Why Automating Nike Sneaker Production Is Difficult

Table of Contents
The Complexity of Nike Sneaker Designs
Nike's success hinges on its diverse range of sneaker styles, each a testament to innovative design and meticulous craftsmanship. This very diversity, however, is a major obstacle to automation. Automating a process that handles a single, simple design is relatively straightforward. However, Nike's production lines must accommodate a vast array of styles, each with its own unique features.
- Different stitching patterns and techniques: From the simple to the incredibly intricate, stitching variations demand adaptable robotic systems capable of handling diverse thread types and tensions.
- Unique material combinations (leather, mesh, synthetic fabrics): The varied properties of leather, mesh, synthetic fabrics, and other materials require specialized handling and processing techniques, making universal automation difficult.
- Complex sole designs and construction: The soles of Nike sneakers often incorporate multiple layers, intricate geometric patterns, and advanced cushioning technologies, posing significant challenges for automated assembly.
- Varied colorways and customized options: The ability to personalize sneakers with custom colors and designs further complicates the automation process, requiring flexible and adaptable systems. Mass customization adds another layer of complexity.
Material Diversity and Handling Challenges
The sheer variety of materials used in Nike sneaker production is another significant hurdle. From supple leathers and breathable textiles to advanced foams and durable synthetics, the properties of these materials differ widely. This diversity presents a formidable challenge for automated systems.
- Different material thicknesses and textures require specialized handling: Robots need to be programmed to handle delicate materials without damage while also managing thicker, more robust components.
- Automation needs to adapt to variations in material properties: Slight inconsistencies in material thickness or texture can disrupt automated processes, leading to errors and inefficiencies.
- Precise cutting and placement are essential and difficult to automate perfectly: Automated cutting systems must achieve exceptional precision to minimize waste and ensure consistent product quality.
- Waste reduction is a significant challenge in automated material handling: Optimizing material usage and minimizing waste is crucial for sustainability and cost-effectiveness, adding complexity to automation efforts.
The Role of Human Craftsmanship and Quality Control
While automation can handle many aspects of sneaker production, certain tasks still require the dexterity, judgment, and experience of skilled human workers. The subtle nuances of craftsmanship and the need for meticulous quality control pose significant challenges to complete automation.
- Fine motor skills required for intricate stitching and assembly: Some stitching and assembly tasks require a level of precision and dexterity that current robotic systems struggle to replicate.
- Visual inspection by human experts remains crucial for quality assurance: Identifying subtle defects or inconsistencies in materials and construction often requires the keen eye and judgment of experienced human inspectors.
- Subjectivity in judging aesthetic quality: Assessing the aesthetic appeal of a finished product involves subjective judgments that are difficult to program into an automated system.
- Difficulty in automating the detection of inconsistencies in materials and construction: Even minor variations in material quality or construction can affect the final product, making automated quality control a complex undertaking.
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI) Considerations
Implementing automation in shoe manufacturing requires a substantial upfront investment. The cost of specialized robotics, automated assembly lines, and the necessary software and training can be prohibitive for many companies. Therefore, a careful assessment of the potential return on investment (ROI) is essential.
- High cost of specialized robotics and automation equipment: The initial investment for advanced robotics and automation systems can be extremely high.
- Need for extensive retooling and retraining of workers: Adapting existing factories and retraining workers to operate and maintain automated systems requires significant resources.
- Potential for downtime and repair costs: Automated systems are susceptible to malfunctions and downtime, leading to potential repair and maintenance costs.
- Uncertainty in the long-term economic benefits of automation: The long-term economic viability of automated sneaker production is uncertain and depends on various factors, including labor costs, production volumes, and technological advancements.
Ethical and Social Implications of Automation
The automation of Nike sneaker production, like any major technological shift, has significant ethical and social implications. The potential displacement of workers in manufacturing communities needs careful consideration.
- Potential job losses for factory workers: Automation could lead to job losses in factories that currently rely on manual labor.
- Need for investment in worker retraining and upskilling programs: To mitigate the negative impact of job displacement, investment in retraining and upskilling programs is crucial.
- Social consequences of job displacement in manufacturing communities: Job losses can have devastating consequences for individuals and communities that rely on manufacturing jobs.
- Ethical considerations surrounding the use of automation in global supply chains: Ethical concerns arise about the impact of automation on workers in different parts of the global supply chain.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Challenges of Automating Nike Sneaker Production
Automating Nike sneaker production presents a complex array of challenges. From the intricate designs and diverse materials to the crucial role of human craftsmanship and quality control, the path to complete automation is fraught with obstacles. The high cost of implementation and the potential ethical and social consequences further complicate the picture. While automation will likely play an increasing role in the future of footwear manufacturing, fully automating the production of Nike sneakers remains a significant challenge. To learn more, research specific aspects of automation in the footwear industry, or explore the "future of footwear manufacturing" and "Nike automation challenges" for further insights.

Featured Posts
-
 Blue Origins Failures A Deeper Dive Than Katy Perrys Mishaps
Apr 22, 2025
Blue Origins Failures A Deeper Dive Than Katy Perrys Mishaps
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Cnn Exposes Just Contact Us Tik Toks Role In Tariff Avoidance Strategies
Apr 22, 2025
Cnn Exposes Just Contact Us Tik Toks Role In Tariff Avoidance Strategies
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Major Canadian Bread Price Fixing Case 500 Million Settlement Hearing In May
Apr 22, 2025
Major Canadian Bread Price Fixing Case 500 Million Settlement Hearing In May
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Actors And Writers Strike The Impact On Hollywood
Apr 22, 2025
Actors And Writers Strike The Impact On Hollywood
Apr 22, 2025 -
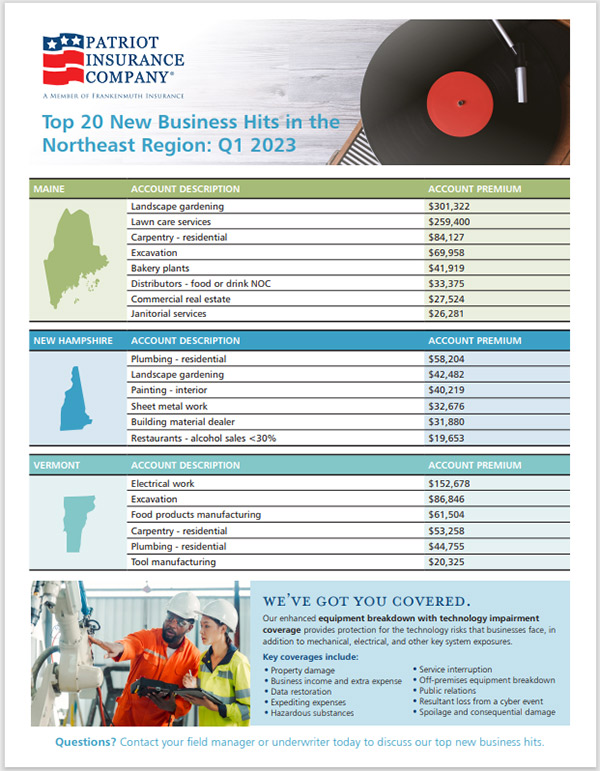 Where To Invest Mapping The Countrys Top New Business Locations
Apr 22, 2025
Where To Invest Mapping The Countrys Top New Business Locations
Apr 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Two Celtics Players Unexpectedly Drop 40 Points Each In Single Game
May 12, 2025
Two Celtics Players Unexpectedly Drop 40 Points Each In Single Game
May 12, 2025 -
 Celtics Magic Division Title Clinched With Dominant Performance
May 12, 2025
Celtics Magic Division Title Clinched With Dominant Performance
May 12, 2025 -
 Celtics Stunning Victory Clinches Division Crown
May 12, 2025
Celtics Stunning Victory Clinches Division Crown
May 12, 2025 -
 Payton Pritchard And The Sixth Man Of The Year Award Statistical Breakdown And Analysis
May 12, 2025
Payton Pritchard And The Sixth Man Of The Year Award Statistical Breakdown And Analysis
May 12, 2025 -
 Celtics Secure Division Title With Dominant Victory
May 12, 2025
Celtics Secure Division Title With Dominant Victory
May 12, 2025
