California's Coastal Crisis: The Devastating Effects Of Toxic Algae Blooms
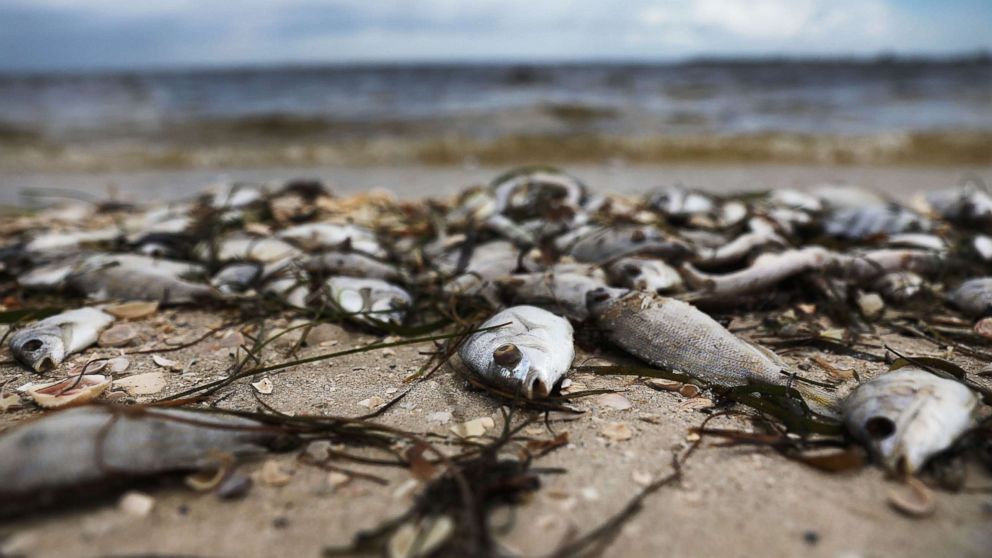

Table of Contents
The Science Behind California's Toxic Algae Blooms
What are Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs)?
Harmful algal blooms are rapid increases in the population of algae in water, often resulting in discoloration of the water (often referred to as red tides, although not all HABs are red). These blooms are caused by various species of microscopic algae, including Pseudo-nitzschia, a producer of domoic acid, and Alexandrium, which produces saxitoxin. Several factors contribute to HAB formation:
- Nutrient Runoff: Excess nutrients from agricultural fertilizers, sewage, and stormwater runoff act as potent fertilizers, fueling algal growth.
- Warming Ocean Temperatures: Climate change is leading to warmer ocean temperatures, creating ideal conditions for the growth of certain toxic algae species.
- Ocean Currents and Upwelling: Changes in ocean currents and upwelling events can bring nutrient-rich waters to the surface, further stimulating algal growth.
Scientific research and monitoring efforts in California, including satellite imagery, water sampling, and toxin analysis, are crucial for tracking and predicting HAB events. These efforts provide valuable data for public health warnings and management strategies.
- Examples of toxic algae species and their toxins:
- Pseudo-nitzschia: Produces domoic acid, causing amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP).
- Alexandrium: Produces saxitoxins, causing paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP).
- Dinophysis: Produces okadaic acid, causing diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP).
The Impact on Marine Ecosystems
The effects of HABs on California's marine ecosystems are profound. Massive fish kills occur when toxins released by algae directly poison fish or deplete oxygen levels in the water. Shellfish, which filter feed, accumulate high concentrations of toxins, leading to shellfish poisoning and impacting the entire food web. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification further exacerbate the problem, as toxins concentrate in the tissues of organisms higher up the food chain.
- Specific examples of marine species affected:
- Sea lions: Suffer neurological damage and mortality from domoic acid poisoning.
- Whales: Experience similar neurological problems and strandings due to toxic algae exposure.
- Seabirds: Can be poisoned by consuming contaminated fish or shellfish.
Numerous marine life die-offs in California have been directly linked to toxic algae blooms, underscoring the devastating impact of these events on marine biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Human Health Impacts of Toxic Algae Blooms in California
Risks to Human Health
Humans are exposed to HAB toxins primarily through the consumption of contaminated seafood (shellfish, finfish) and through recreational water contact (swimming, surfing). Exposure can lead to a range of health problems:
- Neurotoxic Shellfish Poisoning (NSP): Caused by domoic acid, resulting in nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and potentially severe neurological symptoms.
- Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning (ASP): Also caused by domoic acid, leading to short-term memory loss and other neurological impairments.
- Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP): Caused by saxitoxins, causing numbness, tingling, paralysis, and potentially respiratory failure.
- Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP): Caused by okadaic acid, resulting in diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.
Public health agencies in California play a critical role in monitoring HAB events, testing shellfish for toxins, and issuing public health advisories to protect consumers.
Economic Consequences for Coastal Communities
The economic impact of HABs on California's coastal communities is substantial. Closures of shellfish harvesting areas result in significant financial losses for the fishing industry and related businesses. Tourism and recreational activities are also affected, as beaches may be closed due to harmful algal blooms or concerns about seafood safety. The costs associated with monitoring, research, and public health initiatives related to HABs further strain resources.
- Examples of economic losses:
- Reduced shellfish harvests leading to job losses in fishing communities.
- Cancellation of tourism events and decreased visitor spending.
- Increased healthcare costs associated with treating HAB-related illnesses.
Mitigation and Solutions for Toxic Algae Blooms in California
Reducing Nutrient Runoff
Reducing nutrient pollution is crucial for mitigating HABs. This involves implementing strategies to decrease agricultural fertilizer runoff and improve wastewater treatment. Sustainable agricultural practices, such as precision fertilizer application and cover cropping, can minimize nutrient losses. Investing in advanced wastewater treatment technologies is equally important. Strong government regulations and incentives can encourage the adoption of these practices.
- Examples of successful pollution reduction programs:
- Implementation of stricter regulations on fertilizer use in agricultural areas.
- Upgrades to wastewater treatment plants to remove excess nutrients.
- Investment in riparian buffer zones to filter runoff before it reaches waterways.
Climate Change Adaptation
Climate change is exacerbating the frequency and intensity of HABs. Adapting to this changing reality requires a multifaceted approach:
- Improved Forecasting and Monitoring: Investing in advanced monitoring technologies and predictive models to provide timely warnings.
- Early Warning Systems: Developing and implementing effective early warning systems to alert communities and stakeholders.
- Resilience Building: Helping coastal communities build resilience to the economic and social impacts of HABs.
Climate change mitigation efforts are crucial for reducing the long-term threat posed by HABs. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is paramount to slowing the warming of ocean waters and thus reducing favorable conditions for toxic algae growth.
Conclusion
Toxic algae blooms in California pose a significant and multifaceted threat to the state's coastal environment, human health, and economy. Understanding the complex interplay of factors driving HABs and implementing effective mitigation strategies is crucial for protecting this valuable resource. By reducing nutrient runoff, adapting to climate change, investing in research and monitoring, and fostering collaborative efforts among scientists, policymakers, and communities, California can work towards minimizing the devastating effects of toxic algae blooms and ensuring the long-term health of its coast. Let's work together to protect California's coast from the damaging impacts of toxic algae blooms in California! Learn more about how you can contribute to HAB prevention and report any suspected blooms to your local authorities. Take action and be a part of the solution against these devastating harmful algal blooms!

Featured Posts
-
 Norrie Triumphs Over Medvedev At French Open Djokovic Proceeds
May 30, 2025
Norrie Triumphs Over Medvedev At French Open Djokovic Proceeds
May 30, 2025 -
 Competition Bureaus Case Against Google A Constitutional Battle
May 30, 2025
Competition Bureaus Case Against Google A Constitutional Battle
May 30, 2025 -
 Gorillaz To Play First Three Albums Live In London One Off Shows Announced
May 30, 2025
Gorillaz To Play First Three Albums Live In London One Off Shows Announced
May 30, 2025 -
 Post Credits Scenes Are They Worth It In Marvel And Sinner
May 30, 2025
Post Credits Scenes Are They Worth It In Marvel And Sinner
May 30, 2025 -
 Live Now Pay Later Your Guide To Smart Spending
May 30, 2025
Live Now Pay Later Your Guide To Smart Spending
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ai And Learning Navigating The Ethical Challenges
May 31, 2025
Ai And Learning Navigating The Ethical Challenges
May 31, 2025 -
 Up To 30 Off Lavish Hotels This Spring Limited Time Offer
May 31, 2025
Up To 30 Off Lavish Hotels This Spring Limited Time Offer
May 31, 2025 -
 Responsible Ai Acknowledging The Limitations Of Ai Learning
May 31, 2025
Responsible Ai Acknowledging The Limitations Of Ai Learning
May 31, 2025 -
 Book Now 30 Off Luxurious Spring Hotel Packages
May 31, 2025
Book Now 30 Off Luxurious Spring Hotel Packages
May 31, 2025 -
 How Ai Learns And Doesn T A Guide To Responsible Implementation
May 31, 2025
How Ai Learns And Doesn T A Guide To Responsible Implementation
May 31, 2025
