Malaysia Faces US Solar Import Duties: Impact On Industry

Table of Contents
Increased Costs and Reduced Competitiveness
The immediate and most significant impact of the US solar import duties is the substantial increase in costs.
Higher Solar Panel Prices
The added tariffs directly translate to higher prices for solar panels imported from the US, and potentially from other countries indirectly affected by the tariffs. This has several detrimental effects:
- Increased project development costs: Solar projects become less financially attractive, requiring higher upfront investments.
- Reduced return on investment for developers: Profit margins shrink, potentially making projects unviable.
- Potential delays or cancellations of projects: Developers may postpone or abandon projects due to the increased financial risks. This slowdown affects the entire solar value chain, from installers to financiers. The ripple effect is substantial.
Loss of Market Share
Malaysian solar companies reliant on US-sourced components are now at a significant competitive disadvantage. They face increased costs, making them less attractive to both domestic and international clients compared to companies sourcing from tariff-exempt countries.
- Loss of contracts: Malaysian companies may lose bids to competitors offering lower prices.
- Decreased export opportunities: The higher cost of Malaysian-produced solar energy systems reduces their competitiveness in the global market.
- Potential job losses in the industry: Reduced profitability and project cancellations can lead to layoffs and a contraction of the Malaysian solar workforce.
Impact on Renewable Energy Targets
Malaysia has set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption. The US solar import duties threaten to significantly impede progress towards these goals.
Delays in Renewable Energy Adoption
The higher costs associated with solar projects directly translate to slower adoption rates. This means:
- Missed targets for solar capacity additions: Malaysia may struggle to meet its planned increases in solar energy generation capacity.
- Increased reliance on fossil fuels: Slower solar adoption may lead to a continued dependence on less sustainable energy sources.
- Setbacks in achieving carbon neutrality goals: Delays in renewable energy deployment hamper efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Government Policy Response
The Malaysian government needs to act swiftly and strategically to mitigate the negative consequences of these tariffs. A robust policy response is crucial:
- Potential subsidies for solar projects: Government subsidies could help offset the increased costs and incentivize project development.
- Exploration of alternative supply chains: The government should actively support the diversification of supply chains, exploring partnerships with manufacturers in other countries.
- Incentives for local solar panel manufacturing: Investing in domestic manufacturing capabilities can reduce reliance on imports and improve long-term energy security. This includes tax breaks, grants, and other forms of financial support.
Exploring Alternative Sourcing and Mitigation Strategies
To navigate this challenge, Malaysian solar companies and the government must actively pursue alternative solutions.
Diversification of Supply Chains
Reducing reliance on a single source of components is paramount. This requires:
- Negotiating with suppliers in other countries: Exploring alternative suppliers in countries unaffected by the tariffs is essential for securing affordable components.
- Developing stronger relationships with alternative manufacturers: Building long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers ensures a consistent supply of high-quality components.
- Investing in supply chain resilience: Strengthening the resilience of the supply chain makes it less vulnerable to future disruptions. This includes establishing backup suppliers and diversifying logistical routes.
Investment in Domestic Manufacturing
Investing in local solar panel manufacturing is a crucial long-term strategy:
- Government incentives for local manufacturing: Government support is critical in encouraging domestic manufacturers to expand production capacity.
- Technological advancements to boost domestic production capacity: Investing in research and development will enhance the competitiveness of Malaysian manufacturers.
- Attracting foreign investment in manufacturing: Incentivizing foreign investment can help transfer technology and expertise to boost the domestic industry.
Conclusion
The imposition of US solar import duties presents a significant hurdle for Malaysia's solar energy sector. The potential consequences – increased costs, reduced competitiveness, and delays in achieving renewable energy targets – are substantial. Understanding the impact of Malaysia US solar import duties is crucial for all stakeholders. Proactive measures, such as diversifying supply chains, boosting domestic manufacturing through government initiatives and private investment, and implementing effective government policies, are paramount. The future of Malaysian solar energy depends on navigating these challenges effectively. The continued progress towards a sustainable energy future hinges on a robust response to these US solar import duties. Failing to act decisively risks jeopardizing Malaysia's ambitious renewable energy goals and its overall economic competitiveness in the clean energy sector.

Featured Posts
-
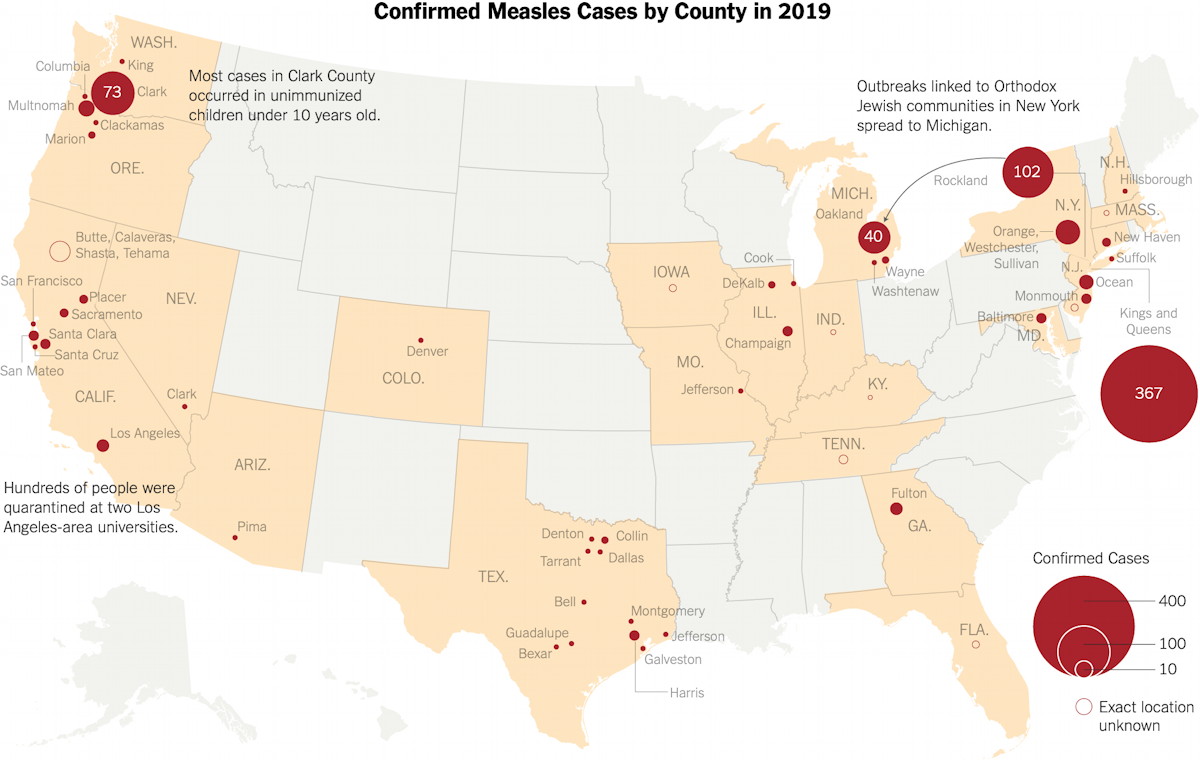 Where Is Measles Spreading In The United States
May 30, 2025
Where Is Measles Spreading In The United States
May 30, 2025 -
 Last Chance Gorillaz Tickets For Londons Copper Box Arena
May 30, 2025
Last Chance Gorillaz Tickets For Londons Copper Box Arena
May 30, 2025 -
 Glastonbury Festival Ticket Resale Prices And Dates Announced
May 30, 2025
Glastonbury Festival Ticket Resale Prices And Dates Announced
May 30, 2025 -
 Den Forogede Eftersporgsel Pa Kasper Dolberg En Dybdegaende Undersogelse
May 30, 2025
Den Forogede Eftersporgsel Pa Kasper Dolberg En Dybdegaende Undersogelse
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm La Guia Definitiva Para Preparar Tu Concierto
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm La Guia Definitiva Para Preparar Tu Concierto
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Partenariat Sanofi Dren Bio Une Avancee Dans Le Traitement Des Cancers
May 31, 2025
Partenariat Sanofi Dren Bio Une Avancee Dans Le Traitement Des Cancers
May 31, 2025 -
 Anticorps Bispecifiques Sanofi Investit Dans La Technologie De Dren Bio
May 31, 2025
Anticorps Bispecifiques Sanofi Investit Dans La Technologie De Dren Bio
May 31, 2025 -
 Dren Bio Et Sanofi Accord Majeur Sur Les Anticorps Bispecifiques
May 31, 2025
Dren Bio Et Sanofi Accord Majeur Sur Les Anticorps Bispecifiques
May 31, 2025 -
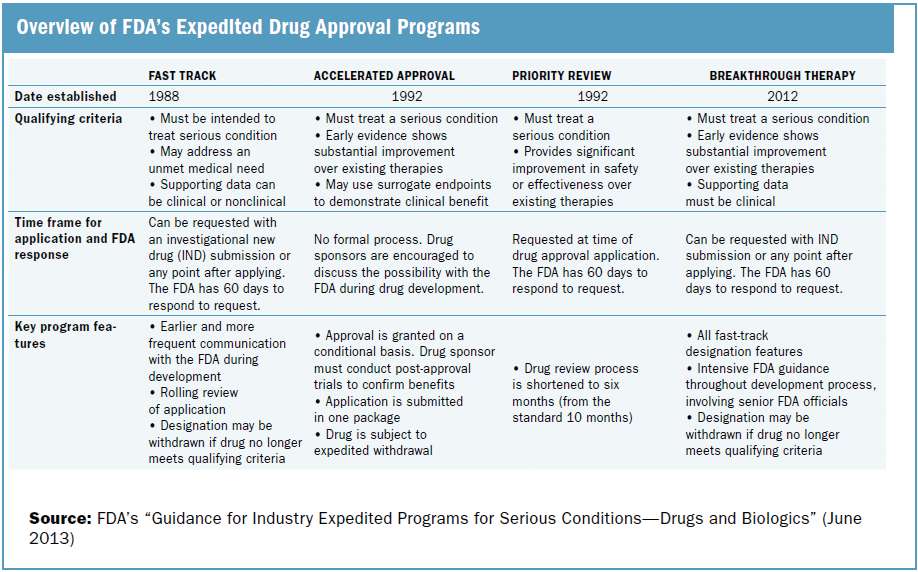 Sanofis Chlamydia Vaccine A Step Closer To Approval With Fda Fast Track Designation
May 31, 2025
Sanofis Chlamydia Vaccine A Step Closer To Approval With Fda Fast Track Designation
May 31, 2025 -
 Sanofi Rachete La Technologie D Anticorps Bispecifiques De Dren Bio
May 31, 2025
Sanofi Rachete La Technologie D Anticorps Bispecifiques De Dren Bio
May 31, 2025
