Greenland And The US-China Rivalry: A Detailed Examination

Table of Contents
Greenland's Strategic Importance
Greenland's significance stems from its unique geopolitical location and its vast untapped natural resources. Its proximity to key shipping lanes, its potential for military basing, and its abundant mineral wealth make it a highly coveted prize in the 21st-century scramble for resources and influence.
Geopolitical Location
Greenland’s location offers unparalleled strategic advantages.
- Strategic location for surveillance of Arctic shipping routes: As Arctic ice melts, new shipping lanes open up, significantly reducing transit times between Asia and Europe. Greenland's position allows for monitoring these crucial routes.
- Potential military bases: The island's geography offers potential locations for military bases, providing a strategic foothold in the Arctic region.
- Access to natural resources: Greenland holds significant reserves of rare earth minerals, uranium, oil, and other valuable resources crucial for modern technology and energy production. Control over these resources could shift global power balances.
Abundant Natural Resources
Greenland's subsurface wealth is attracting significant international attention.
- Rare earth minerals: These essential elements are vital for the production of high-tech electronics, renewable energy technologies, and defense systems. Greenland possesses substantial deposits.
- Uranium: With the ongoing global interest in nuclear energy, Greenland's uranium reserves represent a significant potential energy source.
- Oil and other valuable resources: The potential for oil and gas discoveries adds further to Greenland’s economic attractiveness and geopolitical importance. This has major implications for global energy security and technological advancement.
US Interests in Greenland
The US has long-standing ties with Greenland, and its current interest is multifaceted.
Historical Ties and Strategic Partnerships
The relationship between the US and Greenland has a long history.
- Defense cooperation: The US has a history of defense cooperation with Greenland, including a previous military presence and ongoing scientific research collaborations.
- Scientific research initiatives: Joint research projects focusing on climate change, environmental monitoring, and Arctic science contribute to understanding the region’s evolving dynamics.
- Economic aid: The US has provided economic aid to Greenland, strengthening the bilateral relationship and promoting economic development.
Countering Chinese Influence
The US engagement in Greenland is partly driven by a desire to counter China's growing influence in the Arctic.
- Economic investment competition: Both the US and China are vying for economic influence through investments in Greenland's infrastructure and resource development.
- Infrastructure development: The competition extends to developing crucial infrastructure such as ports and transportation networks.
- Diplomatic efforts to maintain influence: The US is actively engaging in diplomatic efforts to maintain its close relationship with Greenland and limit the inroads made by China.
China's Growing Presence in Greenland
China's increased interest in Greenland is a significant development in Arctic geopolitics.
Economic Investments and Infrastructure Projects
China's engagement in Greenland is primarily focused on economic investment.
- Chinese investment in mining projects: Chinese companies are increasingly involved in Greenland's mining sector, particularly in rare earth minerals and other resources.
- Port development and other infrastructure: Investments in port infrastructure could enhance China's access to Arctic shipping routes.
- Economic benefits and risks for Greenland: While Chinese investment brings potential economic benefits, it also presents risks related to debt sustainability and geopolitical dependence.
Belt and Road Initiative and Arctic Engagement
China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) plays a crucial role in its Arctic strategy.
- Potential participation of Greenland in BRI projects: Greenland could become a key node in China's Arctic ambitions, facilitating increased trade and connectivity with Asia.
- Increased trade and connectivity: BRI projects could significantly improve Greenland's infrastructure and connectivity, but also raise concerns about economic dependency.
- Geopolitical implications for the region: China's engagement through the BRI has broad geopolitical implications for the entire Arctic region and its power dynamics.
Conclusion
Greenland's strategic location, abundant natural resources, and its growing importance in the context of the melting Arctic are making it a focal point in the ongoing US-China rivalry. Both countries are actively vying for influence through economic investment, infrastructure development, and diplomatic engagement. Understanding the nuances of this competition is crucial for comprehending the future of the Arctic and its implications for global power dynamics. Further research into the evolving dynamics of Greenland and the US-China Rivalry is crucial to navigating this complex geopolitical landscape and ensuring a stable and sustainable future for the region.

Featured Posts
-
 Rogues Team A Case For Avengers Or X Men Membership
May 08, 2025
Rogues Team A Case For Avengers Or X Men Membership
May 08, 2025 -
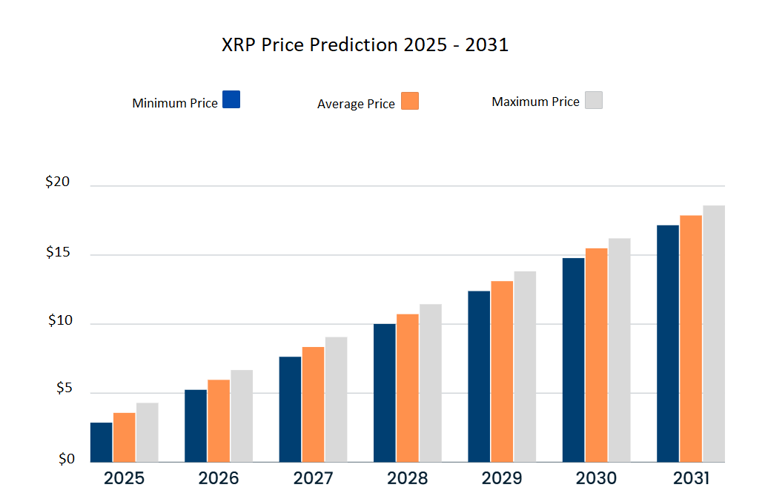 Could Xrp Reach 5 By 2025 A Realistic Analysis
May 08, 2025
Could Xrp Reach 5 By 2025 A Realistic Analysis
May 08, 2025 -
 Tatum On Curry An Honest Post All Star Game Reflection
May 08, 2025
Tatum On Curry An Honest Post All Star Game Reflection
May 08, 2025 -
 Ghas Vehement Rejection Of Proposed Jhl Privatisation
May 08, 2025
Ghas Vehement Rejection Of Proposed Jhl Privatisation
May 08, 2025 -
 Cybercriminal Makes Millions From Executive Office365 Account Hacks
May 08, 2025
Cybercriminal Makes Millions From Executive Office365 Account Hacks
May 08, 2025
