- State and local control over student assignment and school resource allocation could increase. This could lead to variations in integration efforts across different states and localities.
- Laws related to equal educational opportunities could be reinterpreted or weakened. The focus might shift from proactive integration to addressing disparities after they emerge.
This potential shift requires careful monitoring to ensure that the dismantling of desegregation orders doesn't inadvertently lead to a regression in educational equity for minority students.
Socioeconomic Implications of School Re-segregation
The potential end of school desegregation orders raises serious concerns about the resurgence of racial and socioeconomic segregation in schools and its profound consequences.
Increased Racial and Economic Segregation
Ending mandatory desegregation could lead to a dramatic increase in school segregation, exacerbating existing inequalities.
- Achievement gaps between racial and socioeconomic groups are likely to widen. Studies consistently demonstrate a strong correlation between school segregation and lower academic achievement for minority students.
- Resource disparities between schools in predominantly minority and majority-white neighborhoods are expected to persist and potentially grow. This includes disparities in teacher quality, curriculum resources, and access to advanced courses.
- Opportunities for social mobility could decrease significantly for students from marginalized communities. Integrated schools often provide exposure to diverse perspectives and networks, fostering upward mobility.
The long-term implications for students from marginalized communities are particularly concerning, potentially perpetuating cycles of poverty and inequality.
Impact on Community Relations and Social Cohesion
Increased school segregation can severely damage community relations and social cohesion.
- Racial tensions and misunderstandings could escalate. Homogenous school environments limit opportunities for cross-cultural interaction and understanding.
- Social polarization could increase, with communities becoming more divided along racial and socioeconomic lines. This could hinder collaborative efforts to address shared challenges.
- Social capital, crucial for community development, could weaken. Integrated schools play a significant role in building bridges between different groups and fostering a sense of shared identity.
Promoting understanding and tolerance requires diverse learning environments that foster empathy and cross-cultural interaction.
Strategies for Promoting School Integration in a Post-Desegregation Era
Even without mandatory desegregation orders, proactive strategies can promote school integration.
Innovative Approaches to School Integration
Despite the potential end of mandated school desegregation, various strategies can still foster integration:
- Magnet schools: These specialized schools can attract students from diverse backgrounds, promoting integration through shared academic interests.
- Open enrollment programs: Allowing students to attend schools outside their assigned districts can create more diverse student populations.
- Controlled choice plans: These plans prioritize diversity while offering parents a degree of choice in their children's school placement.
- Busing programs (where feasible and supported): While controversial, strategically designed busing can continue to be a valuable tool in certain circumstances to achieve integration goals.
The effectiveness of these approaches depends on careful planning, community support, and ongoing evaluation.
The Role of Community Engagement and Advocacy
Community engagement is crucial for maintaining and enhancing school integration.
- Parental involvement: Parents play a vital role in advocating for their children's access to integrated schools and diverse educational experiences.
- Community organizations: These groups can serve as powerful advocates for school integration, mobilizing community resources and support.
- Grassroots movements: Activist groups can raise awareness, organize campaigns, and challenge discriminatory practices.
Collaboration between stakeholders—parents, educators, community leaders, and policymakers—is essential for achieving meaningful school integration.
Conclusion
The potential end of school desegregation orders presents significant legal, socioeconomic, and practical challenges. While legal precedents surrounding school desegregation may be tested, the underlying need for equitable educational opportunities remains paramount. The socioeconomic implications of re-segregation are severe, potentially widening achievement gaps, exacerbating inequalities, and hindering social cohesion. To counteract these challenges, we must actively pursue innovative approaches to school integration and foster strong community engagement. The fight for school desegregation continues; ensuring effective school desegregation remains a crucial goal. We urge readers to actively participate in the ongoing dialogue, research the topic thoroughly, contact their representatives, and support organizations working to maintain and enhance school integration in their communities. The future of equitable education depends on our collective commitment to this vital cause.

Featured Posts
-
 How Much Does The Fortnite Cowboy Bebop Faye Valentine And Spike Spiegel Bundle Cost
May 03, 2025
How Much Does The Fortnite Cowboy Bebop Faye Valentine And Spike Spiegel Bundle Cost
May 03, 2025 -
 Eneco Inaugure Le Plus Grand Parc De Batteries De Belgique A Au Roeulx
May 03, 2025
Eneco Inaugure Le Plus Grand Parc De Batteries De Belgique A Au Roeulx
May 03, 2025 -
 Sydney Harbour Surveillance Heightened Following Recent Chinese Vessel Activity
May 03, 2025
Sydney Harbour Surveillance Heightened Following Recent Chinese Vessel Activity
May 03, 2025 -
 Lee Anderson Welcomes Councillors Defection To Reform
May 03, 2025
Lee Anderson Welcomes Councillors Defection To Reform
May 03, 2025 -
 El Sistema Penitenciario Recibe 7 Nuevos Vehiculos Para Mejorar Sus Operaciones
May 03, 2025
El Sistema Penitenciario Recibe 7 Nuevos Vehiculos Para Mejorar Sus Operaciones
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Future Of Rail Wind Energy For Cleaner More Efficient Trains
May 04, 2025
The Future Of Rail Wind Energy For Cleaner More Efficient Trains
May 04, 2025 -
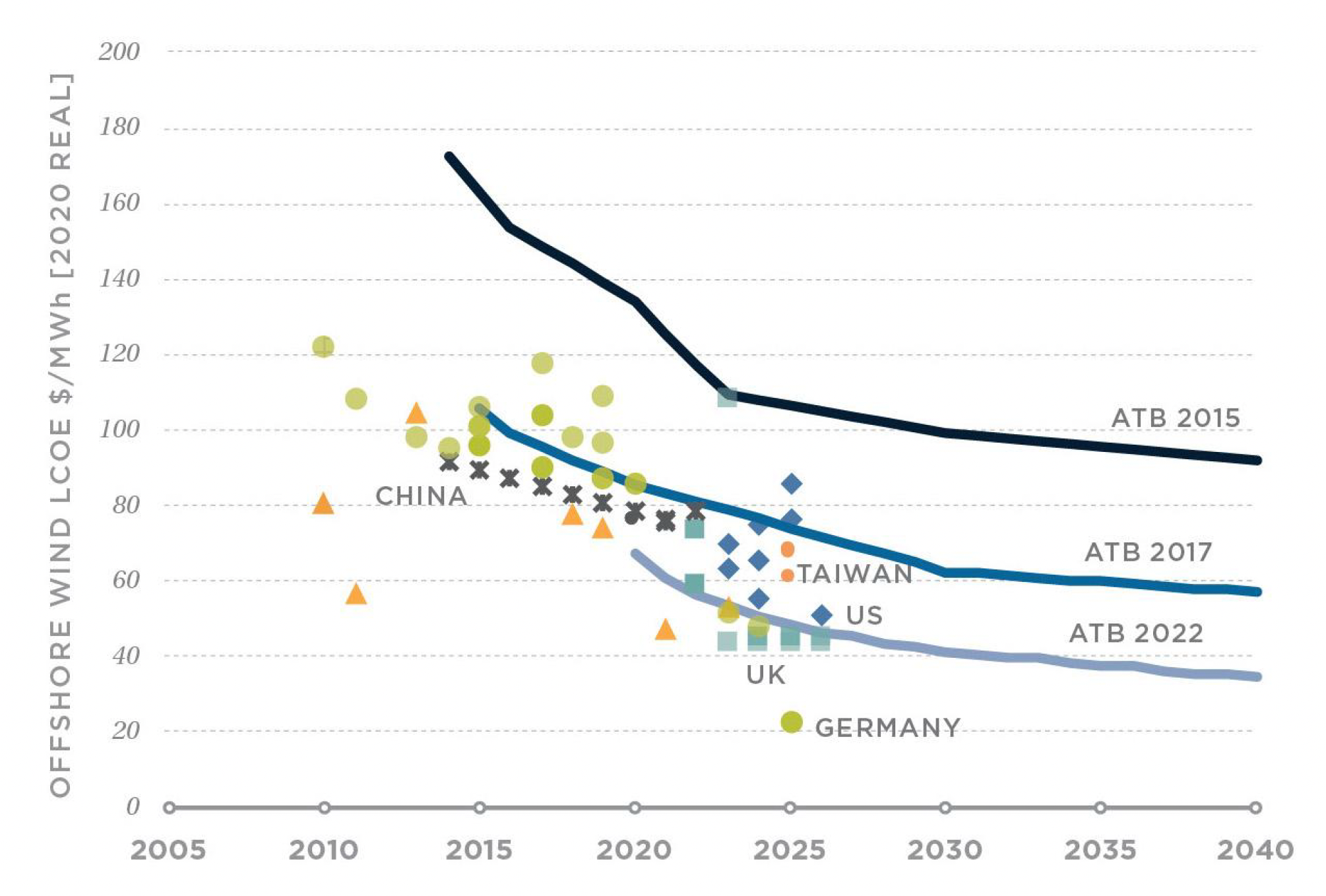 Is The Offshore Wind Boom Over Examining The Cost Factor
May 04, 2025
Is The Offshore Wind Boom Over Examining The Cost Factor
May 04, 2025 -
 Sustainable Rail Travel Exploring The Potential Of Wind Powered Trains
May 04, 2025
Sustainable Rail Travel Exploring The Potential Of Wind Powered Trains
May 04, 2025 -
 Harnessing The Wind How Wind Powered Trains Can Reduce Pollution And Save Energy
May 04, 2025
Harnessing The Wind How Wind Powered Trains Can Reduce Pollution And Save Energy
May 04, 2025 -
 Peak Solar Power In The Netherlands Utility Trial On Lower Tariffs
May 04, 2025
Peak Solar Power In The Netherlands Utility Trial On Lower Tariffs
May 04, 2025
