Trade Disruptions: How The Bubble Blaster Crisis Affects Chinese Exports
Table of Contents
Impact on Specific Export Sectors
The COVID-19 pandemic severely impacted numerous export sectors in China. The ripple effect was felt across global supply chains, leading to significant challenges for Chinese businesses.
Electronics and Technology Exports
The electronics and technology sector, a major contributor to Chinese exports, faced considerable difficulties. The pandemic caused widespread supply chain disruptions, affecting the production and export of various goods.
- Specific products affected: Smartphones, laptops, computers, and other electronic components experienced production delays and shipping bottlenecks.
- Disruption in component supply: Lockdowns in various regions hampered the supply of crucial components, leading to production halts and shortages.
- Increased production costs: The disruption in supply chains, coupled with increased transportation costs, significantly increased the cost of production.
- Delays in shipping: Port congestion and reduced shipping capacity caused significant delays in the delivery of goods to global markets. According to a report by the World Trade Organization, global trade volumes fell by 5.3% in 2020.
Textile and Garment Exports
The textile and garment industry, another significant export sector for China, experienced substantial challenges due to the pandemic. Lockdowns, labor shortages, and transportation difficulties severely hampered production and export activities.
- Impact on specific garment types: Production of various garment types, particularly those requiring intricate labor, faced significant delays.
- Order cancellations: Many international buyers cancelled orders due to decreased demand and uncertainty in the global market.
- Factory closures: Numerous factories were forced to temporarily or permanently close due to lockdowns and economic hardship.
- Effects on SMEs: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the textile and garment sector were particularly vulnerable, facing financial difficulties and struggling to adapt to the changing market conditions.
Other Affected Sectors
Beyond electronics and textiles, other major export sectors in China also faced significant challenges.
- Machinery: The pandemic disrupted global supply chains for machinery components, leading to production delays and increased costs.
- Automotive parts: Similar to electronics, the automotive parts sector experienced shortages of key components, impacting production and delivery timelines.
- Agricultural products: Restrictions on transportation and border closures disrupted the export of agricultural products, affecting both producers and consumers globally.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Logistics Challenges
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, causing significant disruptions and logistical challenges for Chinese exporters.
Port Congestion and Shipping Delays
Port congestion became a major issue globally, particularly in China. Lockdowns and health protocols slowed down port operations, leading to massive shipping delays and increased freight costs.
- Examples of specific ports affected: Major ports in China and other countries experienced significant congestion, leading to lengthy delays in cargo handling.
- Increased shipping rates: The shortage of shipping containers and increased demand led to a substantial surge in shipping rates, increasing the cost of exports.
- Longer transit times: Delays at ports and reduced shipping capacity resulted in significantly longer transit times for goods.
- Impact on just-in-time manufacturing: The disruptions severely impacted just-in-time manufacturing models, which rely on timely delivery of components.
Raw Material Shortages
The pandemic also caused shortages of raw materials essential for Chinese manufacturing. Lockdowns, disruptions in transportation, and factory closures hampered the supply of these crucial inputs.
- Examples of specific raw materials affected: Various raw materials, including metals, plastics, and chemicals, experienced shortages, impacting production.
- Price increases: The scarcity of raw materials led to significant price increases, further adding to the cost of production.
- Alternative sourcing strategies: Many Chinese manufacturers were forced to explore alternative sourcing strategies, adding complexity and cost.
- Impact on production capacity: The shortage of raw materials significantly reduced the production capacity of numerous factories.
Economic and Political Implications
The COVID-19 pandemic had profound economic and geopolitical implications for China and the global economy.
Impact on Chinese GDP Growth
The disruption in exports significantly impacted China's overall economic growth. The export sector's contribution to the GDP experienced a considerable decline.
- Estimate of potential decrease in GDP growth: The pandemic caused a significant drop in China's GDP growth in 2020.
- Government's response to the crisis: The Chinese government implemented various stimulus packages and support measures to mitigate the economic impact.
- Support measures for affected businesses: The government offered financial assistance and tax breaks to support businesses struggling with the pandemic's effects.
Geopolitical Consequences
The pandemic highlighted the interconnectedness of global supply chains and the geopolitical implications of trade disruptions.
- Potential trade wars: The pandemic exacerbated existing trade tensions between countries, potentially leading to trade wars or protectionist measures.
- Diversification of supply chains: Many countries are now actively pursuing strategies to diversify their supply chains and reduce dependence on any single country.
- Impact on China's position in the global economy: The pandemic’s effects challenged China's position as a dominant player in global manufacturing and exports.
Conclusion: Navigating Trade Disruptions Caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic dealt a significant blow to Chinese exports, causing widespread supply chain disruptions, logistical challenges, and significant economic consequences. The impact was felt across numerous sectors, from electronics and textiles to machinery and agriculture. Challenges included port congestion, shipping delays, raw material shortages, and increased production costs. The pandemic also highlighted the need for greater resilience and diversification in global supply chains. Understanding the long-term effects of this crisis on Chinese exports is crucial for businesses involved in global trade. Stay updated on the latest developments and adapt your strategies accordingly to navigate these trade disruptions. Proactive risk management, diversification of supply sources, and technological advancements will be essential for businesses to thrive in this evolving global landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Is Palantir Stock A Buy Right Now A Comprehensive Analysis
May 09, 2025
Is Palantir Stock A Buy Right Now A Comprehensive Analysis
May 09, 2025 -
 Elon Musk Net Worth Dips Impact Of Tesla Stock And Economic Headwinds
May 09, 2025
Elon Musk Net Worth Dips Impact Of Tesla Stock And Economic Headwinds
May 09, 2025 -
 Pam Bondis Response To Congressman Comers Epstein Files Accusations
May 09, 2025
Pam Bondis Response To Congressman Comers Epstein Files Accusations
May 09, 2025 -
 Young Thugs Back Outside Album Rollout Anticipation Builds
May 09, 2025
Young Thugs Back Outside Album Rollout Anticipation Builds
May 09, 2025 -
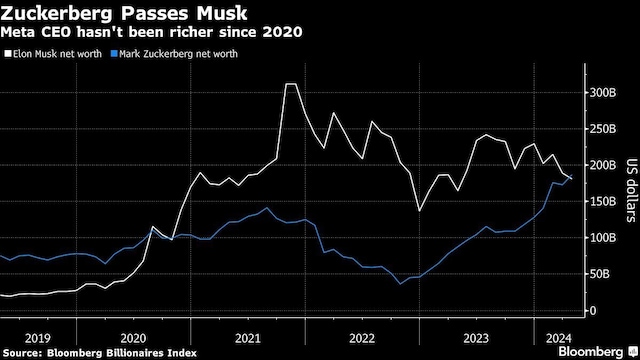 How Much Wealth Did Musk Bezos And Zuckerberg Lose Since Trumps Inauguration
May 09, 2025
How Much Wealth Did Musk Bezos And Zuckerberg Lose Since Trumps Inauguration
May 09, 2025
