Recent Measles Outbreaks: Affected Areas In The United States
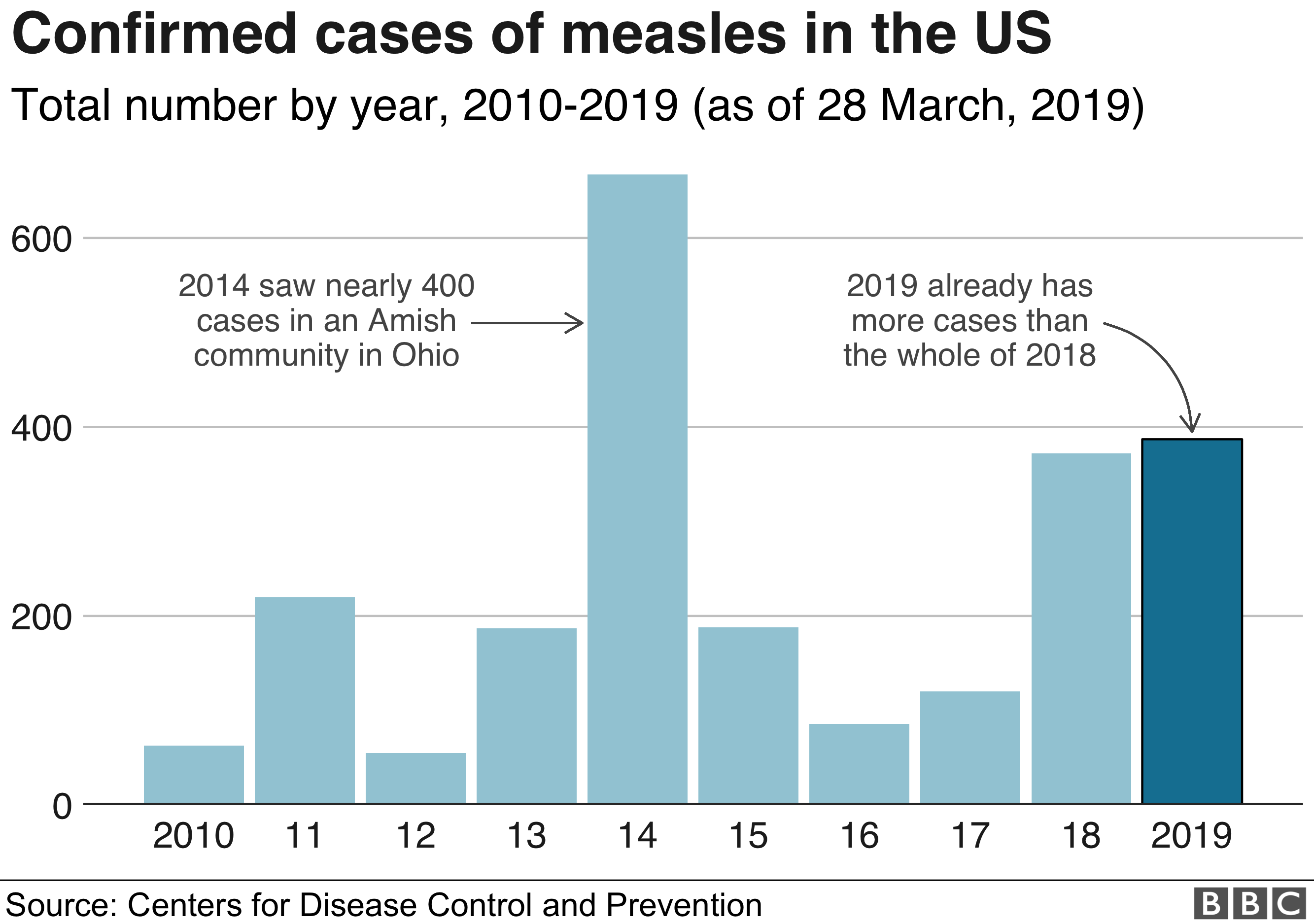
Table of Contents
Geographic Distribution of Recent Measles Outbreaks
Understanding the geographic spread of measles is crucial for targeted intervention strategies. Analyzing the distribution helps public health officials allocate resources effectively and implement focused vaccination campaigns.
Outbreaks by State
Several states have experienced significant measles outbreaks in recent years. While precise, up-to-the-minute case numbers fluctuate, consistent monitoring by the CDC provides valuable insights. (Note: Specific case numbers and dates would need to be replaced with current data from reliable sources like the CDC website).
- State A (e.g., New York): Experienced a large outbreak in [Year], with over [Number] confirmed cases, primarily affecting [Specific communities, e.g., Orthodox Jewish communities]. This outbreak highlighted the vulnerability of communities with lower vaccination rates.
- State B (e.g., Washington): [Number] cases were reported in [Year], linked to [Contributing factor, e.g., an unvaccinated individual returning from international travel]. This outbreak underscored the role of international travel in spreading measles.
- State C (e.g., California): Similar to other outbreaks, California experienced a significant number of cases in [Year], primarily concentrated in [Specific regions/demographics]. [Link to a relevant CDC map showing outbreak distribution would be inserted here].
Urban vs. Rural Outbreaks
The distribution of measles outbreaks isn't uniform. While densely populated urban areas might seem more susceptible due to increased person-to-person contact, rural areas also face unique challenges.
- Challenges in Rural Areas: Limited access to healthcare facilities, lower vaccination rates due to geographical barriers, and vaccine hesitancy contribute to higher risks in rural communities. Reaching these communities with vaccination campaigns requires innovative strategies.
- Urban Outbreak Dynamics: Large urban populations facilitate rapid transmission, particularly in settings with lower vaccination rates or among unvaccinated individuals. Outbreaks in densely populated areas often require swift and extensive public health interventions.
Tracking the Spread
Public health agencies employ robust surveillance systems to track and control measles outbreaks. Effective monitoring relies heavily on reporting and contact tracing.
- The CDC's Role: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays a vital role in coordinating national surveillance, providing guidance to state and local health departments, and disseminating critical information to the public.
- Contact Tracing: This crucial process involves identifying individuals who have been in close contact with infected persons, assessing their risk, and recommending appropriate interventions such as vaccination or quarantine. Rapid and effective contact tracing is essential to prevent further spread.
Contributing Factors to Measles Outbreaks
Several factors contribute to the resurgence of measles in the United States. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies.
Low Vaccination Rates
A strong correlation exists between low vaccination rates and measles outbreaks. Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by misinformation and distrust, remains a significant challenge.
- Misinformation's Impact: The spread of misinformation regarding vaccine safety and efficacy, often amplified through social media, significantly contributes to vaccine hesitancy. Combating misinformation requires disseminating accurate, evidence-based information through trusted sources.
- Role of Social Media: Social media platforms, while offering valuable communication tools, can also be vectors for the spread of misleading and harmful information about vaccines. Critical evaluation of online information is vital.
- Trusted Sources: Reliable information from credible sources, such as the CDC and WHO, is essential to counter misinformation and promote informed decision-making regarding vaccination.
International Travel
International travel plays a crucial role in introducing and spreading measles into communities with low vaccination coverage.
- Challenges in Monitoring: Monitoring and preventing the introduction of measles from international travelers is challenging, particularly given the virus's incubation period and the large volume of international travel.
- Importance of Pre-Travel Vaccination: Vaccination before international travel is highly recommended to protect individuals and prevent the importation of measles into communities with low vaccination rates.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors significantly influence access to healthcare and vaccination, thus impacting the prevalence of measles outbreaks.
- Poverty and Healthcare Access: Poverty and limited access to healthcare services create significant barriers to vaccination, leaving vulnerable populations at increased risk.
- Addressing Disparities: Targeted interventions addressing socioeconomic inequalities, such as increased access to affordable healthcare and community-based vaccination programs, are essential to ensure equitable vaccine access for all populations.
Conclusion
Recent measles outbreaks in the US highlight the critical importance of high vaccination rates in preventing the resurgence of this highly contagious disease. Outbreaks have been concentrated in several states, with contributing factors including low vaccination rates, international travel, and socioeconomic disparities. Understanding the geographic distribution and underlying causes of these outbreaks is crucial for effective prevention and control.
Key Takeaways: The resurgence of measles emphasizes the continued need for widespread vaccination. Addressing vaccine hesitancy through education and public health campaigns is crucial, as is ensuring equitable access to healthcare and vaccination for all populations.
Protect yourself and your community: Learn more about recent measles outbreaks in the US and the importance of vaccination. Visit the CDC website for up-to-date information and resources. [Insert link to CDC measles information page here].

Featured Posts
-
 Como Obtener Tu Reembolso Por La Cancelacion Del Festival Axe Ceremonia 2025 En Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025
Como Obtener Tu Reembolso Por La Cancelacion Del Festival Axe Ceremonia 2025 En Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025 -
 Shyft Alshrq Alawst Awstabynkw Twasl Tqdmha Fy Btwlat Altrab
May 30, 2025
Shyft Alshrq Alawst Awstabynkw Twasl Tqdmha Fy Btwlat Altrab
May 30, 2025 -
 2025s Leading Music Lawyers Your Essential Resource
May 30, 2025
2025s Leading Music Lawyers Your Essential Resource
May 30, 2025 -
 Fewer Excessive Heat Warnings Explaining The Recent Decrease
May 30, 2025
Fewer Excessive Heat Warnings Explaining The Recent Decrease
May 30, 2025 -
 Eventims Positive Financial Performance Year On Year Growth Analysis
May 30, 2025
Eventims Positive Financial Performance Year On Year Growth Analysis
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Alcaraz Cruises To Straight Sets Win At Barcelona Open
May 31, 2025
Alcaraz Cruises To Straight Sets Win At Barcelona Open
May 31, 2025 -
 Sage Hill Volleyball Cif Ss Finals Bound Following Victory Over Crean Lutheran
May 31, 2025
Sage Hill Volleyball Cif Ss Finals Bound Following Victory Over Crean Lutheran
May 31, 2025 -
 Beatles Biopic Cast Announced Whos Playing Who
May 31, 2025
Beatles Biopic Cast Announced Whos Playing Who
May 31, 2025 -
 The Beatles Cast Revealed A Look At The Actors
May 31, 2025
The Beatles Cast Revealed A Look At The Actors
May 31, 2025 -
 Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser A Deeper Dive Into The New Season
May 31, 2025
Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser A Deeper Dive Into The New Season
May 31, 2025
