Secular And Religious Influences On Gender In Egypt: The Case Of Al-Riyada (1820-1936)
Table of Contents
The Religious Landscape and its Influence on Women's Lives in al-Riyada
Interpretations of Islamic Law and Women's Rights
The interpretations of Islamic law significantly shaped women's legal status and social standing in 19th and 20th-century Egypt. During the al-Riyada period, various scholarly opinions on women's rights existed, leading to diverse practices and realities.
- Differing interpretations of inheritance laws: Some scholars emphasized women's right to inherit, while others advocated for reduced shares compared to men, leading to discrepancies in women's economic autonomy.
- Varying views on marriage and divorce: Disagreements existed regarding women's agency in marriage and the ease of obtaining a divorce, impacting women's control over their lives and relationships.
- The role of religious courts (Sharia courts): These courts played a critical role in adjudicating family matters, often reflecting prevailing interpretations of Islamic law, sometimes limiting women's rights.
The Influence of Sufi Orders and Religious Piety on Women's Roles
Sufi orders offered women avenues for religious engagement and social interaction. Religious piety often shaped women's daily lives, creating both constraints and opportunities.
- Women's participation in Sufi rituals and practices: Many women actively participated in Zikr ceremonies and other Sufi practices, fostering a sense of community and spiritual fulfillment.
- Social networks within Sufi orders: These orders provided women with social support networks and opportunities for leadership within religious contexts.
- Agency within religious frameworks: While religious norms constrained women in some ways, Sufi orders also allowed some women to exercise a degree of agency and influence within their communities.
Religious Discourse and Representations of Women in al-Riyada
Religious discourse, including sermons and religious literature, significantly impacted the social norms and expectations surrounding women's behavior and morality.
- Idealized depictions of women: Sermons and religious texts often emphasized women's roles as wives and mothers, emphasizing piety and domesticity as ideal qualities.
- Moral codes and social control: Religious discourse reinforced moral codes that governed women's behavior in public and private spheres, often restricting their freedoms.
- The impact of religious education: The religious instruction received by women shaped their understanding of their roles and responsibilities within society.
Secular Influences and the Changing Role of Women
The Impact of Modernization and Westernization
The increasing influence of European ideas and educational reforms challenged traditional views on gender roles.
- Introduction of Western educational models: The establishment of schools for girls, albeit limited, introduced new ideas about women's potential and capabilities.
- Exposure to Western feminist thought: The dissemination of Western feminist ideas through translated texts and intellectual exchanges challenged existing patriarchal structures.
- Rise of nationalist movements: Nationalist movements often incorporated women's rights within their agendas, recognizing the importance of women's participation in nation-building.
Secular Legal Reforms and Women's Rights
Secular legal reforms introduced during this period sought to improve women's legal status.
- Changes in marriage and divorce laws: Some reforms aimed to grant women greater autonomy in marriage and divorce, although implementation varied.
- Reforms concerning inheritance: Efforts were made to address inequalities in inheritance laws, although these reforms often faced resistance from traditionalists.
- Limitations of secular reforms: The impact of secular reforms was often limited by the persistence of traditional customs and social norms.
The Emergence of Women's Activism and Public Life
The al-Riyada period witnessed the rise of women's activism and participation in public life.
- Women's participation in nationalist movements: Women played significant roles in nationalist movements, challenging gendered expectations and participating in political activism.
- Social reform campaigns: Women actively participated in social reform campaigns focused on education, health, and women's rights.
- Establishment of women's organizations: The formation of women's organizations provided platforms for advocacy and collective action.
The Case of al-Riyada: A Microcosm of Broader Trends
Specific examples of women's lives in al-Riyada
Examining the lives of women from different social classes in al-Riyada reveals the complexities of gender roles in this period.
- Stories of working-class women: Research into the lives of working-class women reveals their struggles and resilience in the face of economic hardship and social constraints.
- Experiences of women from elite families: The lives of women from elite families highlight the interplay of tradition and modernity in shaping their experiences.
- Individual achievements and challenges: Examining individual stories reveals the diversity of women's experiences and challenges in navigating their roles within society.
Analyzing the interplay of secular and religious forces
The interplay between secular and religious forces shaped the lives of women in al-Riyada in complex ways.
- Resistance to reforms: Traditionalists resisted secular reforms that challenged established norms and practices.
- Negotiating religious and secular spheres: Women often negotiated the tension between religious expectations and the possibilities offered by secular reforms.
- The evolution of gender roles: The period witnessed a gradual shift in gender roles, reflecting the dynamic interaction between secular and religious influences.
Conclusion: Understanding the Complexities of Gender in Egyptian History
This analysis of secular and religious influences on gender in Egypt during the al-Riyada period (1820-1936) reveals a complex and dynamic interplay of forces. Religious interpretations and discourses significantly shaped women's lives, but secular reforms and the rise of women's activism challenged traditional norms. The experiences of women in al-Riyada highlight the diverse ways in which individuals navigated the tension between tradition and modernity. Understanding this complex interaction is vital for a nuanced understanding of Egyptian history. Further research into the secular and religious influences on gender in Egypt, particularly focusing on the experiences of women beyond al-Riyada and exploring comparative analyses with other historical periods, is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of Egyptian gender history.

Featured Posts
-
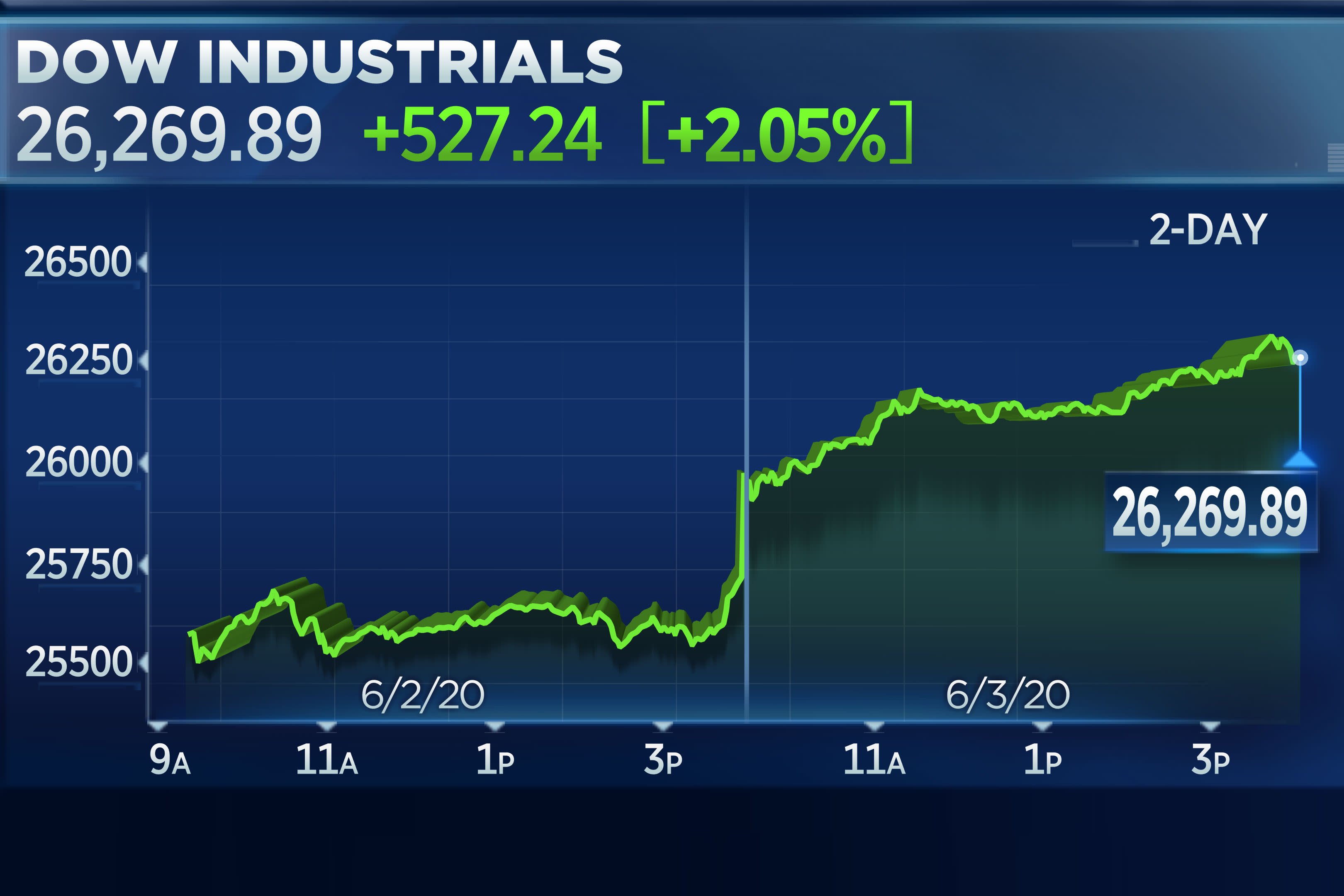 Stock Market Today Dow And S And P 500 Live Updates For April 23rd
Apr 24, 2025
Stock Market Today Dow And S And P 500 Live Updates For April 23rd
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Nba Probe Into Ja Morant Incident What We Know So Far
Apr 24, 2025
Nba Probe Into Ja Morant Incident What We Know So Far
Apr 24, 2025 -
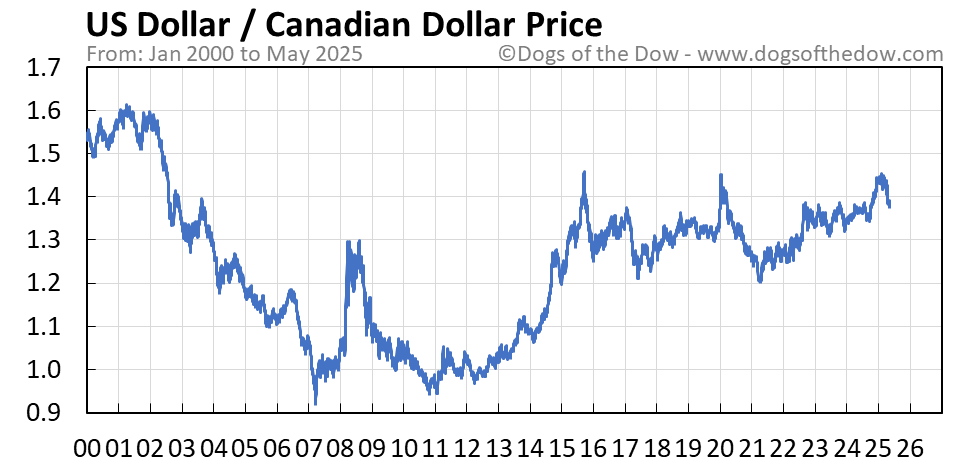 Recent Shifts In The Canadian Dollar Exchange Rate An In Depth Look
Apr 24, 2025
Recent Shifts In The Canadian Dollar Exchange Rate An In Depth Look
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Chalet Girls Unveiling The Reality Of Luxury Ski Season Work
Apr 24, 2025
Chalet Girls Unveiling The Reality Of Luxury Ski Season Work
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Zaboravljeni Projekt Tarantino I Travolta Film Koji Nikad Nisu Pogledali
Apr 24, 2025
Zaboravljeni Projekt Tarantino I Travolta Film Koji Nikad Nisu Pogledali
Apr 24, 2025
