France's Juvenile Justice System: Facing Calls For Reform

Table of Contents
The Current State of Juvenile Justice in France
The French juvenile justice system, governed by the Code de la justice pénale des mineurs (CJPM), aims to balance punishment with rehabilitation. It distinguishes between minors (under 18) and adults, employing distinct procedures and sanctions. The system involves various actors including judges, social workers, educators, and probation officers, all working towards reintegrating young offenders into society.
- Age of criminal responsibility: The age of criminal responsibility in France is 13, although younger children can be subject to educational measures if deemed responsible for an offense.
- Types of sanctions: Sanctions range from warnings and fines to probation, community service, placement in specialized educational institutions, and, in serious cases, detention in juvenile facilities. The focus is on individualized measures tailored to the needs of the young offender.
- Role of educational and social services: A crucial aspect of the French system is the integration of educational and social services. These aim to address underlying issues contributing to the young person's offending behavior, such as poverty, family problems, or educational difficulties.
- Focus on rehabilitation vs. punishment: While punishment is a component, the overarching goal is rehabilitation and reintegration. The system emphasizes individualized plans, aiming to equip young offenders with the skills and support necessary to avoid future crime.
- Statistics on youth crime and recidivism rates in France: Official statistics show fluctuating rates of youth crime, with certain offenses like theft and vandalism being more prevalent. Recidivism rates, while not publicly available in a consistently detailed manner, remain a significant concern, prompting calls for improved rehabilitation efforts.
- Recent significant legislative changes: Recent years have witnessed minor legislative adjustments, primarily focusing on improved data collection and inter-agency collaboration. However, major systemic overhaul remains a subject of ongoing debate.
Criticisms and Concerns
Despite the stated aims of rehabilitation, the French juvenile justice system faces significant criticism. These criticisms frequently center on the system's effectiveness and fairness.
- High recidivism rates among young offenders in France: Relatively high recidivism rates among young offenders highlight the system's shortcomings in preventing repeat offenses. This suggests a need for more effective rehabilitation and reintegration programs.
- Concerns about racial and socioeconomic disparities in sentencing: Critics point to evidence suggesting disparities in sentencing based on race and socioeconomic background. Minority youth are disproportionately represented in the juvenile justice system, raising concerns about systemic bias.
- Over-reliance on detention as a primary sanction: The use of detention, although intended as a last resort, remains a significant concern. Critics argue that detention can be counterproductive, potentially exacerbating existing problems and increasing the likelihood of recidivism.
- Inadequate access to rehabilitation and support services: Access to crucial services such as education, job training, and mental health support varies considerably, impacting the effectiveness of rehabilitation efforts. Geographical disparities also play a significant role.
- Lack of preventative measures addressing the root causes of youth crime: Critics argue that the system lacks sufficient investment in preventative measures that address the social, economic, and educational factors contributing to youth crime.
- Specific examples of cases or reports highlighting systemic issues: Reports from human rights organizations and academic studies have highlighted specific cases and broader trends illustrating systemic issues within the French juvenile justice system, particularly regarding the disproportionate impact on minority youth.
The Issue of Racial Disparities in the French Juvenile Justice System
A critical concern is the disproportionate impact of the French juvenile justice system on minority groups. Studies indicate that young people from minority ethnic backgrounds are overrepresented at every stage, from arrest to detention.
- Statistical evidence of racial bias in arrests, sentencing, and detention: While official statistics may not explicitly categorize data by ethnicity, various studies and reports strongly suggest racial bias exists throughout the system, influencing arrests, sentencing decisions, and the likelihood of detention.
- Analysis of potential contributing factors (e.g., socioeconomic inequality, policing practices): Socioeconomic inequality, discriminatory policing practices, and implicit biases within the system are potential contributing factors to these disparities. Addressing these underlying issues is crucial for achieving a more equitable system.
- Calls for addressing systemic racism within the system: Advocacy groups and academics are calling for urgent action to address systemic racism within the French juvenile justice system, promoting greater transparency, accountability, and cultural sensitivity in all aspects of the process.
Proposed Reforms and Future Directions
Numerous proposals aim to address the shortcomings of the French juvenile justice system and enhance its effectiveness and fairness.
- Increased investment in preventative measures (e.g., early intervention programs, community-based initiatives): Investing in early intervention programs, community-based initiatives, and educational support can prevent young people from entering the justice system in the first place.
- Emphasis on rehabilitation and restorative justice practices: A greater emphasis on restorative justice, focusing on repairing harm and reintegrating offenders into their communities, could reduce recidivism rates.
- Reduced reliance on detention, with greater focus on alternative sanctions: Reducing reliance on detention and increasing the use of alternative sanctions, such as community service and intensive supervision, could create a more humane and effective system.
- Improved access to education, job training, and mental health services for young offenders: Providing young offenders with access to quality education, job training, and mental health services is crucial for successful rehabilitation and reintegration.
- Strengthening of collaboration between justice system actors and social services: Improved collaboration between judges, social workers, educators, and other relevant actors is essential for developing and implementing effective individualized plans.
- Ongoing debates or legislative proposals for reform: Currently, debates are ongoing regarding the implementation of more comprehensive reforms, with various legislative proposals under discussion.
Conclusion
France's juvenile justice system faces significant challenges, including high recidivism rates, concerns about fairness, and the need for more effective rehabilitation programs. Addressing racial disparities and strengthening preventative measures are crucial aspects of any reform effort. The proposed reforms, focusing on increased investment in prevention, a greater emphasis on rehabilitation and restorative justice, and reduced reliance on detention, hold significant potential for improving the system's effectiveness and ensuring a fairer justice system for all young people in France. The need for comprehensive reform of France's juvenile justice system is undeniable. Continued engagement with the issues surrounding France's juvenile justice system is vital for building a more just and equitable future. Further research, public discourse, and political will are essential to achieving meaningful and lasting change within France's juvenile justice system.

Featured Posts
-
 Serious Crash On M56 Current Traffic Conditions And Diversion Routes
May 24, 2025
Serious Crash On M56 Current Traffic Conditions And Diversion Routes
May 24, 2025 -
 Macron Faces Criticism From Former French Prime Minister
May 24, 2025
Macron Faces Criticism From Former French Prime Minister
May 24, 2025 -
 Top 10 Fastest Standard Production Ferraris On Their Home Track
May 24, 2025
Top 10 Fastest Standard Production Ferraris On Their Home Track
May 24, 2025 -
 Allegations Against Annie Kilner After Kyle Walkers Night Out
May 24, 2025
Allegations Against Annie Kilner After Kyle Walkers Night Out
May 24, 2025 -
 Sergey Yurskiy 90 Let Zhizni I Tvorchestva Velikogo Aktera
May 24, 2025
Sergey Yurskiy 90 Let Zhizni I Tvorchestva Velikogo Aktera
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 La Fires The Rise Of Rental Prices And Allegations Of Exploitation
May 24, 2025
La Fires The Rise Of Rental Prices And Allegations Of Exploitation
May 24, 2025 -
 Sses Revised Spending Plan 3 Billion Reduction Announced
May 24, 2025
Sses Revised Spending Plan 3 Billion Reduction Announced
May 24, 2025 -
 Investigating Thames Waters Executive Bonus Scheme A Critical Examination
May 24, 2025
Investigating Thames Waters Executive Bonus Scheme A Critical Examination
May 24, 2025 -
 Pilbara Iron Ore Mining A Response To Environmental Concerns From Andrew Forrest
May 24, 2025
Pilbara Iron Ore Mining A Response To Environmental Concerns From Andrew Forrest
May 24, 2025 -
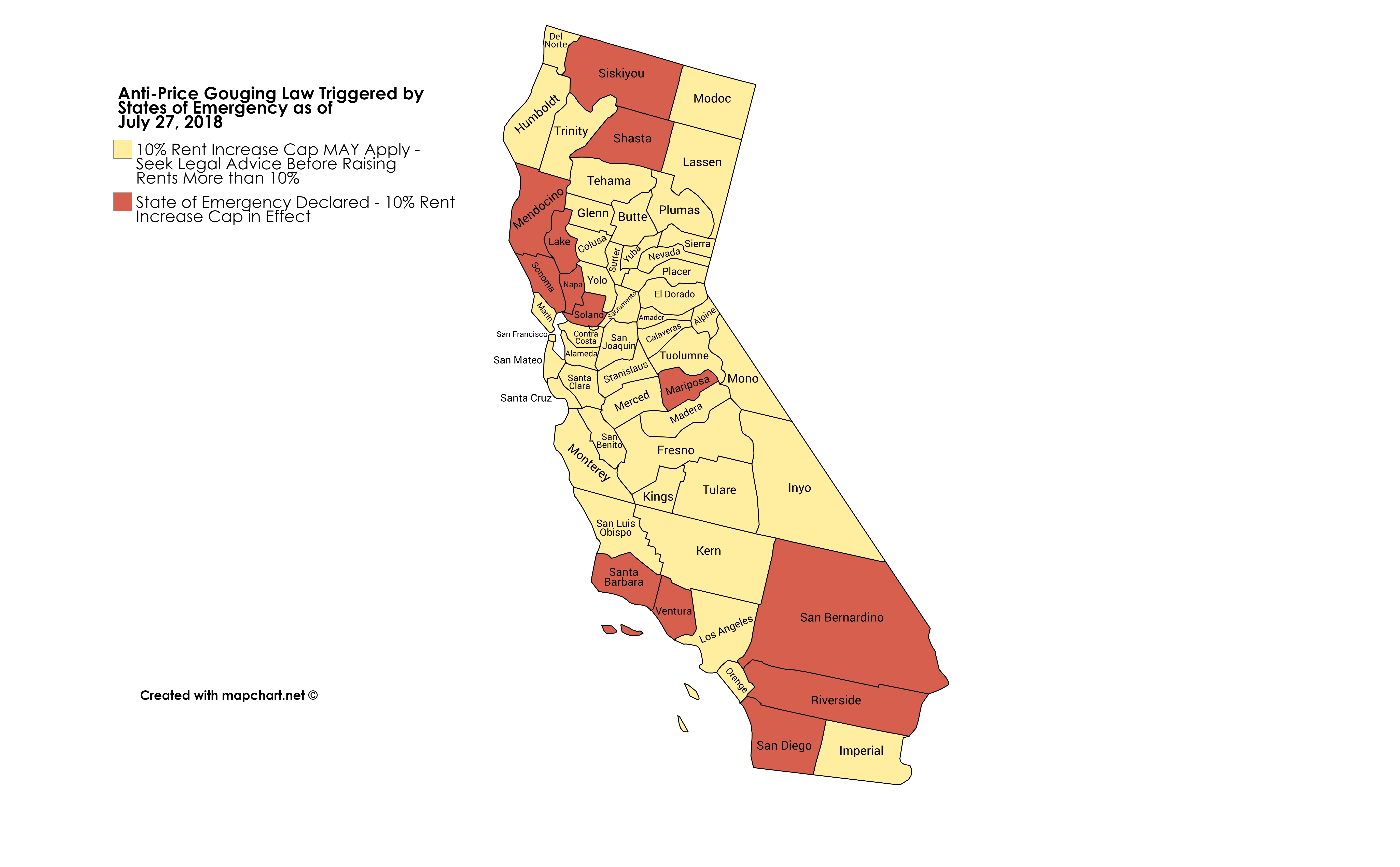 The Impact Of La Fires On Rent Prices A Price Gouging Investigation
May 24, 2025
The Impact Of La Fires On Rent Prices A Price Gouging Investigation
May 24, 2025
