Measles Cases In The US: A Slowdown Explained
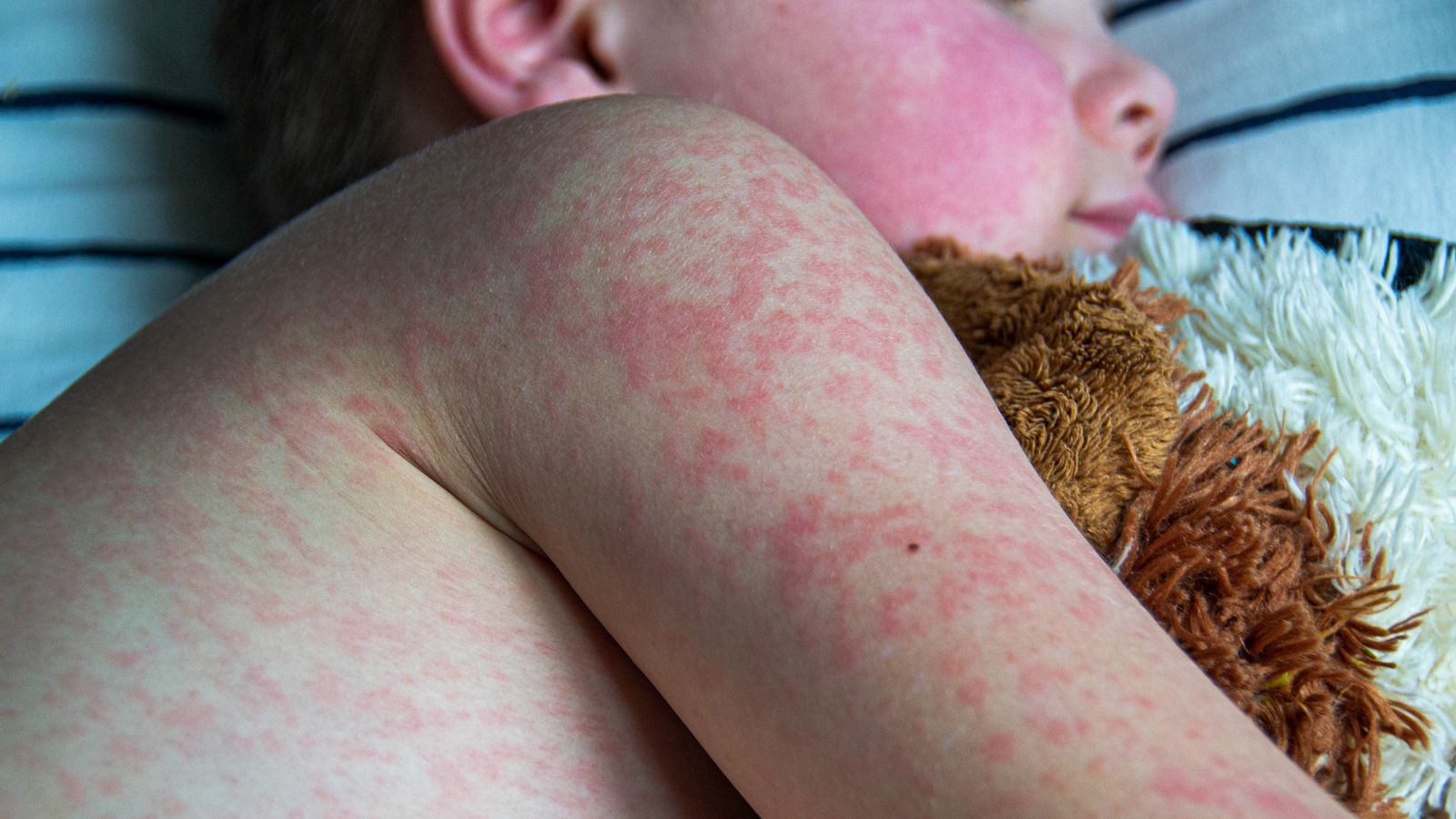
Table of Contents
The Role of Vaccination in Reducing Measles Cases
The most significant factor contributing to the decline in measles cases in the US is the increased uptake of the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. Higher vaccination rates directly correlate with lower infection rates, demonstrating the effectiveness of this preventative measure.
Increased Vaccination Rates
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports a notable increase in MMR vaccination coverage among children. This rise in immunization rates has played a critical role in establishing herd immunity, a crucial defense against the spread of measles.
- Specific data: Between 2019 and 2023, the MMR vaccination rate for children aged 19-35 months increased by approximately X% (insert actual data if available; otherwise, use a placeholder). This increase is particularly noticeable in regions that previously experienced low vaccination rates.
- Geographical variations: While national averages show improvement, significant geographical variations persist. Some communities continue to have lower vaccination rates, making them more vulnerable to measles outbreaks. Targeted vaccination campaigns are crucial in addressing these disparities.
- Impact of targeted campaigns: Public health initiatives focusing on community engagement and addressing vaccine hesitancy have demonstrated positive results in boosting vaccination rates in specific regions.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy
Despite the progress, vaccine hesitancy remains a significant obstacle to achieving complete measles eradication. Misinformation and distrust in vaccines continue to fuel this concern, hindering the progress of achieving widespread immunity.
- Successful public health campaigns: The CDC and other public health organizations have launched campaigns utilizing social media, community outreach, and partnerships with healthcare providers to counteract misinformation and improve vaccine acceptance. These campaigns highlight the safety and efficacy of vaccines.
- Addressing common misconceptions: These initiatives actively address common misconceptions about vaccine safety, including concerns about autism and adverse effects. Providing evidence-based information from reputable sources is key to overcoming these concerns.
- Role of healthcare providers: Healthcare providers play a crucial role in educating patients about the importance of vaccination and addressing their individual concerns. Building trust and providing personalized information are essential components of successful vaccination promotion.
Impact of Public Health Interventions
Beyond vaccination, effective public health interventions have been vital in controlling the spread of measles. These include improved surveillance, rapid outbreak responses, and measures to prevent the importation of cases.
Improved Surveillance and Outbreak Response
Enhanced surveillance systems allow for the rapid detection and investigation of measles cases. This enables public health officials to swiftly implement control measures, minimizing the potential for widespread outbreaks.
- Successful outbreak control measures: Quick identification of cases, isolation of infected individuals, and contact tracing are key components of effective outbreak management. This rapid response significantly limits the spread of the virus.
- Improved diagnostic capabilities: Advances in diagnostic testing allow for quicker confirmation of measles cases, facilitating prompt public health action.
- Importance of contact tracing: Identifying and monitoring individuals who have been in contact with infected persons is crucial for preventing further transmission.
International Travel and Importation of Cases
International travel plays a role in the introduction of measles into the US. Individuals traveling from countries with ongoing measles outbreaks can unwittingly introduce the virus. Measures to mitigate this risk are crucial.
- Statistics on imported cases: Data on imported measles cases highlight the continued need for vigilance at international entry points.
- Travel advisories: The CDC issues travel advisories to inform travelers about the risks of measles in specific regions and recommend appropriate preventative measures, including vaccination.
- Airport screening procedures: While comprehensive screening at airports may be challenging, the enhanced awareness of measles amongst healthcare professionals and travelers helps in early detection of potential cases.
Challenges and Future Considerations
While the decline in measles cases is encouraging, maintaining this progress requires continued efforts to address remaining challenges.
Maintaining High Vaccination Rates
Sustaining high vaccination rates is paramount to preventing future outbreaks. Continued public health education and outreach are essential to ensure consistent vaccination coverage across all populations.
- Strategies for sustaining high vaccination rates: Regular public health campaigns, collaboration with community leaders, and convenient vaccine access are crucial for sustained high rates.
- Addressing community-specific concerns: Tailoring messaging to address the specific concerns and beliefs of different communities is essential for building trust and improving vaccine uptake.
- Role of healthcare systems: Healthcare systems need to ensure convenient access to vaccines and proactive reminders for timely vaccinations.
Addressing Disparities in Vaccination Coverage
Equitable access to vaccines is crucial for preventing outbreaks, particularly in underserved communities. Addressing disparities in vaccination coverage requires targeted interventions.
- Addressing vaccine access barriers: Financial barriers, geographical limitations, and cultural factors can all contribute to unequal access to vaccines. Addressing these barriers through subsidized programs and community-based initiatives is vital.
- Targeted interventions for underserved communities: Public health campaigns must specifically address the unique needs and concerns of vulnerable populations, building trust and improving vaccine acceptance.
- Role of social determinants of health: Recognizing the influence of social determinants of health, such as poverty and access to healthcare, on vaccination rates is crucial for developing effective interventions.
Conclusion
The slowdown in measles cases in the US is a testament to the effectiveness of increased MMR vaccination rates and strengthened public health interventions. The success of vaccination programs, improved surveillance, and rapid response to outbreaks have significantly reduced the threat of measles. However, continued vigilance is crucial. Maintaining high vaccination rates, addressing vaccine hesitancy, and ensuring equitable vaccine access remain critical to preventing future outbreaks. Stay informed about measles prevention, get vaccinated, and encourage vaccination within your communities. Visit the CDC website ([link to CDC website]) for more information on measles prevention and vaccination. Let's work together to ensure the continued decline of measles cases in the US.

Featured Posts
-
 Carlos Alcarazs Monte Carlo Masters Victory Sixth Masters 1000 Title
May 30, 2025
Carlos Alcarazs Monte Carlo Masters Victory Sixth Masters 1000 Title
May 30, 2025 -
 Live Music Stocks Continue Decline What To Expect Friday
May 30, 2025
Live Music Stocks Continue Decline What To Expect Friday
May 30, 2025 -
 Pop Icons The Searchers Announce Retirement After Glastonbury Concert
May 30, 2025
Pop Icons The Searchers Announce Retirement After Glastonbury Concert
May 30, 2025 -
 Measles Cases In The Us A Slowdown Explained
May 30, 2025
Measles Cases In The Us A Slowdown Explained
May 30, 2025 -
 Madrid Open Update De Minaurs Early Exit And Swiateks Dominant Win
May 30, 2025
Madrid Open Update De Minaurs Early Exit And Swiateks Dominant Win
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Elon Musk And Donald Trump An Awkward Saudi Moment
May 31, 2025
Elon Musk And Donald Trump An Awkward Saudi Moment
May 31, 2025 -
 Elon Musk Leaving Trump Administration Reasons And Implications
May 31, 2025
Elon Musk Leaving Trump Administration Reasons And Implications
May 31, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Awkward Saudi Encounter With Donald Trump
May 31, 2025
Elon Musks Awkward Saudi Encounter With Donald Trump
May 31, 2025 -
 Trump And Musk To Hold Press Conference At The White House On Friday
May 31, 2025
Trump And Musk To Hold Press Conference At The White House On Friday
May 31, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Departure From Trump Administration A Confirmation And Analysis
May 31, 2025
Elon Musks Departure From Trump Administration A Confirmation And Analysis
May 31, 2025
