New COVID-19 Variant Driving Up Infections Worldwide: WHO Report
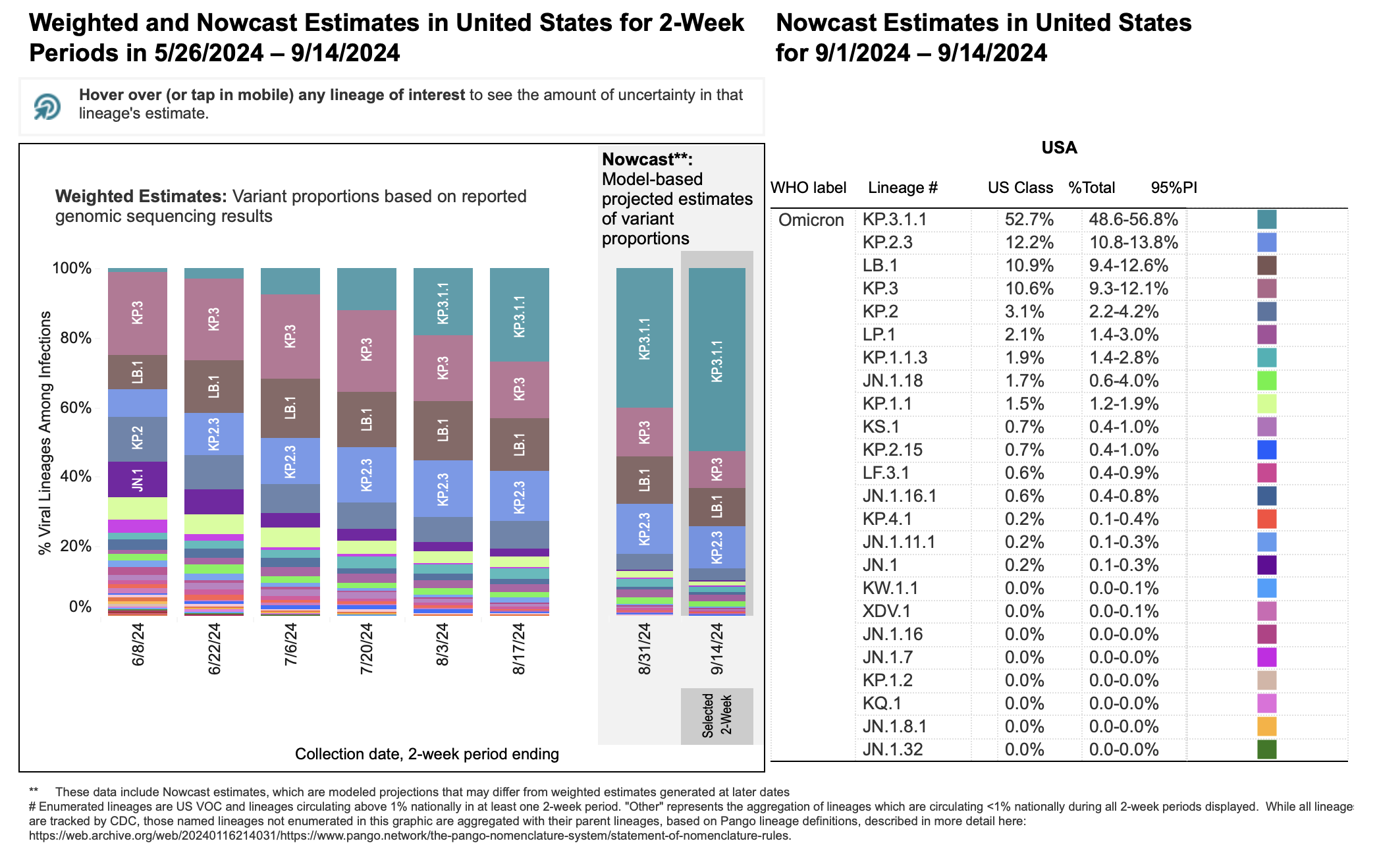
Table of Contents
The Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant
Understanding the characteristics of this new COVID-19 variant is crucial for effective public health responses. Key aspects include its transmissibility, severity, symptoms, and potential for immune evasion.
-
Mutations and Transmissibility: The new variant, tentatively named [Insert hypothetical variant name here – e.g., Omicron-2], possesses several key mutations, particularly in the spike protein. These mutations may affect its ability to bind to human cells and potentially increase its transmissibility compared to previous variants. Preliminary data suggests [Insert hypothetical data – e.g., a 20% increase] in its transmission rate. Further research is ongoing to confirm these findings.
-
Severity and Hospitalization Rates: While early data is still being analyzed, initial observations suggest [Insert hypothetical data – e.g., a similar or slightly higher] rate of severe illness and hospitalization compared to previous variants. However, this may vary depending on factors such as vaccination status and underlying health conditions. Mortality rates associated with this variant are currently under investigation.
-
Symptoms: The symptoms associated with this new variant appear largely similar to those seen with previous variants, including fever, cough, fatigue, loss of taste or smell, and shortness of breath. However, there are reports of [Insert hypothetical data – e.g., a higher incidence of gastrointestinal symptoms] in some cases. Further studies are needed to characterize the full spectrum of symptoms.
-
Immune Evasion: One of the major concerns surrounding new variants is their potential to evade the immune response provided by vaccines or prior infection. Preliminary studies suggest [Insert hypothetical data – e.g., a partial ability to evade existing immunity], but more comprehensive analysis is required.
-
Potential for Further Mutation: Viruses constantly evolve through mutation. Understanding the potential for this new COVID-19 variant to undergo further mutations is critical for predicting its future behavior and developing effective countermeasures. Continued genomic surveillance is essential to track any significant changes.
Global Impact and Infection Rates
The new COVID-19 variant is rapidly spreading globally, impacting various regions at different levels. Monitoring infection rates and their geographic distribution are crucial for informed decision-making.
-
Global Distribution: The variant has been identified in [Insert hypothetical data – e.g., over 50 countries] across all continents. Regions with [Insert hypothetical data – e.g., lower vaccination rates or weaker public health infrastructure] are particularly vulnerable to more significant outbreaks. [Insert a hypothetical map or graph showing global spread].
-
Infection Rate Trends: Infection rates are increasing in many parts of the world. [Insert hypothetical data and charts or graphs showing infection rate trends over time]. These trends highlight the variant's high transmissibility and the need for immediate action.
-
Strain on Healthcare Systems: The surge in infections puts a significant strain on healthcare systems worldwide, leading to [Insert hypothetical data – e.g., increased hospitalizations, shortages of medical staff, and potential delays in treatment for other conditions].
-
International Collaboration: International collaboration is crucial in addressing this global health threat. [Insert hypothetical examples – e.g., information sharing between countries, coordinated vaccine distribution efforts, and joint research initiatives] are essential components of an effective global response.
Public Health Measures and Prevention Strategies
Effective public health measures are critical for mitigating the spread of the new COVID-19 variant and preventing further outbreaks. These measures must be comprehensive and implemented consistently.
-
Vaccination and Booster Shots: Vaccination remains the most effective tool for protecting against severe illness and death from COVID-19. Getting vaccinated and receiving booster shots, as recommended, is paramount in mitigating the impact of the new variant.
-
Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions: Non-pharmaceutical interventions, such as mask-wearing in indoor settings, maintaining social distancing, and avoiding crowded places, continue to play a vital role in slowing the spread of the virus.
-
Hygiene Practices: Good hygiene practices, including regular handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and cleaning and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces, remain essential for preventing transmission.
-
Updated Public Health Guidelines: Individuals should stay informed and follow the latest public health guidelines and recommendations from organizations like the WHO and their national public health authorities.
-
Continued Genomic Surveillance: Genomic surveillance is crucial for tracking the emergence and spread of new variants, allowing for early detection and enabling rapid responses.
The Role of Genomic Surveillance in Tracking Variants
Genomic surveillance is a critical component of pandemic preparedness and response. It plays a vital role in understanding the evolution and spread of the virus.
-
Early Detection: Genomic surveillance allows for the early detection of new variants, providing valuable time to implement effective control measures.
-
Tracking Spread and Evolution: By analyzing the genetic sequences of the virus, scientists can track the spread of variants and monitor their evolution, including the emergence of new mutations.
-
Challenges and Limitations: Genomic surveillance faces challenges such as access to sufficient samples, timely sequencing, and data sharing across borders. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for enhancing the effectiveness of surveillance efforts.
Conclusion
The emergence of the new COVID-19 variant presents a significant public health challenge, demanding a renewed and coordinated global response. The data indicates a concerning rise in infections, highlighting the need for continued vigilance and proactive measures. Understanding the characteristics and global impact of this new COVID-19 variant is crucial for effective pandemic preparedness.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the latest updates on this new COVID-19 variant from reliable sources like the WHO. Practice good hygiene, get vaccinated and boosted, and follow public health guidelines to help protect yourself and your community from this new COVID-19 variant and future outbreaks. Effective management of this new COVID-19 variant relies on collective action and responsible behavior.

Featured Posts
-
 El Croque Monsieur Mas Facil Receta Paso A Paso Con Fotos
May 31, 2025
El Croque Monsieur Mas Facil Receta Paso A Paso Con Fotos
May 31, 2025 -
 Rome Masters Alcaraz And Passaro Shine At Italian International
May 31, 2025
Rome Masters Alcaraz And Passaro Shine At Italian International
May 31, 2025 -
 Nikola Jokics One Handed Highlight Key To Nuggets Blowout Win Over Jazz
May 31, 2025
Nikola Jokics One Handed Highlight Key To Nuggets Blowout Win Over Jazz
May 31, 2025 -
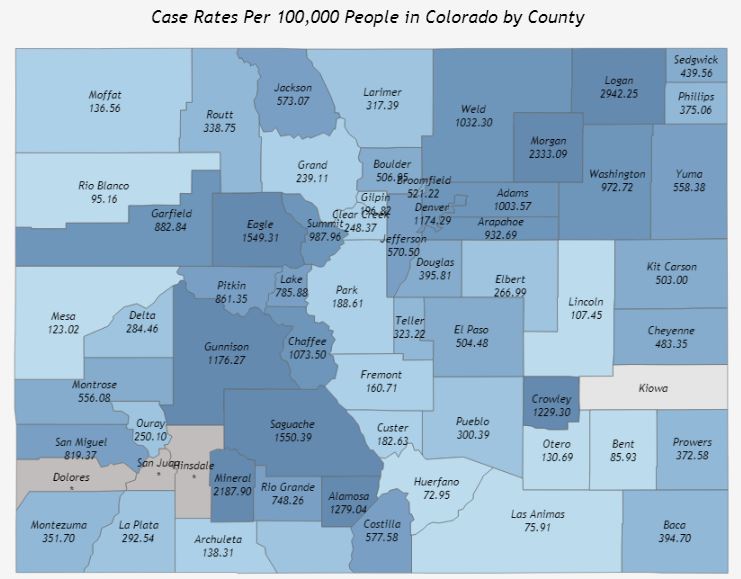 Covid 19 Variant Surge Increased Cases Reported Nationally
May 31, 2025
Covid 19 Variant Surge Increased Cases Reported Nationally
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguias Revenge Dominant Victory Over Surace In Rematch
May 31, 2025
Munguias Revenge Dominant Victory Over Surace In Rematch
May 31, 2025
