Inside Our ADHD Minds: Understanding The ADHD Brain
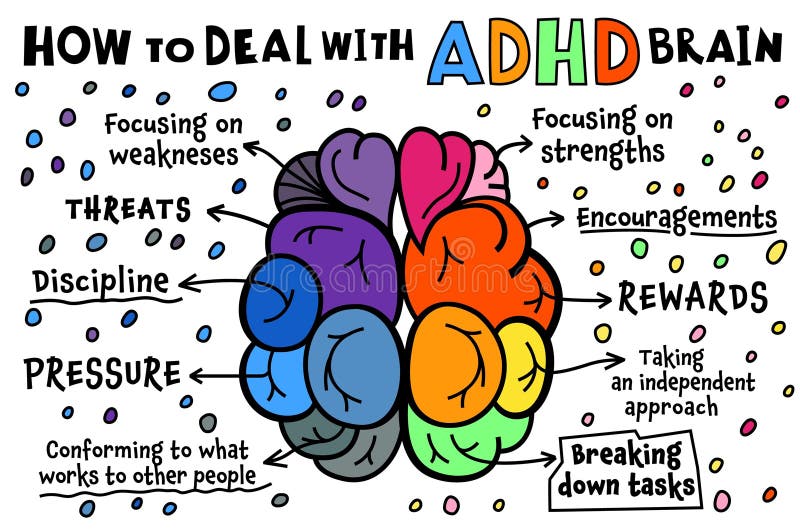
Table of Contents
Neurological Differences in the ADHD Brain
The ADHD brain differs neurologically from a neurotypical brain in several key areas. These differences contribute to the characteristic symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
Executive Function Deficits
The prefrontal cortex, the brain's command center responsible for executive functions, plays a crucial role. Executive functions encompass crucial cognitive skills like planning, organization, time management, working memory, and impulse control. In individuals with ADHD, these functions are often impaired.
- Difficulty with planning and prioritizing tasks: Individuals with ADHD may struggle to break down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps. This can lead to feelings of overwhelm and avoidance.
- Problems with time management and organization: Time blindness and disorganization are common challenges. This can manifest as missed deadlines, lost belongings, and difficulty managing schedules.
- Impulsivity and difficulty inhibiting responses: This can lead to interrupting conversations, acting without thinking, and making rash decisions.
- Challenges with working memory: Holding information in mind and manipulating it is challenging, impacting learning and task completion. This affects everything from remembering instructions to following multi-step directions.
Dopamine and Norepinephrine Imbalances
Neurotransmitters, chemical messengers in the brain, play a vital role in ADHD. Dopamine and norepinephrine are particularly crucial for attention, motivation, and reward processing. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters are strongly implicated in ADHD symptoms.
- Lower dopamine levels linked to inattention and difficulty with motivation: Dopamine is essential for focusing attention and experiencing reward. Low levels make it harder to stay on task and find activities motivating.
- Norepinephrine imbalances contributing to impulsivity and hyperactivity: Norepinephrine regulates arousal and alertness. Imbalances can lead to restlessness, impulsivity, and difficulty regulating behavior.
- Impact on reward processing and seeking stimulation: Individuals with ADHD may seek out intense stimulation or risk-taking behaviors to compensate for their altered reward pathways. This can manifest as restlessness or engaging in activities that provide immediate gratification.
Structural and Functional Brain Differences
Research using neuroimaging techniques like fMRI and MRI has revealed subtle structural and functional differences in the brains of individuals with ADHD compared to neurotypical individuals.
- Variations in brain volume in areas like the prefrontal cortex and basal ganglia: These areas are involved in executive functions and motor control, respectively. Variations may contribute to the cognitive and behavioral symptoms of ADHD.
- Differences in brain activity during tasks requiring attention and focus: Neuroimaging studies often show differences in brain activation patterns during attention-demanding tasks, highlighting the neural basis of attention deficits.
- Ongoing research exploring the complexities of brain structure and function in ADHD: Scientists continue to investigate the intricate relationship between brain structure, function, and ADHD symptoms, aiming for more precise diagnostic tools and treatments.
The Impact of ADHD on Daily Life
The neurological differences in the ADHD brain significantly impact various aspects of daily life, presenting unique challenges across different settings.
Challenges in Academic and Professional Settings
The difficulties with attention, organization, and time management inherent in ADHD significantly affect academic and professional performance.
- Difficulty concentrating and completing tasks: This results in incomplete assignments, poor grades, and reduced productivity at work.
- Challenges with organization and time management: This leads to missed deadlines, disorganized workspaces, and difficulty prioritizing tasks.
- Increased risk of procrastination and missed deadlines: Procrastination becomes a coping mechanism to avoid the frustration of starting and completing tasks.
- Impact on academic achievement and career progression: These challenges can negatively affect academic success and career advancement opportunities.
Social and Emotional Impacts of ADHD
ADHD also impacts social interactions, self-esteem, and emotional regulation.
- Difficulties with social interaction and maintaining friendships: Impulsivity, difficulty with turn-taking, and emotional dysregulation can strain relationships.
- Increased risk of emotional dysregulation and mood swings: This can lead to frustration, anger outbursts, and difficulty managing emotions.
- Challenges with self-esteem and self-confidence: Repeated failures and social difficulties can negatively impact self-perception.
- Impact on family relationships: The challenges of ADHD can strain family dynamics and require significant adaptation from family members.
Comorbid Conditions
ADHD frequently co-occurs with other conditions, further complicating diagnosis and treatment.
- Increased risk of anxiety disorders: Anxiety and ADHD often share underlying neurological factors and symptoms.
- Higher prevalence of depression: The challenges of ADHD can contribute to feelings of hopelessness and low self-esteem, increasing the risk of depression.
- Frequent co-occurrence with learning disabilities, like dyslexia: These conditions often share similar underlying neurological mechanisms and require integrated treatment approaches.
- Importance of comprehensive assessment and treatment: A holistic approach addressing both ADHD and comorbid conditions is crucial for effective management.
Conclusion
Understanding the ADHD brain involves recognizing the complex interplay of neurobiological factors and their impact on daily life. While challenges exist, comprehending the neurological underpinnings of ADHD empowers individuals, families, and professionals to seek effective strategies for management and support. Learning about the neurological differences in the ADHD brain fosters empathy, improves understanding, and encourages a more supportive approach to treatment. Continue your journey to learn more about ADHD and its effective management. Seek out resources and professionals who specialize in ADHD to develop a personalized plan to address the challenges and harness the strengths of the ADHD brain. Remember, understanding your ADHD brain is the first step toward living your best life.

Featured Posts
-
 Inside Our Adhd Minds Understanding The Adhd Brain
May 13, 2025
Inside Our Adhd Minds Understanding The Adhd Brain
May 13, 2025 -
 Sir Ian Mc Kellens Early Coronation Street Appearance A Stepping Stone To Success
May 13, 2025
Sir Ian Mc Kellens Early Coronation Street Appearance A Stepping Stone To Success
May 13, 2025 -
 Diskriminatsi A Roma Uni A Roma Srbi E Reagu E Na Iz Ave Marinike Tepi
May 13, 2025
Diskriminatsi A Roma Uni A Roma Srbi E Reagu E Na Iz Ave Marinike Tepi
May 13, 2025 -
 Live Streaming Serie A Oi Kalyteres Platformes
May 13, 2025
Live Streaming Serie A Oi Kalyteres Platformes
May 13, 2025 -
 Gibraltar At Sidoti Small Cap Conference A Focus On Specific Area Of Presentation If Known
May 13, 2025
Gibraltar At Sidoti Small Cap Conference A Focus On Specific Area Of Presentation If Known
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Report Veteran Actor Sam Elliott Joins Landman Season 2
May 13, 2025
Report Veteran Actor Sam Elliott Joins Landman Season 2
May 13, 2025 -
 Landman Season 2 Sam Elliott Cast In Supporting Role Report Confirms
May 13, 2025
Landman Season 2 Sam Elliott Cast In Supporting Role Report Confirms
May 13, 2025 -
 Sam Elliott Joins Landman Season 2 Cast Official Report
May 13, 2025
Sam Elliott Joins Landman Season 2 Cast Official Report
May 13, 2025 -
 Final Destination 25th Anniversary Devon Sawa Teases Franchise Comeback
May 13, 2025
Final Destination 25th Anniversary Devon Sawa Teases Franchise Comeback
May 13, 2025 -
 The Landman Debate Billy Bob Thorntons Response To The Ali Larter And Angela Norris Controversy
May 13, 2025
The Landman Debate Billy Bob Thorntons Response To The Ali Larter And Angela Norris Controversy
May 13, 2025
