Justice Department's Decision To End School Desegregation: Analysis And Impact
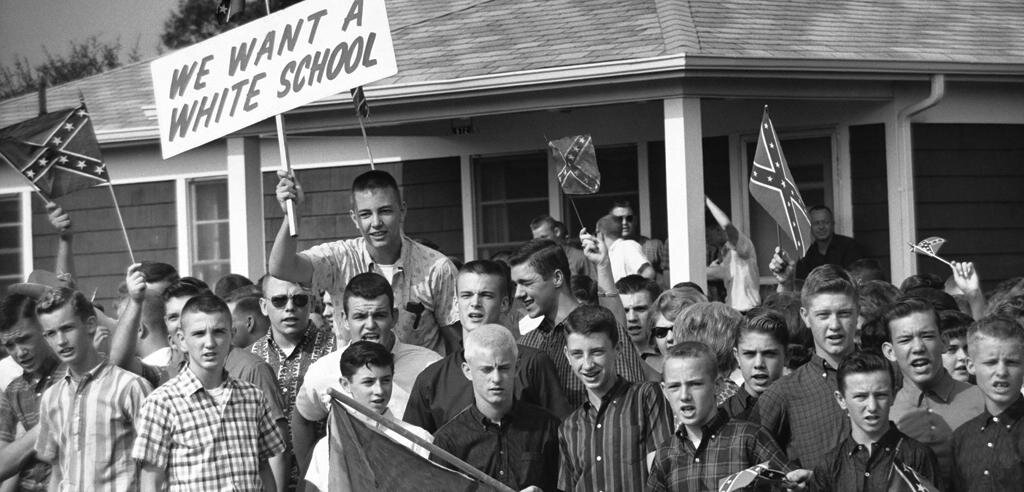

Table of Contents
Historical Context of School Desegregation and the DOJ's Role
Understanding the Justice Department's decision requires examining the long and often turbulent history of school desegregation in the US. The landmark 1954 Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court case declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. However, the ruling's implementation was far from immediate or straightforward, met with significant resistance in many parts of the country.
The Justice Department played a crucial role in enforcing desegregation orders, particularly during periods of active intervention in the Civil Rights era. This involved filing lawsuits against school districts, implementing court-ordered busing programs, and monitoring compliance with desegregation plans. The level of DOJ involvement fluctuated over the decades, often reflecting shifts in national priorities and political climate.
The recent shift represents a significant departure from this historical role. The reasoning behind the change, often cited by proponents, focuses on a belief that the federal government's role in desegregation should be diminished, emphasizing local control over education.
- Key legislation related to school desegregation: Civil Rights Act of 1964, Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965.
- Significant court cases impacting school desegregation: Swann v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education (1971), Milliken v. Bradley (1974).
- Examples of DOJ interventions in past decades: The department's involvement in desegregation efforts in southern states during the 1960s and 1970s.
- Specific examples of successful desegregation initiatives: Court-ordered busing programs that led to increased racial integration in some school districts.
Legal Ramifications of Reduced Enforcement
The decision to reduce enforcement carries significant legal ramifications. Proponents argue that the federal government has overstepped its authority and that school desegregation should be primarily addressed at the state and local levels. Opponents, however, contend that this shift undermines existing desegregation orders and consent decrees, potentially leading to a resurgence of de facto segregation in schools.
The potential impact on existing desegregation orders and consent decrees is a major area of concern. The legal challenges facing school districts, previously protected by federal oversight, could significantly increase. Civil rights organizations are expected to play a critical role in challenging the legality and fairness of this change, leading to a series of potential legal battles.
- Analysis of relevant Supreme Court cases: Examining how past Supreme Court decisions might inform future challenges to the DOJ's new approach.
- Discussion of legal challenges to the DOJ's new approach: Anticipating the types of legal arguments that will be brought before the courts.
- Potential legal battles facing school districts: Identifying the legal risks faced by districts that might revert to more segregated practices.
- The role of civil rights organizations in legal challenges: Highlighting the role of organizations like the NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund in defending desegregation efforts.
Impact on Educational Equity and Student Achievement
The potential impact of reduced desegregation enforcement on educational equity and student achievement is profound and deeply concerning. Decades of research strongly correlate school segregation with achievement gaps between minority and majority students. Segregated schools often lack the resources, experienced teachers, and advanced programs available in more affluent, predominantly white schools.
A reduction in federal oversight risks exacerbating these existing inequalities. The potential impact on school resources and funding is particularly worrying, with under-resourced schools likely to become even more disadvantaged. The quality and diversity of the teaching staff is also impacted; segregated schools often have a less diverse faculty.
- Statistical data on achievement gaps: Presenting relevant statistics on the persistent disparities in academic outcomes.
- Studies correlating school segregation and academic performance: Citing research demonstrating the negative impact of segregation on student achievement.
- Discussion of resource disparities between segregated schools: Highlighting the unequal distribution of resources between schools in predominantly minority and predominantly white neighborhoods.
- The impact on teacher quality and diversity in segregated schools: Exploring the correlation between teacher diversity and positive student outcomes.
Arguments For and Against Reduced Enforcement of School Desegregation
The debate surrounding the Justice Department's decision involves complex arguments on both sides. Proponents of reduced federal intervention often emphasize the principle of local control over education, arguing that decisions about school policies should be made at the community level. They may also suggest that federal intervention has been ineffective or even counterproductive in some cases.
Opponents, however, maintain that strong federal oversight remains crucial to prevent a return to widespread segregation and to ensure equitable access to quality education for all students, regardless of race. They argue that the achievement gap cannot be effectively addressed without federal action to promote integration and address systemic inequalities. The potential unintended consequences of reduced enforcement, such as increased racial isolation and further exacerbation of the achievement gap, are major concerns.
- Proponents' arguments for local control of education: Presenting the arguments for increased autonomy at the local level.
- Opponents' arguments for the need for federal oversight: Highligting the importance of federal intervention to ensure equitable access to education.
- Discussion of potential unintended consequences: Exploring the various negative outcomes that could result from reduced enforcement.
- Consideration of differing perspectives on the role of government: Analyzing different viewpoints regarding the appropriate level of government intervention in education.
Conclusion
The Justice Department's decision to lessen its enforcement of school desegregation carries significant implications for educational equity and racial integration. The historical context, legal ramifications, and potential impact on student achievement highlight the complexities surrounding this controversial issue. Continued monitoring and discussion are crucial to ensure equitable access to quality education for all students. Further research and advocacy are needed to understand the long-term effects of this policy shift. We must continue to advocate for robust policies that promote true school desegregation and educational equity for all. Keywords: School Desegregation, Educational Equity, Racial Justice, School Integration, Desegregation Enforcement

Featured Posts
-
 La Laport 3 20
May 02, 2025
La Laport 3 20
May 02, 2025 -
 Valorant Mobile Tencents Pubg Mobile Studio Developing A Mobile Version
May 02, 2025
Valorant Mobile Tencents Pubg Mobile Studio Developing A Mobile Version
May 02, 2025 -
 Viral Cat Posts Cause Concern Among Kashmirs Cat Owners
May 02, 2025
Viral Cat Posts Cause Concern Among Kashmirs Cat Owners
May 02, 2025 -
 Un Bebe Normand Gagne Son Poids En Chocolat
May 02, 2025
Un Bebe Normand Gagne Son Poids En Chocolat
May 02, 2025 -
 Culinary Delights Await Explore Windstars Cruise Itineraries
May 02, 2025
Culinary Delights Await Explore Windstars Cruise Itineraries
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nat West Settles De Banking Claim With Nigel Farage
May 03, 2025
Nat West Settles De Banking Claim With Nigel Farage
May 03, 2025 -
 Farages New Reform Slogan A Controversial Jimmy Savile Reference
May 03, 2025
Farages New Reform Slogan A Controversial Jimmy Savile Reference
May 03, 2025 -
 Tensions A Gaza Macron S Inquiete De La Militarisation Possible De L Aide Humanitaire
May 03, 2025
Tensions A Gaza Macron S Inquiete De La Militarisation Possible De L Aide Humanitaire
May 03, 2025 -
 Reform Party Imploding Leaked Whats Apps Reveal Farage Integrity Dispute
May 03, 2025
Reform Party Imploding Leaked Whats Apps Reveal Farage Integrity Dispute
May 03, 2025 -
 Farage Reaches Agreement With Nat West After De Banking Row
May 03, 2025
Farage Reaches Agreement With Nat West After De Banking Row
May 03, 2025
