Mayotte's Status: A Colonial Legacy Questioned By Rokhaya Diallo

Table of Contents
The Historical Context of Mayotte's Status
The historical context of Mayotte's relationship with France is crucial to understanding the current debate surrounding its status. French colonization of the Comoros Islands began in the 19th century, gradually extending French influence over the archipelago. However, unlike its neighboring islands, Mayotte chose a different path.
-
French colonization of the Comoros Islands: France's colonial presence brought both development and exploitation, shaping the islands' political and economic landscape.
-
The 1974 referendum and Mayotte's choice to remain French: In 1974, a referendum was held in the Comoros Islands on independence. While three of the four islands (Grande Comore, Anjouan, and Mohéli) voted for independence, Mayotte voted overwhelmingly to remain under French rule. This decision has been a source of ongoing tension with the independent nation of Comoros.
-
The legal framework establishing Mayotte as an overseas department: Following the referendum, Mayotte's status was solidified through French legislation, establishing it as an overseas department, enjoying the same rights and responsibilities as those on the mainland.
-
Ongoing disputes with Comoros over sovereignty: Comoros continues to claim sovereignty over Mayotte, leading to persistent diplomatic tensions and legal challenges before international bodies. This territorial dispute is a key element of the ongoing debate about Mayotte's status.
Rokhaya Diallo's Critique and Key Arguments
Rokhaya Diallo, a prominent French writer and activist, offers a critical perspective on Mayotte's status, emphasizing its colonial legacy and its impact on the island's population. Her analysis challenges the narrative of a freely chosen affiliation with France.
-
Diallo's perspective on the neo-colonial aspects of Mayotte's relationship with France: Diallo argues that even though Mayotte is officially an overseas department, the relationship is still characterized by power imbalances reminiscent of colonialism.
-
Critique of French policies and their impact on the local population: She criticizes specific French policies, highlighting how they might perpetuate inequalities and marginalize certain segments of the Mahorais population.
-
Analysis of socio-economic disparities and inequalities: Diallo's work sheds light on the socio-economic disparities that exist within Mayotte, arguing that the island's status hasn't necessarily led to equitable development for all its inhabitants.
-
Discussion of the rights and representation of the Mahorais people: A central theme in Diallo's critique is the question of whether the Mahorais people have genuine self-determination and adequate representation within the French system.
The Socio-economic Realities of Mayotte
The socio-economic realities of Mayotte are complex and intertwined with its political status. While Mayotte benefits from being a French department, significant challenges persist.
-
High rates of poverty and unemployment: Poverty and unemployment remain significant problems, disproportionately affecting certain sectors of the population.
-
Challenges related to immigration from neighboring islands: The influx of migrants from the Comoros Islands creates pressure on resources and infrastructure, fueling social tensions.
-
Access to healthcare and education: While improvements have been made, access to quality healthcare and education remains unevenly distributed across the island.
-
Infrastructure development and its impact: Development projects, though aiming for improvement, can sometimes exacerbate existing social and environmental inequalities.
Perspectives of the Mahorais People
The Mahorais people hold diverse opinions regarding their relationship with France. There is no monolithic viewpoint on the issue of Mayotte's status.
-
Support for maintaining the status quo: Many Mahorais believe that remaining an overseas department of France offers economic and social advantages, including access to French citizenship, social security, and financial aid.
-
Arguments for greater autonomy or independence: Others advocate for greater autonomy or even independence, believing that it would better serve their cultural identity and political aspirations.
-
Concerns regarding cultural identity and preservation: The preservation of Mahoran culture and language is a significant concern among many inhabitants, as the influence of French culture can lead to assimilation.
-
The role of local political movements and activism: Various local political movements and activist groups play an important role in shaping the debate and advocating for different visions for Mayotte's future.
International Law and Mayotte's Status
Mayotte's status has significant international legal implications, primarily due to the ongoing dispute with Comoros.
-
The UN's stance on Mayotte's status: The UN has consistently recognized Comoros' claim to sovereignty over Mayotte, highlighting the unresolved nature of the territorial dispute.
-
International legal arguments regarding self-determination and sovereignty: The principles of self-determination and sovereignty are central to the legal arguments surrounding Mayotte's status.
-
The impact of Mayotte's status on regional stability: The unresolved dispute has potential ramifications for regional stability in the Indian Ocean.
-
Potential pathways for resolution of the dispute: Finding a lasting solution requires dialogue, negotiation, and consideration of all parties' concerns. International mediation could play a significant role.
Conclusion
Rokhaya Diallo's analysis of Mayotte's status highlights the complex interplay of history, politics, and socio-economic realities. The decision in 1974 to remain with France, while seemingly a choice of the Mahorais people, is viewed by some as a continuation of a colonial legacy, perpetuating inequalities and challenging the principle of self-determination. The socio-economic realities of Mayotte, marked by poverty, immigration challenges, and uneven access to resources, further complicate the issue. The diverse perspectives of the Mahorais people, ranging from support for the status quo to calls for greater autonomy, emphasize the need for nuanced understanding and inclusive dialogue. The unresolved territorial dispute with Comoros underscores the international legal complexities surrounding Mayotte's status.
Further research and discussion on "Mayotte's Status" are crucial for a nuanced understanding of this complex issue. Engaging with various perspectives and exploring potential solutions will help foster a more equitable and just future for Mayotte and its people. Continue the conversation about Mayotte’s status and its implications for the future of the island and its inhabitants. A thorough examination of Mayotte’s status is essential for informed decision-making and the pursuit of a just and sustainable future for the island.

Featured Posts
-
 Nhl Standings Who Will Claim The Western Conference Wild Card Spots
May 04, 2025
Nhl Standings Who Will Claim The Western Conference Wild Card Spots
May 04, 2025 -
 Harry Claims King Charles Wont Speak To Him Over Security Dispute
May 04, 2025
Harry Claims King Charles Wont Speak To Him Over Security Dispute
May 04, 2025 -
 Nhl Playoffs Showdown Saturday Standings And Key Matchups
May 04, 2025
Nhl Playoffs Showdown Saturday Standings And Key Matchups
May 04, 2025 -
 Vehicle Subsystem Issue Grounds Blue Origin Rocket
May 04, 2025
Vehicle Subsystem Issue Grounds Blue Origin Rocket
May 04, 2025 -
 Post Reynoso Garcia And Lopez To Train Under Paternal Guidance
May 04, 2025
Post Reynoso Garcia And Lopez To Train Under Paternal Guidance
May 04, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Investing In Middle Management A Strategy For Enhanced Company Performance And Employee Retention
May 05, 2025
Investing In Middle Management A Strategy For Enhanced Company Performance And Employee Retention
May 05, 2025 -
 Googles Search Ai Data Sources And User Privacy
May 05, 2025
Googles Search Ai Data Sources And User Privacy
May 05, 2025 -
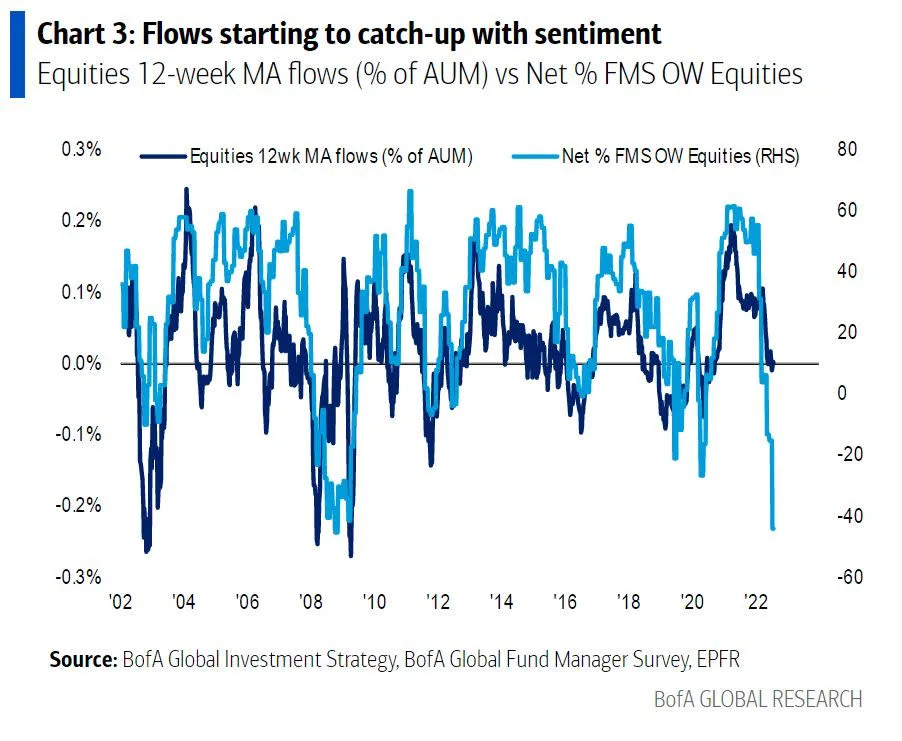 Should Investors Worry About Current Stock Market Valuations Bof As View
May 05, 2025
Should Investors Worry About Current Stock Market Valuations Bof As View
May 05, 2025 -
 Rethinking Middle Management Their Vital Contribution To Organizational Success
May 05, 2025
Rethinking Middle Management Their Vital Contribution To Organizational Success
May 05, 2025 -
 Understanding Googles Search Ai Training And User Data
May 05, 2025
Understanding Googles Search Ai Training And User Data
May 05, 2025
