The Fed's Stance On Interest Rate Cuts: A Comparative Analysis
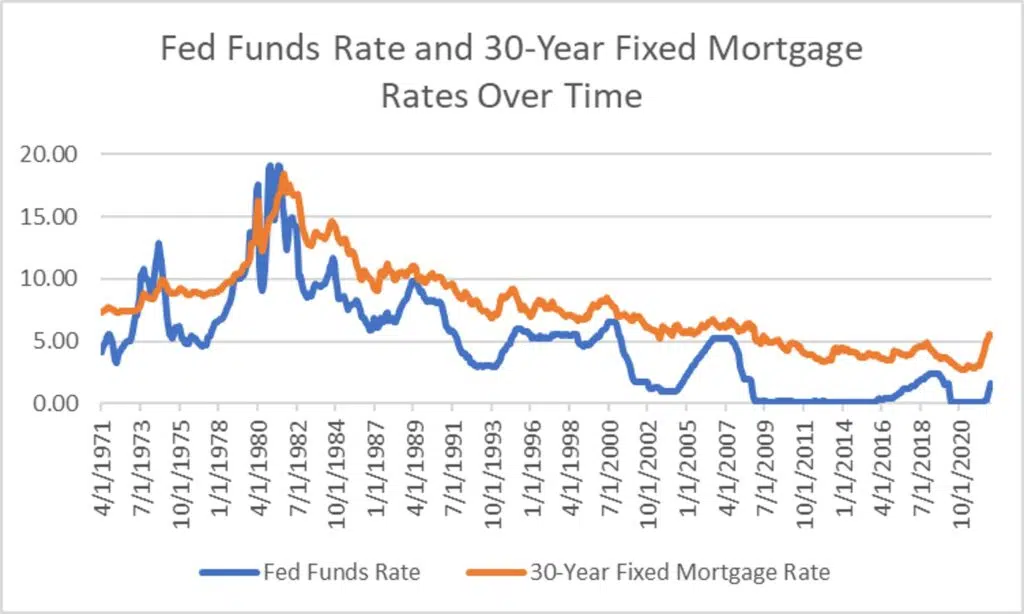
Table of Contents
<p>The Federal Reserve's decisions regarding <strong>Fed interest rate cuts</strong> significantly impact the US and global economy. These adjustments to the benchmark interest rates, a key component of monetary policy, ripple through financial markets and influence borrowing costs, investment decisions, and overall economic growth. This article provides a comparative analysis of the Fed's stance on interest rate cuts across different economic periods, examining the factors influencing these decisions and their subsequent effects. We'll explore the historical context, current economic indicators, and potential future implications of the Fed's interest rate policy, including considerations of inflation, recession risks, and quantitative easing.</p>
<h2>Historical Context: Examining Past Interest Rate Cuts by the Fed</h2>
<h3>The Dot-Com Bubble and 2001 Recession:</h3>
<p>The bursting of the dot-com bubble in 2000 led to a significant economic slowdown, culminating in a mild recession in 2001. In response, the Fed implemented a series of aggressive <strong>interest rate cuts</strong>, lowering the federal funds rate from 6.5% in January 2001 to 1.75% by the end of the year. This proactive approach aimed to stimulate borrowing and investment, thereby boosting economic activity.</p>
<ul> <li><strong>Aggressive rate cuts:</strong> The Fed's rapid reduction of interest rates was unprecedented at the time.</li> <li><strong>Effectiveness of the policy:</strong> While the rate cuts helped to mitigate the severity of the recession, the recovery was relatively slow.</li> <li><strong>Economic recovery timeline:</strong> The economy began to recover gradually in 2002, but the full impact of the rate cuts was felt over several years. </li> </ul>
<p>The 2001 experience highlighted the complex relationship between <strong>interest rate cuts</strong> and asset bubbles. While rate cuts can stimulate growth, they can also contribute to inflating asset prices if not carefully managed, potentially leading to future instability.</p>
<h3>The 2008 Financial Crisis and the Great Recession:</h3>
<p>The 2008 financial crisis presented an even greater challenge. The collapse of the housing market triggered a global financial panic, leading to the most severe recession since the Great Depression. The Fed responded with unprecedented measures, including slashing <strong>interest rate</strong>s to near zero and implementing quantitative easing (QE).</p>
<ul> <li><strong>Near-zero interest rates:</strong> The federal funds rate was reduced to a target range of 0-0.25%.</li> <li><strong>Quantitative easing (QE):</strong> The Fed purchased large quantities of government bonds and mortgage-backed securities to inject liquidity into the financial system.</li> <li><strong>Effectiveness of unconventional monetary policy:</strong> While QE and near-zero rates prevented a complete collapse of the financial system, the economic recovery was slow and uneven.</li> </ul>
<p>The 2008 crisis demonstrated the limitations of traditional monetary policy tools during a severe financial crisis. The reliance on unconventional measures like QE highlighted the need for a broader range of policy responses in times of extreme economic stress.</p>
<h3>Post-2008 Recovery and Gradual Rate Hikes:</h3>
<p>Following the Great Recession, the Fed gradually increased <strong>interest rates</strong>, a process known as monetary policy normalization. This cautious approach aimed to balance economic growth with concerns about inflation.</p>
<ul> <li><strong>Factors influencing rate hikes:</strong> The Fed considered factors such as unemployment, inflation, and economic growth projections.</li> <li><strong>Concerns about inflation:</strong> The gradual approach was intended to avoid triggering runaway inflation.</li> <li><strong>Economic growth projections:</strong> The Fed aimed to support sustainable economic growth without overheating the economy.</li> </ul>
<p>The post-2008 period showed the challenges of unwinding unconventional monetary policies and managing the economy during a period of slow but steady recovery. Finding the right balance between stimulating growth and controlling inflation remains a central challenge for central bankers.</p>
<h2>Current Economic Landscape and the Fed's Current Stance</h2>
<h3>Inflationary Pressures and Interest Rate Decisions:</h3>
<p>Currently, inflation is a major concern. High inflation rates influence the Fed's decisions regarding <strong>interest rate cuts</strong>. The Fed closely monitors indicators like the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) to assess inflationary pressures.</p>
<ul> <li><strong>CPI and PPI data:</strong> These indices provide crucial insights into price changes across various goods and services.</li> <li><strong>Inflation targets:</strong> The Fed typically aims for a 2% inflation target.</li> <li><strong>Potential for further interest rate hikes or cuts:</strong> The Fed's response to inflation will likely involve adjusting interest rates, potentially further hikes or, if inflation falls significantly, cuts.</li> </ul>
<p>The trade-off between controlling inflation and supporting economic growth is a constant balancing act for the Fed. High inflation erodes purchasing power, while aggressive rate hikes can slow down economic activity, potentially leading to a recession.</p>
<h3>Employment Data and its Influence on Interest Rate Policy:</h3>
<p>The unemployment rate is another critical factor influencing the Fed's <strong>interest rate</strong> decisions. A strong labor market, characterized by low unemployment and robust job growth, can support higher interest rates. Conversely, high unemployment may necessitate <strong>interest rate cuts</strong> to stimulate job creation.</p>
<ul> <li><strong>Job growth figures:</strong> These figures provide insights into the health of the labor market.</li> <li><strong>Wage growth:</strong> Rapid wage growth can fuel inflation, influencing the Fed's policy decisions.</li> <li><strong>Labor market dynamics:</strong> The Fed carefully analyzes the overall dynamics of the labor market to inform its policy choices.</li> </ul>
<p>The relationship between employment and <strong>interest rate</strong> policy is complex. The Fed aims to achieve full employment without fueling excessive inflation.</p>
<h3>Global Economic Conditions and Their Impact on the Fed:</h3>
<p>The US economy is deeply intertwined with the global economy. Global economic events, such as geopolitical instability or disruptions to global supply chains, can significantly impact the Fed's <strong>interest rate</strong> decisions.</p>
<ul> <li><strong>Geopolitical risks:</strong> International conflicts and political uncertainty can create economic volatility.</li> <li><strong>Global supply chains:</strong> Disruptions to global supply chains can drive up prices and fuel inflation.</li> <li><strong>International trade relations:</strong> Trade wars and protectionist policies can have a significant impact on global economic growth.</li> </ul>
<p>The interconnectedness of the global economy underscores the challenges faced by the Fed in managing domestic monetary policy. External shocks can require adjustments to <strong>interest rate</strong> policy to mitigate their impact on the US economy.</p>
<h2>Forecasting Future Interest Rate Movements</h2>
<h3>Potential Scenarios and Their Implications:</h3>
<p>Predicting future <strong>interest rate</strong> movements is challenging, requiring careful consideration of various economic indicators and potential risks. Several scenarios are possible, each with different implications.</p>
<ul> <li><strong>Scenario planning:</strong> The Fed and economists develop various scenarios to assess potential outcomes.</li> <li><strong>Probabilistic forecasting:</strong> Sophisticated models are used to assign probabilities to different economic scenarios.</li> <li><strong>Sensitivity analysis:</strong> Economists test the robustness of their forecasts by varying key assumptions.</li> </ul>
<p>Analyzing these scenarios helps to assess the potential impact of different <strong>interest rate</strong> paths on various market sectors, including stocks, bonds, and real estate.</p>
<h3>The Role of Forward Guidance in Shaping Expectations:</h3>
<p>The Fed's communication strategy, including forward guidance, plays a crucial role in shaping market expectations regarding future <strong>interest rate</strong> decisions. Clear communication helps to manage market volatility and improve the effectiveness of monetary policy.</p>
<ul> <li><strong>Fed statements:</strong> Official statements from the Fed provide insights into its policy intentions.</li> <li><strong>Press conferences:</strong> Press conferences by the Fed chair provide opportunities for clarifying policy decisions and expectations.</li> <li><strong>Economic projections:</strong> The Fed releases economic projections that outline its assessment of the economic outlook.</li> </ul>
<p>Transparency and clear communication are essential for the Fed to effectively manage market expectations and maintain stability in the financial system. Uncertainty about future <strong>interest rate</strong> policies can lead to market volatility, hindering economic growth.</p>
<h2>Conclusion</h2>
<p>The Federal Reserve's stance on <strong>interest rate cuts</strong> is a complex issue, shaped by a multitude of economic factors. A comparative analysis of past decisions reveals the challenges of managing the economy through monetary policy, particularly during times of crisis. Examining the current economic landscape and forecasting future movements allows for a more nuanced understanding of the Fed’s likely actions regarding <strong>interest rate</strong> adjustments, whether hikes or cuts. Staying informed about the Fed's <strong>interest rate policy</strong> is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike. To remain updated on the latest developments concerning <strong>Fed interest rate cuts</strong> and their implications, continue to follow reliable financial news sources and analyses. Understanding the intricacies of the Fed's <strong>interest rate</strong> decisions is key to navigating the ever-changing economic landscape. Careful consideration of <strong>Fed interest rate cuts</strong> and their impact on various sectors is crucial for informed decision-making.</p>

Featured Posts
-
 Proposed Changes To Bond Forward Regulations For Indian Insurers
May 09, 2025
Proposed Changes To Bond Forward Regulations For Indian Insurers
May 09, 2025 -
 Liam Lawsons Future Uncertain As Colapinto Rises
May 09, 2025
Liam Lawsons Future Uncertain As Colapinto Rises
May 09, 2025 -
 Materialist Premiere Dakota Johnson And Family Show Support
May 09, 2025
Materialist Premiere Dakota Johnson And Family Show Support
May 09, 2025 -
 Police Misconduct Meeting Scheduled Amid Nottingham Attacks Investigation
May 09, 2025
Police Misconduct Meeting Scheduled Amid Nottingham Attacks Investigation
May 09, 2025 -
 Vegas Golden Nayts Pobedil Minnesotu V Overtayme Pley Off
May 09, 2025
Vegas Golden Nayts Pobedil Minnesotu V Overtayme Pley Off
May 09, 2025
