Middle Managers: Bridging The Gap Between Leadership And Employees

Table of Contents
Effective Communication: The Cornerstone of Middle Management
Clear and open communication is paramount for successful middle managers. It's a two-way street, requiring both upward communication (relaying employee feedback to leadership) and downward communication (clearly conveying company goals and expectations to employees). This bidirectional flow is essential for building trust, maintaining morale, and driving productivity.
- Strategies for effectively communicating company goals and expectations to employees: Use clear, concise language; break down complex information into digestible chunks; use multiple communication channels (meetings, emails, intranet); provide opportunities for questions and clarification.
- Techniques for gathering and relaying employee feedback to upper management: Conduct regular team meetings; implement anonymous feedback mechanisms (surveys, suggestion boxes); actively listen to employee concerns; synthesize feedback accurately and objectively; advocate for your team's needs.
- The role of active listening in building trust and understanding: Pay attention to both verbal and non-verbal cues; ask clarifying questions; summarize to ensure understanding; show empathy and respect.
- Importance of transparency in maintaining morale and productivity: Be open and honest about company performance, challenges, and changes; explain the rationale behind decisions; address rumors and misinformation proactively.
- Examples of communication tools and strategies to improve flow: Regular team meetings, open-door policies, instant messaging platforms (Slack, Microsoft Teams), project management software (Asana, Trello), company-wide newsletters.
Team Building and Motivation: Fostering a Productive Workforce
Middle managers play a crucial role in creating a positive and productive work environment. This involves building strong teams, motivating employees, and recognizing their achievements. Effective delegation and mentorship are key components of this process.
- Strategies for building strong teams and fostering collaboration: Organize team-building activities; encourage open communication and collaboration; establish clear roles and responsibilities; create a shared sense of purpose; recognize and celebrate team accomplishments.
- Methods for motivating employees and recognizing achievements: Provide regular positive feedback; offer opportunities for professional development; reward exceptional performance; create a culture of appreciation and recognition; delegate tasks that challenge and engage employees.
- Effective delegation techniques and the importance of trust: Clearly define tasks and expectations; provide necessary resources and support; trust employees to perform their work; avoid micromanagement; provide regular check-ins without excessive oversight.
- Mentoring and developing employees' skills and careers: Identify employees' strengths and weaknesses; provide coaching and guidance; offer opportunities for skill development; support career advancement; act as a role model.
- Understanding different leadership styles and adapting to individual team needs: Employ a variety of leadership styles (transformational, transactional, servant leadership) depending on team dynamics and individual needs; be adaptable and flexible.
Performance Management and Accountability: Driving Results
Middle managers are directly responsible for ensuring their teams meet organizational objectives. This requires effective performance management, including setting clear goals, providing regular feedback, and holding team members accountable.
- Setting clear and measurable goals for teams and individuals: Use the SMART framework (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound); ensure alignment with overall organizational goals; involve team members in the goal-setting process.
- Implementing effective performance review processes: Conduct regular performance reviews; provide constructive feedback; document performance; identify areas for improvement; develop performance improvement plans.
- Providing constructive feedback and coaching for improvement: Focus on specific behaviors and results; offer specific examples; provide actionable suggestions for improvement; create a safe and supportive environment for feedback.
- Holding team members accountable for their performance: Establish clear expectations and consequences; monitor progress; address performance issues promptly and fairly; provide support and resources to help employees succeed.
- Using KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to track progress and identify areas for improvement: Identify relevant KPIs; track progress regularly; analyze data to identify trends and areas for improvement; use data to inform decision-making.
Problem-Solving and Conflict Resolution: Navigating Challenges
Middle managers frequently face workplace conflicts and challenges. Effective problem-solving and conflict resolution skills are crucial for maintaining a positive and productive work environment.
- Identifying and analyzing workplace conflicts: Recognize the signs of conflict; understand the root causes; gather information from all parties involved; remain neutral and objective.
- Developing effective conflict resolution strategies: Facilitate open communication; encourage collaboration; help parties find mutually acceptable solutions; mediate disputes; enforce company policies fairly.
- Making sound decisions under pressure: Gather relevant information; assess risks and benefits; consider different perspectives; make timely and decisive decisions; accept responsibility for the outcomes.
- Utilizing negotiation and mediation techniques: Help parties find common ground; identify areas of compromise; facilitate constructive dialogue; promote win-win solutions.
- Escalating issues appropriately when necessary: Know when to seek help from upper management or HR; document issues thoroughly; follow established escalation procedures.
Conclusion
Effective middle managers are essential for bridging the gap between leadership and employees. Their key responsibilities include fostering open communication, building strong teams, managing performance effectively, and resolving conflicts constructively. By mastering these skills, middle managers significantly contribute to overall organizational success and employee engagement. Invest in your middle managers today and strengthen the bridge between leadership and employee success. Learn more about effective middle management strategies and unlock your organization's full potential.

Featured Posts
-
 Decades Old School Desegregation Order Terminated A Turning Point
May 03, 2025
Decades Old School Desegregation Order Terminated A Turning Point
May 03, 2025 -
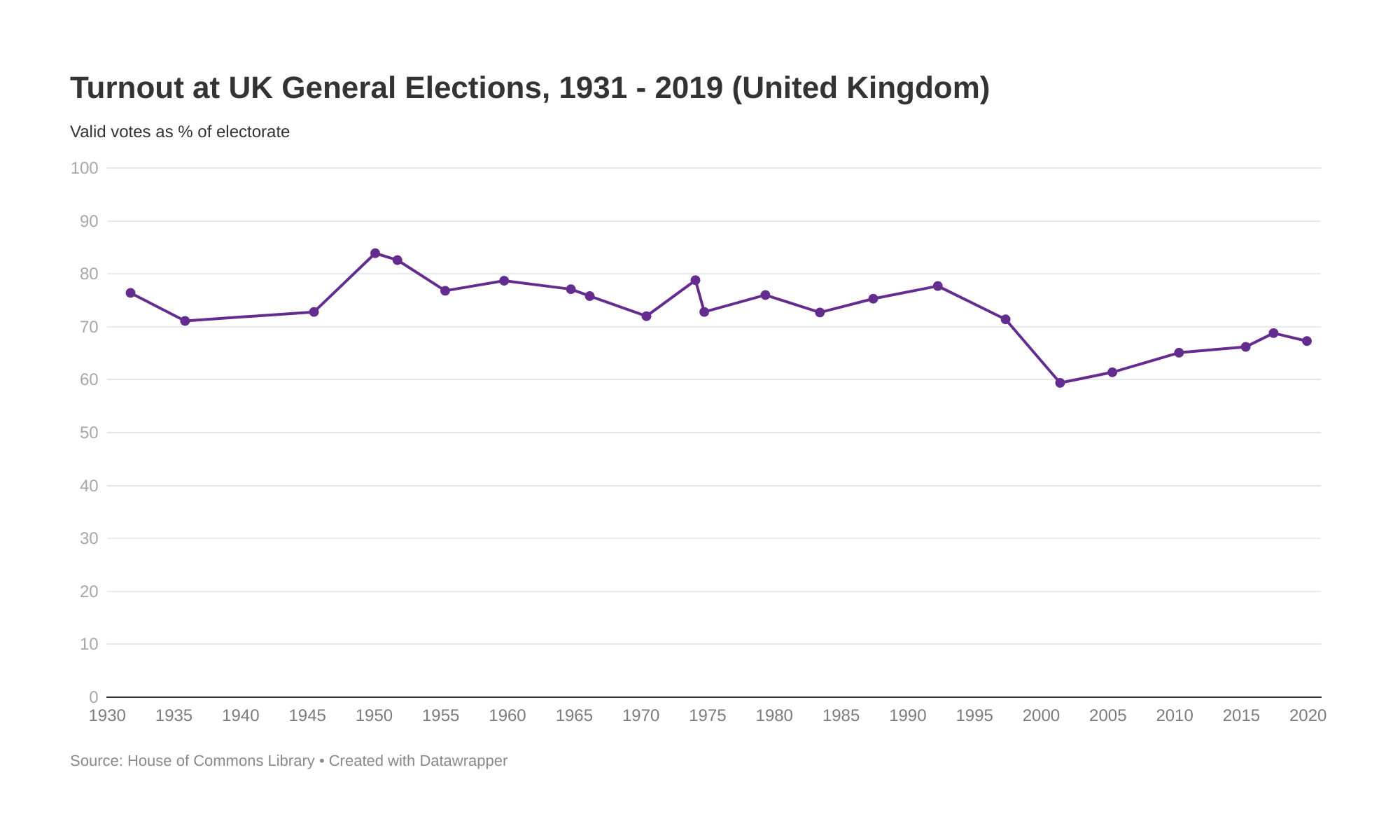 Florida And Wisconsin Election Results What The Turnout Reveals
May 03, 2025
Florida And Wisconsin Election Results What The Turnout Reveals
May 03, 2025 -
 Bidens Economic Policies Impact And Analysis Of Current Slowdown
May 03, 2025
Bidens Economic Policies Impact And Analysis Of Current Slowdown
May 03, 2025 -
 Enhanced Cloud Streaming On Play Station Portal A Wider Selection Of Classic Games
May 03, 2025
Enhanced Cloud Streaming On Play Station Portal A Wider Selection Of Classic Games
May 03, 2025 -
 Why Facts Alone Dont Defeat Misinformation According To Cnn Experts
May 03, 2025
Why Facts Alone Dont Defeat Misinformation According To Cnn Experts
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 45 000 Book Bookstores Remarkable Discovery
May 04, 2025
45 000 Book Bookstores Remarkable Discovery
May 04, 2025 -
 Thunderbolts A Deep Dive Into Marvels Latest Team
May 04, 2025
Thunderbolts A Deep Dive Into Marvels Latest Team
May 04, 2025 -
 Hidden Treasure Bookstore Uncovers 45 000 Rare Novel
May 04, 2025
Hidden Treasure Bookstore Uncovers 45 000 Rare Novel
May 04, 2025 -
 Analyzing Marvels Thunderbolts Success Or Failure
May 04, 2025
Analyzing Marvels Thunderbolts Success Or Failure
May 04, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Grand Theft Auto Vi Trailer New Insights
May 04, 2025
Analyzing The Grand Theft Auto Vi Trailer New Insights
May 04, 2025
