Record-Breaking Global Forest Loss: The Devastating Impact Of Wildfires
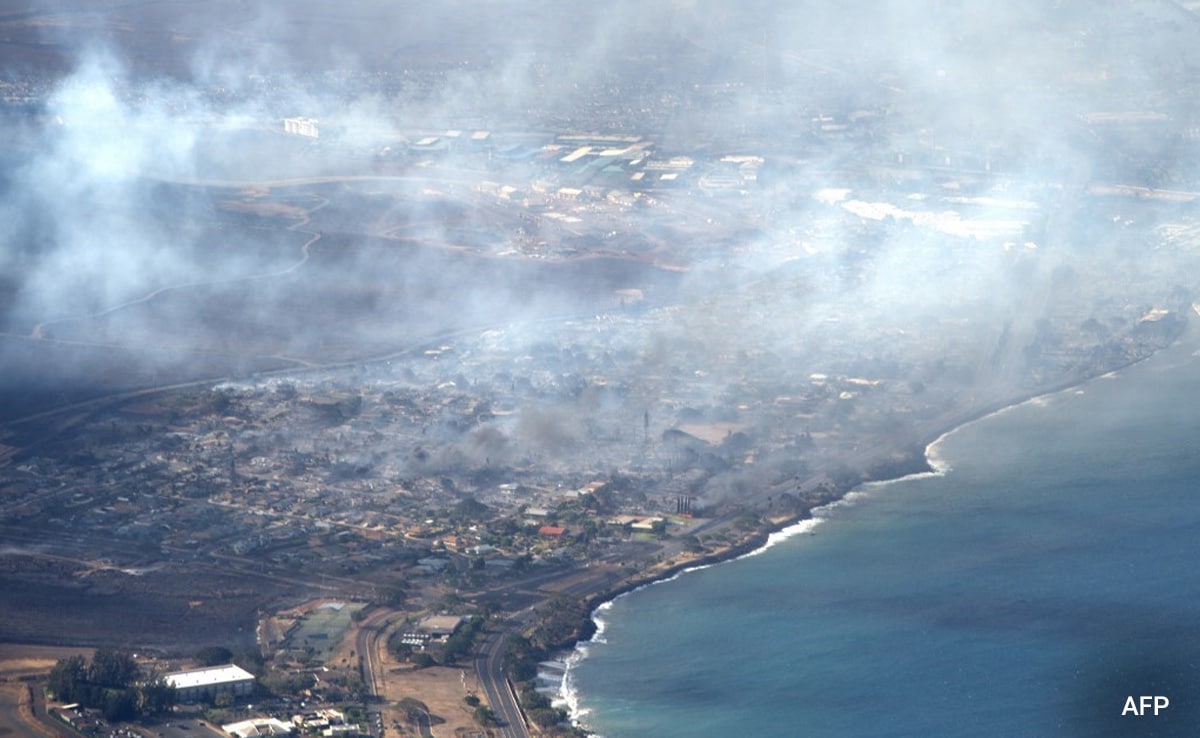

Table of Contents
The Scale of the Problem: Understanding Record Global Forest Loss
Global forest loss refers to the permanent removal of forest cover, resulting in a decline in forest area. The current rate is alarming, with millions of hectares lost annually. Recent years have shown a drastic increase, surpassing previous records by a significant margin. [Insert image/graph here showing the increase in global forest loss over the past decade]. This represents not just a loss of trees, but a loss of vital ecosystems.
- Regions experiencing significant loss: The Amazon rainforest, the boreal forests of Canada and Russia, and Indonesian rainforests are particularly hard hit.
- Types of forests affected: The impact extends across all types of forests, including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, and boreal forests, each with unique ecosystems and vital roles in the global environment.
- Economic consequences: The economic impact is substantial, affecting the timber industry, tourism, and countless livelihoods dependent on forest resources. Loss of timber revenue, decreased tourism, and the increased costs of fighting wildfires all contribute to a significant economic burden.
The Role of Wildfires in Global Forest Loss
The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires are a major driver of global forest loss. Climate change plays a significant role, creating conditions ripe for devastating fires through prolonged droughts, intense heatwaves, and altered weather patterns. Human activities, including deforestation for agriculture and unsustainable land management practices, further exacerbate the risk. Natural causes, such as lightning strikes, also contribute, but their impact is often magnified by the conditions created by climate change and human activity.
- Devastating wildfires: The recent wildfires in Australia (2019-2020), California (multiple years), and Siberia (ongoing) serve as stark examples of the scale and destructive power of these events.
- Climate change impact: Climate change is lengthening fire seasons, creating drier fuels, and increasing the intensity of wildfires, making them harder to contain and leading to greater areas of global forest loss.
- Human activities: Deforestation for agriculture, logging practices that leave behind flammable debris, and the expansion of human settlements into fire-prone areas all increase wildfire risk and contribute significantly to global forest loss.
The Devastating Consequences of Global Forest Loss
The consequences of global forest loss are far-reaching and devastating:
-
Biodiversity loss: Habitat destruction leads to species extinction and threatens countless others, disrupting delicate ecological balances.
-
Climate change exacerbation: Forests act as vital carbon sinks, absorbing atmospheric CO2. Their destruction releases stored carbon, accelerating climate change and contributing to a vicious cycle of increased wildfire risk. Reduced carbon sequestration further intensifies the greenhouse effect.
-
Social and economic consequences: Local communities reliant on forests for their livelihoods (e.g., subsistence farming, timber harvesting) face displacement, poverty, and food insecurity.
-
Examples of endangered species: Orangutans in Indonesia, numerous Amazonian bird species, and boreal forest mammals are among the countless species directly threatened by habitat loss.
-
Forests and carbon sequestration: Forests play a crucial role in regulating the global climate by absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide. Their loss significantly reduces this capacity, contributing to global warming.
-
Impact on local communities: Indigenous communities and other populations dependent on forests for their survival face significant challenges, including displacement, loss of traditional livelihoods, and increased vulnerability to climate change impacts.
Protecting Biodiversity Through Forest Conservation
Protecting biodiversity requires concerted conservation efforts. Successful strategies include establishing protected areas, implementing sustainable forestry practices, combating illegal logging, and promoting reforestation and afforestation initiatives. Organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), Greenpeace, and The Nature Conservancy are actively involved in global forest conservation efforts.
Combating Wildfires and Mitigating Global Forest Loss
Combating wildfires and reducing global forest loss requires a multi-pronged approach:
-
Wildfire prevention: Controlled burns (under careful management), improved forest management practices (reducing fuel loads), and community-based fire prevention programs are vital.
-
Early detection and response: Advanced technology, including satellite monitoring and early warning systems, is crucial for rapid response to emerging fires.
-
International cooperation: Global collaboration is essential to address this global challenge, sharing best practices, coordinating resources, and tackling deforestation at an international level.
-
Effective wildfire prevention techniques: Creating firebreaks, thinning dense forests, and implementing prescribed burns are essential strategies for reducing wildfire risk.
-
Technology in wildfire detection: Satellite imagery, drones, and advanced sensor technology significantly improve early detection capabilities.
-
International agreements: The Paris Agreement and other international agreements aim to reduce deforestation and promote sustainable forest management.
Conclusion
The record-breaking global forest loss due to wildfires is a catastrophic event with far-reaching consequences for biodiversity, climate change, and human societies. The urgency of the situation demands immediate and sustained action. We must invest in wildfire prevention and management, strengthen conservation efforts, and promote sustainable land use practices. By working together at local, national, and international levels, we can mitigate the devastating impacts of wildfires and reduce global forest loss. Learn more about the devastating impact of wildfires and take action to help prevent further global forest loss. Visit [link to relevant organization] today to discover how you can contribute.

Featured Posts
-
 Massachusetts Gun Trafficking Bust 100 Firearms Seized 18 Brazilians Charged
May 24, 2025
Massachusetts Gun Trafficking Bust 100 Firearms Seized 18 Brazilians Charged
May 24, 2025 -
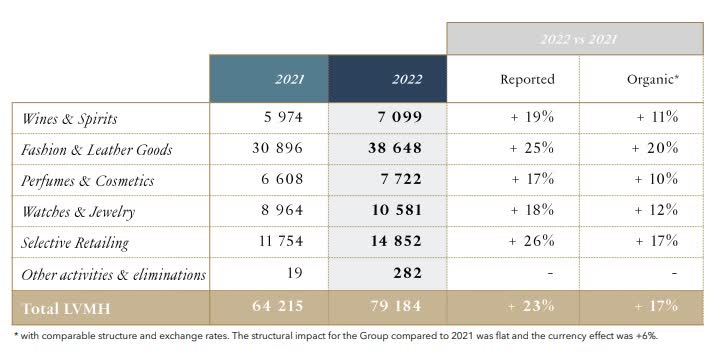 Lvmh Stock Drops After Missing Q1 Sales Targets
May 24, 2025
Lvmh Stock Drops After Missing Q1 Sales Targets
May 24, 2025 -
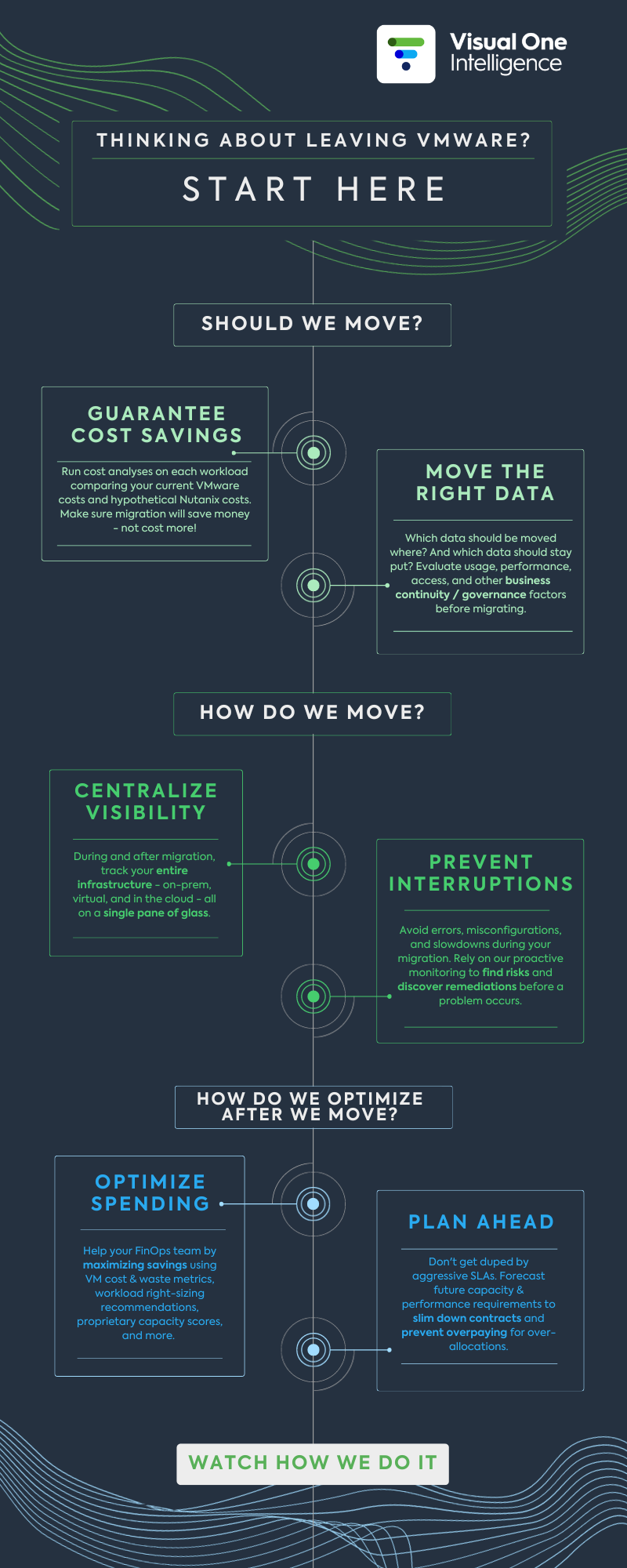 1 050 V Mware Price Increase At And Ts Outcry Against Broadcoms Acquisition
May 24, 2025
1 050 V Mware Price Increase At And Ts Outcry Against Broadcoms Acquisition
May 24, 2025 -
 Porsche Cayenne Gts Coupe Test I Recenzja Suv Marzen
May 24, 2025
Porsche Cayenne Gts Coupe Test I Recenzja Suv Marzen
May 24, 2025 -
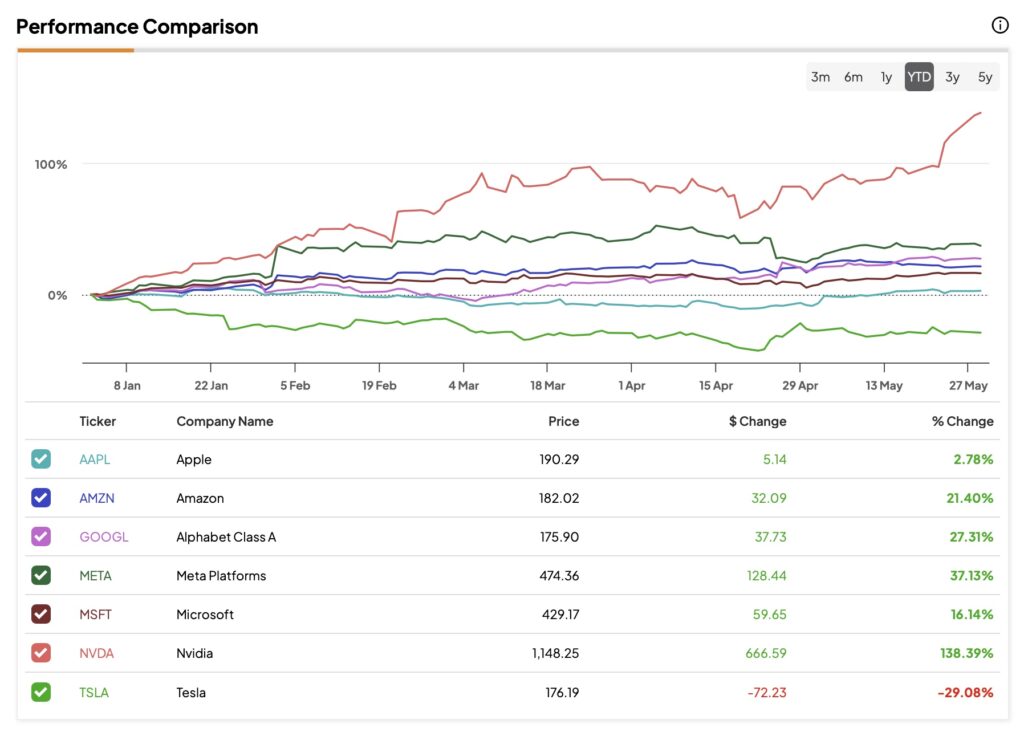 Apple Price Target Lowered But Is Wedbush Right To Remain Bullish
May 24, 2025
Apple Price Target Lowered But Is Wedbush Right To Remain Bullish
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Zekanin Sirri Burclar Ve Entelektueel Yetenekler
May 24, 2025
Zekanin Sirri Burclar Ve Entelektueel Yetenekler
May 24, 2025 -
 Dahilik Genleri Hangi Burclarda Goeruelueyor
May 24, 2025
Dahilik Genleri Hangi Burclarda Goeruelueyor
May 24, 2025 -
 Seytan Tueyuene Sahip Burclar Cekim Guecuenuen Analizi
May 24, 2025
Seytan Tueyuene Sahip Burclar Cekim Guecuenuen Analizi
May 24, 2025 -
 Horoscope Predictions For March 20 2025 5 Lucky Zodiac Signs
May 24, 2025
Horoscope Predictions For March 20 2025 5 Lucky Zodiac Signs
May 24, 2025 -
 Burclar Ve Zeka En Yueksek Iq Ya Sahip Burclar
May 24, 2025
Burclar Ve Zeka En Yueksek Iq Ya Sahip Burclar
May 24, 2025
