School Desegregation: The End Of An Era?

Table of Contents
The Legacy of Brown v. Board of Education
The Ruling's Impact and Initial Successes
The Brown v. Board decision sparked initial progress in some regions, leading to the desegregation of schools in certain areas. The ruling's impact was immediate, though its implementation was far from uniform across the country. The initial successes were largely concentrated in the South, fueled by federal court orders and the involvement of civil rights activists.
- Initial progress in certain regions: Many southern states initially resisted, but federal intervention gradually led to increased integration.
- Challenges encountered in implementing desegregation: Massive resistance in the form of protests, violence, and legal challenges hindered progress in many areas.
- Examples of successful integration strategies: Some school districts successfully implemented busing programs and other strategies to achieve more diverse student populations.
Resistance and Continued Segregation
Despite initial successes, resistance to school desegregation persisted in numerous forms, significantly hindering the progress toward true racial integration.
- The role of housing segregation in perpetuating school segregation: Residential segregation, often stemming from discriminatory housing policies, continues to create and reinforce segregated school districts.
- Examples of legal challenges and loopholes used to circumvent desegregation mandates: Legal maneuvering and the creation of loopholes allowed some districts to delay or avoid desegregation.
- The impact of "white flight" on school demographics: The phenomenon of "white flight," where white families moved to suburban areas to avoid integrated schools, significantly impacted school demographics and exacerbated segregation.
The Current State of School Segregation
De Facto Segregation
Today, school segregation often takes the form of de facto segregation—segregation that exists in practice, but not as a result of official laws or policies. This form of segregation is perpetuated by factors like residential patterns, school district boundaries, and socioeconomic disparities.
- Statistics on racial and socioeconomic segregation in schools: Numerous studies reveal persistent racial and socioeconomic segregation in schools across the United States.
- Examples of school districts with high levels of segregation: Many urban and suburban school districts continue to exhibit stark racial and socioeconomic disparities in student populations.
- The role of housing patterns and school district boundaries: The design and boundaries of school districts often reflect and reinforce existing housing patterns, contributing to de facto segregation.
Achievement Gaps and Educational Inequality
The persistent link between school segregation and achievement gaps cannot be ignored. Segregated schools often lack the resources and opportunities needed to provide equitable education for all students.
- The impact of segregation on academic performance: Studies show a strong correlation between school segregation and lower academic achievement among students of color.
- Differences in resource allocation between segregated schools: Segregated schools often receive less funding and have fewer qualified teachers than their more affluent counterparts.
- The role of teacher quality and student demographics: The quality of teaching and the availability of advanced courses often vary significantly between segregated schools, perpetuating inequalities.
Efforts Towards Desegregation Today
Legal Challenges and Policy Initiatives
Despite the ongoing challenges, various legal challenges and policy initiatives strive to promote school integration.
- Recent court cases related to school desegregation: Several recent court cases have addressed issues of school segregation, highlighting the continued relevance of this issue.
- Examples of successful desegregation programs: Some school districts have implemented successful programs to promote integration, such as magnet schools and inter-district transfers.
- Policy recommendations for achieving greater school diversity: Experts recommend policies that address housing segregation, promote equitable resource allocation, and foster diverse school environments.
The Role of Community Involvement
Community engagement is crucial for promoting school integration and fostering a sense of shared responsibility for equitable education.
- The impact of parental involvement and community activism: Actively involved parents and communities can play a significant role in advocating for desegregation and promoting inclusive school environments.
- Strategies for building bridges between different communities: Building strong relationships between diverse communities through collaborative efforts can help to overcome barriers to school integration.
- Collaborative efforts to improve educational opportunities for all students: Shared goals and collaborative initiatives are essential for creating more equitable and integrated schools.
Conclusion
While significant progress has been made since Brown v. Board, the fight for truly integrated and equitable schools remains far from over. The persistent challenges of de facto segregation, achievement gaps, and inequitable resource allocation underscore the continuing need for proactive measures. The complex legacy of school desegregation requires ongoing vigilance and concerted efforts to achieve genuine educational equity and school diversity for all students. Learn more about school desegregation in your community and take action to promote educational equity and school diversity. The fight for a truly desegregated educational system requires the collective efforts of individuals, communities, and policymakers. Join the movement for school desegregation and help build a more just and equitable future for all children.

Featured Posts
-
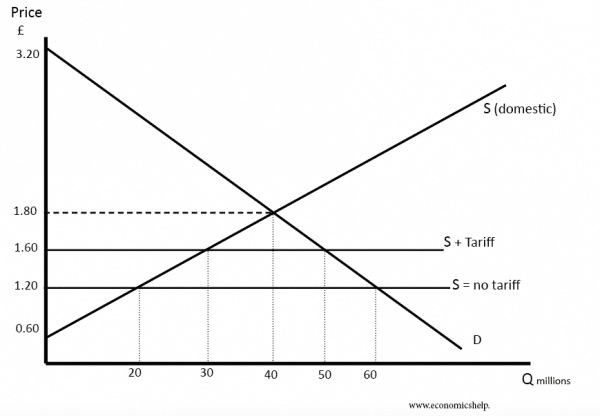 Impact Of Tariffs On Brookfields Manufacturing Investment In The Us
May 03, 2025
Impact Of Tariffs On Brookfields Manufacturing Investment In The Us
May 03, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Nigel Farage On Reform Uks Political Standing
May 03, 2025
The Impact Of Nigel Farage On Reform Uks Political Standing
May 03, 2025 -
 Keller Williams Welcomes New Arkansas Affiliate
May 03, 2025
Keller Williams Welcomes New Arkansas Affiliate
May 03, 2025 -
 Key Themes In Alan Rodens Spectator Articles
May 03, 2025
Key Themes In Alan Rodens Spectator Articles
May 03, 2025 -
 Kivinin Kabugunu Yemek Faydalari Zararlari Ve Dikkat Edilmesi Gerekenler
May 03, 2025
Kivinin Kabugunu Yemek Faydalari Zararlari Ve Dikkat Edilmesi Gerekenler
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Indias Pm Modis France Trip Key Events Including Ai Summit And Ceo Forum
May 03, 2025
Indias Pm Modis France Trip Key Events Including Ai Summit And Ceo Forum
May 03, 2025 -
 Reaction De Macron Face A La Souffrance Visite Emouvante Aupres De Victimes Israeliennes
May 03, 2025
Reaction De Macron Face A La Souffrance Visite Emouvante Aupres De Victimes Israeliennes
May 03, 2025 -
 La Rencontre Poignante De Macron Avec Les Victimes Israeliennes Une Image Forte
May 03, 2025
La Rencontre Poignante De Macron Avec Les Victimes Israeliennes Une Image Forte
May 03, 2025 -
 L Emotion De Macron Apres Son Entretien Avec Les Victimes De L Armee Israelienne
May 03, 2025
L Emotion De Macron Apres Son Entretien Avec Les Victimes De L Armee Israelienne
May 03, 2025 -
 Macron Rencontre Des Victimes Israeliennes Une Image Rare D Emotion
May 03, 2025
Macron Rencontre Des Victimes Israeliennes Une Image Rare D Emotion
May 03, 2025
