Social Media And The D.C. Midair Collision: A Case Study In Misinformation

Table of Contents
The Initial Spread of Misinformation
Unverified Sources and Sensationalism
The initial hours following the D.C. midair collision saw a deluge of unverified information flooding social media. Social media algorithms, designed to prioritize engagement, amplified these reports regardless of their accuracy. Many posts lacked credible sources, relying instead on speculation and sensationalism to garner attention. For example, numerous tweets claimed specific pilot error or equipment malfunction without any credible evidence to support these assertions.
- Lack of fact-checking before sharing: Users often shared information without verifying its authenticity from reputable sources.
- Emotional language used to attract attention: Sensational headlines and emotionally charged language were used to increase engagement and virality.
- Role of hashtags in spreading misinformation: Irresponsible use of relevant hashtags further amplified the reach of inaccurate information.
The Echo Chamber Effect
Social media algorithms, designed to show users content aligned with their existing interests, inadvertently created echo chambers around the D.C. midair collision. This reinforced pre-existing beliefs and biases, hindering the spread of accurate information from official sources. Groups and pages dedicated to specific theories (e.g., blaming air traffic control or a particular airline) shared only information confirming their views, actively ignoring contradicting evidence.
- Limited exposure to diverse perspectives: Users within these echo chambers were largely shielded from alternative viewpoints and factual corrections.
- Confirmation bias: Users actively sought and shared information confirming their initial assumptions, reinforcing their biases.
- Filter bubbles: Algorithms created filter bubbles, limiting exposure to information that challenged pre-existing beliefs about the incident.
The Role of Visual Content in Misinformation
Manipulated Images and Videos
The rapid spread of misinformation was further exacerbated by the use of manipulated or out-of-context visual content. Altered photos suggesting a closer proximity between the aircraft than actually occurred were widely circulated. Similarly, misleading video edits were used to support false narratives about the incident.
- Deepfakes: While not confirmed in this specific instance, the potential for deepfakes to create convincing but fabricated evidence highlights a significant threat.
- Image manipulation software: Readily available image and video editing software makes it easy to create and distribute misleading visual content.
- Difficulty in verifying authenticity of online visual content: The ease with which visual content can be manipulated makes verification challenging, adding to the spread of misinformation.
Misinterpretation of Official Footage
Even official footage released by authorities was misinterpreted and misused to support false claims. Selective framing of video clips and misrepresentation of audio recordings from air traffic control were prevalent. This highlights the importance of critical thinking and media literacy in interpreting online information.
- Lack of context in shared clips: Short clips taken out of their broader context can easily be misleading.
- Biased editing to support a narrative: Users often edited clips to selectively highlight information supporting their pre-existing beliefs.
Fact-Checking and Combating Misinformation
The Challenges of Rapid Response
Fact-checkers and authorities faced significant challenges in rapidly addressing the misinformation spreading online. The sheer volume and speed of false information made it difficult to verify information quickly enough to counter false narratives effectively.
- Resource limitations: Fact-checking organizations often lack the resources to address every instance of misinformation in real-time.
- Pressure to provide immediate responses: The demand for immediate answers often compromises thoroughness and accuracy.
- Delays in official investigations: Official investigations often take time, leaving a vacuum filled by speculation and misinformation.
Strategies for Effective Counter-Messaging
Effective counter-messaging strategies are crucial in combating misinformation surrounding events like the D.C. midair collision. These strategies need to focus on clear, concise, and credible information disseminated through trusted channels.
- Utilizing trusted news sources: Promoting reliance on established news organizations and official sources is key.
- Employing visual aids to clarify factual information: Using infographics and clear visuals can aid understanding and counter misleading images and videos.
- Partnering with social media platforms: Collaboration between authorities and social media platforms is essential for rapid identification and removal of false information.
- Importance of transparency: Open communication from authorities about the investigation process builds trust and reduces the spread of speculation.
- Providing easily understandable information: Information should be tailored to a broad audience, avoiding jargon and technical details.
- Targeted dissemination strategies: Counter-narratives should be strategically targeted to reach specific groups and demographics susceptible to misinformation.
Conclusion
The D.C. midair collision serves as a stark reminder of social media's potential to amplify misinformation rapidly, potentially impacting public perception and even endangering aviation safety. Combating this requires a multi-pronged approach involving faster fact-checking, clear and timely communication from authorities, improved media literacy education, and collaborative efforts from social media platforms to quickly identify and remove misleading content. By understanding the dynamics of misinformation spread related to the D.C. midair collision and similar events, we can develop more effective strategies to combat the spread of false information on social media and prioritize accuracy and reliable information. Learn more about the dangers of social media misinformation and how to spot it – your awareness is crucial in preventing future incidents fueled by unreliable information.

Featured Posts
-
 Auto Dealers Intensify Fight Against Ev Sales Requirements
Apr 29, 2025
Auto Dealers Intensify Fight Against Ev Sales Requirements
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Rekordiniai Porsche Pardavimai Lietuvoje 2024 Metais
Apr 29, 2025
Rekordiniai Porsche Pardavimai Lietuvoje 2024 Metais
Apr 29, 2025 -
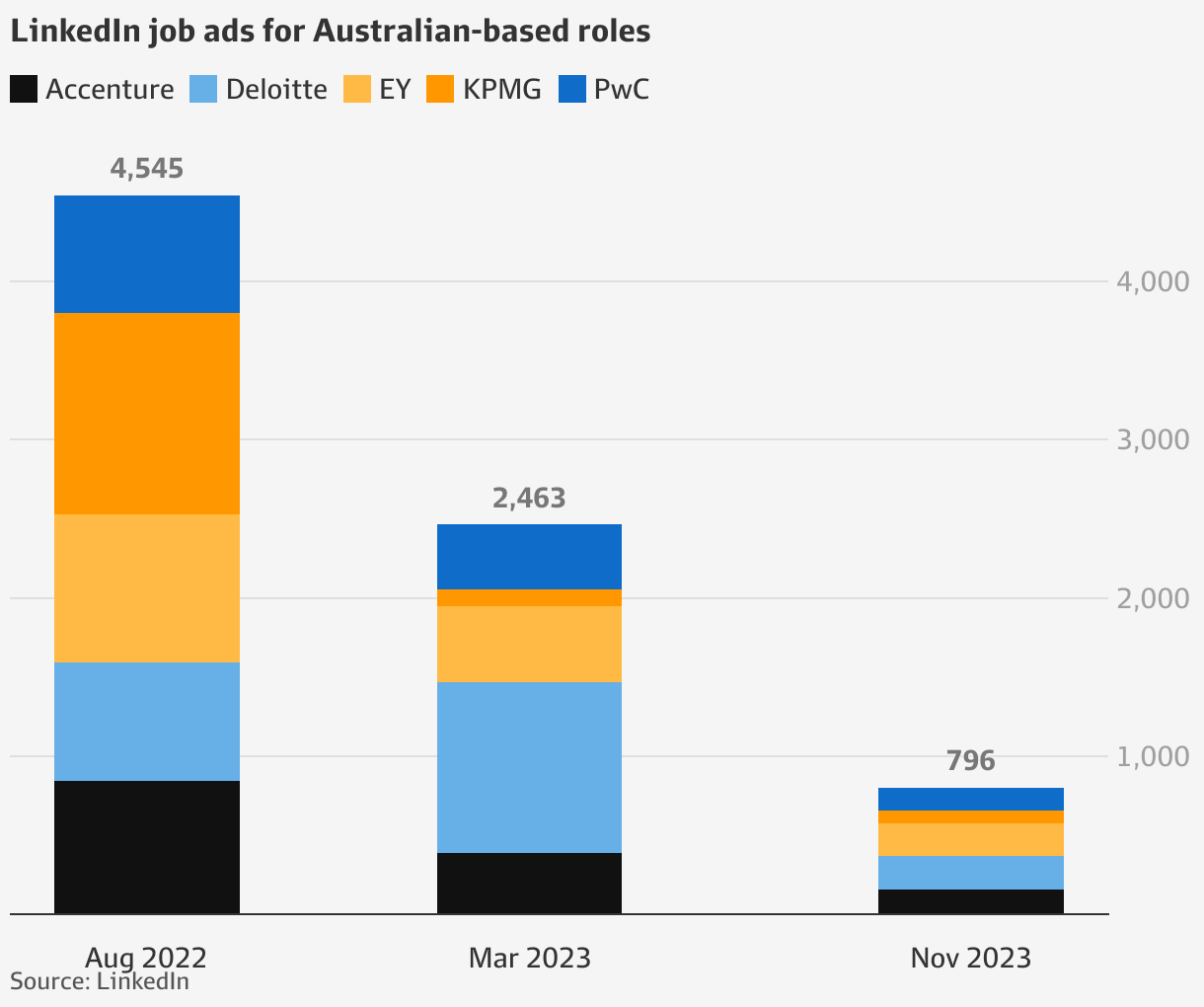 Scandal Hit Pw C Shrinks Global Footprint Exits From More Than A Dozen Countries
Apr 29, 2025
Scandal Hit Pw C Shrinks Global Footprint Exits From More Than A Dozen Countries
Apr 29, 2025 -
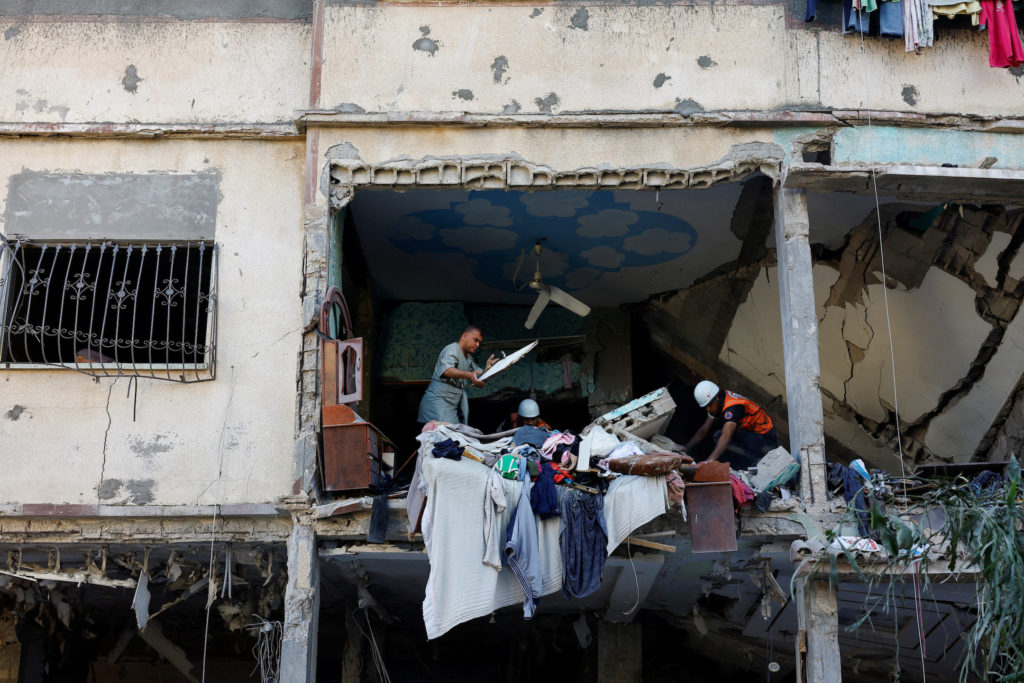 Pressure Builds On Israel To Address Gazas Humanitarian Emergency
Apr 29, 2025
Pressure Builds On Israel To Address Gazas Humanitarian Emergency
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Older Adults And You Tube A Growing Trend Of Classic Show Viewing
Apr 29, 2025
Older Adults And You Tube A Growing Trend Of Classic Show Viewing
Apr 29, 2025
