Westpac (WBC) Financial Report: Lower Profits Due To Margin Squeeze

Table of Contents
Detailed Analysis of Westpac's (WBC) Financial Performance
Westpac's (WBC) latest financial report paints a picture of reduced profitability, primarily driven by a shrinking net interest margin (NIM). Understanding the specifics of this decline is crucial to assessing the bank's overall financial health.
Net Interest Margin (NIM) Decline
The most significant finding is the noticeable contraction in Westpac's NIM. The report showed a [Insert Percentage]% decrease in NIM compared to the [Previous Quarter/Year], indicating a substantial decline in the difference between the interest the bank earns on loans and what it pays on deposits. This NIM compression is a direct result of interest rate sensitivity and reduced lending margins. The shrinking difference between lending and borrowing rates significantly impacts the bank's profitability.
Impact on Key Financial Metrics
The reduction in NIM had a ripple effect across other key financial metrics. We observed:
- Return on Equity (ROE): A [Insert Percentage]% decrease, reflecting lower returns on shareholder investments.
- Return on Assets (ROA): A [Insert Percentage]% drop, indicating less efficient asset utilization.
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): A decline of [Insert Percentage]%, impacting shareholder earnings directly.
These figures underscore the severity of the margin squeeze and its impact on Westpac's overall financial performance.
Comparison with Competitors
Comparing Westpac's performance to its major Australian banking competitors – ANZ, CBA (Commonwealth Bank of Australia), and NAB (National Australia Bank) – reveals a similar trend across the sector, although the degree of impact varies. While all banks experienced some level of NIM compression, Westpac's [Insert Comparative Data, e.g., percentage decline] highlights the challenges it faces compared to industry benchmarks in the current competitive landscape.
Factors Contributing to the Margin Squeeze
Several interconnected factors contributed to the margin squeeze experienced by Westpac (WBC) and the broader Australian banking sector.
Increased Competition
The Australian banking sector faces intensifying competition. The rise of fintech companies offering innovative and often cheaper financial products and services is disrupting traditional banking models. Furthermore, alternative lending options are becoming increasingly attractive to borrowers, further eroding traditional banks' market share and impacting lending margins. This competitive landscape puts pressure on traditional banks like Westpac to maintain or enhance their value propositions to retain and attract customers.
Rising Operating Costs
Westpac, like other banks, faces increasing operating costs. These include:
- Technology Investments: Significant expenditure on upgrading technology infrastructure to enhance digital banking capabilities and compete with fintechs.
- Regulatory Compliance: The ever-increasing regulatory burden necessitates substantial investments in compliance measures.
- Employee Expenses: Salary increases and the need to attract and retain skilled professionals contribute to higher operating costs.
These escalating costs directly reduce profitability, exacerbating the impact of the margin squeeze.
Interest Rate Environment
Fluctuations in interest rates significantly impact a bank's profitability. While rising interest rates initially seem beneficial, their impact on lending margins can be complex. The Reserve Bank of Australia's (RBA) monetary policy directly influences interest rate sensitivity. Rapid increases can lead to increased borrowing costs for customers, potentially impacting loan demand, and the speed at which these increases translate to lending rates can impact overall NIM. Similarly, falling rates can compress margins further.
Loan Growth and Portfolio Composition
The composition and growth of Westpac's loan portfolio play a critical role in its profitability. Slower loan growth or a shift towards lower-yielding loan products can negatively impact the NIM. Effective portfolio diversification and management of credit risk are essential for mitigating this risk.
Westpac's (WBC) Strategic Response to the Margin Squeeze
Westpac is actively responding to the margin squeeze through various strategic initiatives.
Cost-cutting Measures
To offset the impact of the margin squeeze, Westpac has implemented several cost-cutting measures. These include:
- Restructuring Initiatives: Reorganizing operations to improve efficiency and reduce redundancies.
- Branch Closures: Consolidating branches to reduce operational overhead.
- Efficiency Improvements: Implementing process improvements across various departments to minimize costs.
Investment in New Technologies
Westpac is investing heavily in digital transformation, including:
- AI Adoption: Leveraging artificial intelligence to enhance efficiency and customer service.
- Digital Banking: Expanding and improving its digital banking platform to improve customer experience and reduce operational costs.
Focus on Specific Market Segments
Westpac is focusing on specific high-margin customer segments and developing niche products tailored to meet their unique financial needs. This targeted approach aims to enhance profitability and increase its value proposition.
Future Outlook and Guidance
Westpac's future outlook and guidance remain cautious, reflecting the challenges posed by the margin squeeze and the competitive landscape. The bank's projections suggest a [Insert details from the report about future profitability and growth] outlook.
Conclusion: Understanding the Westpac (WBC) Financial Report and its Implications for Investors
Westpac's (WBC) recent financial report reveals a challenging environment for the Australian banking sector, characterized by a significant margin squeeze impacting profitability. Several factors, including increased competition, rising operating costs, and interest rate sensitivity, contributed to this decline. Westpac's strategic response, encompassing cost-cutting measures, investments in new technologies, and a focused approach to specific market segments, aims to mitigate these challenges. However, understanding these factors and their impact on key financial metrics, such as ROE, ROA, and EPS, is critical for investors seeking to make informed decisions. The implications for investors are significant, demanding careful monitoring of future Westpac (WBC) financial reports and analyses to assess the bank's ability to navigate this challenging period and achieve future growth. Stay informed about upcoming Westpac financial reports and conduct thorough WBC stock analysis to gain valuable Australian banking sector insights and make well-informed investment decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Aposta No Paulistao Corinthians Ou Santos Analise Das Casas De Apostas
May 05, 2025
Aposta No Paulistao Corinthians Ou Santos Analise Das Casas De Apostas
May 05, 2025 -
 Gold Fields A 3 7 Billion Gold Road Acquisition Implications For Investors
May 05, 2025
Gold Fields A 3 7 Billion Gold Road Acquisition Implications For Investors
May 05, 2025 -
 Alleged Torture Starvation And Beatings Stepfather Charged In 16 Year Old Stepsons Death
May 05, 2025
Alleged Torture Starvation And Beatings Stepfather Charged In 16 Year Old Stepsons Death
May 05, 2025 -
 Anna Kendricks Concise Blake Lively Opinion Captivates Fans
May 05, 2025
Anna Kendricks Concise Blake Lively Opinion Captivates Fans
May 05, 2025 -
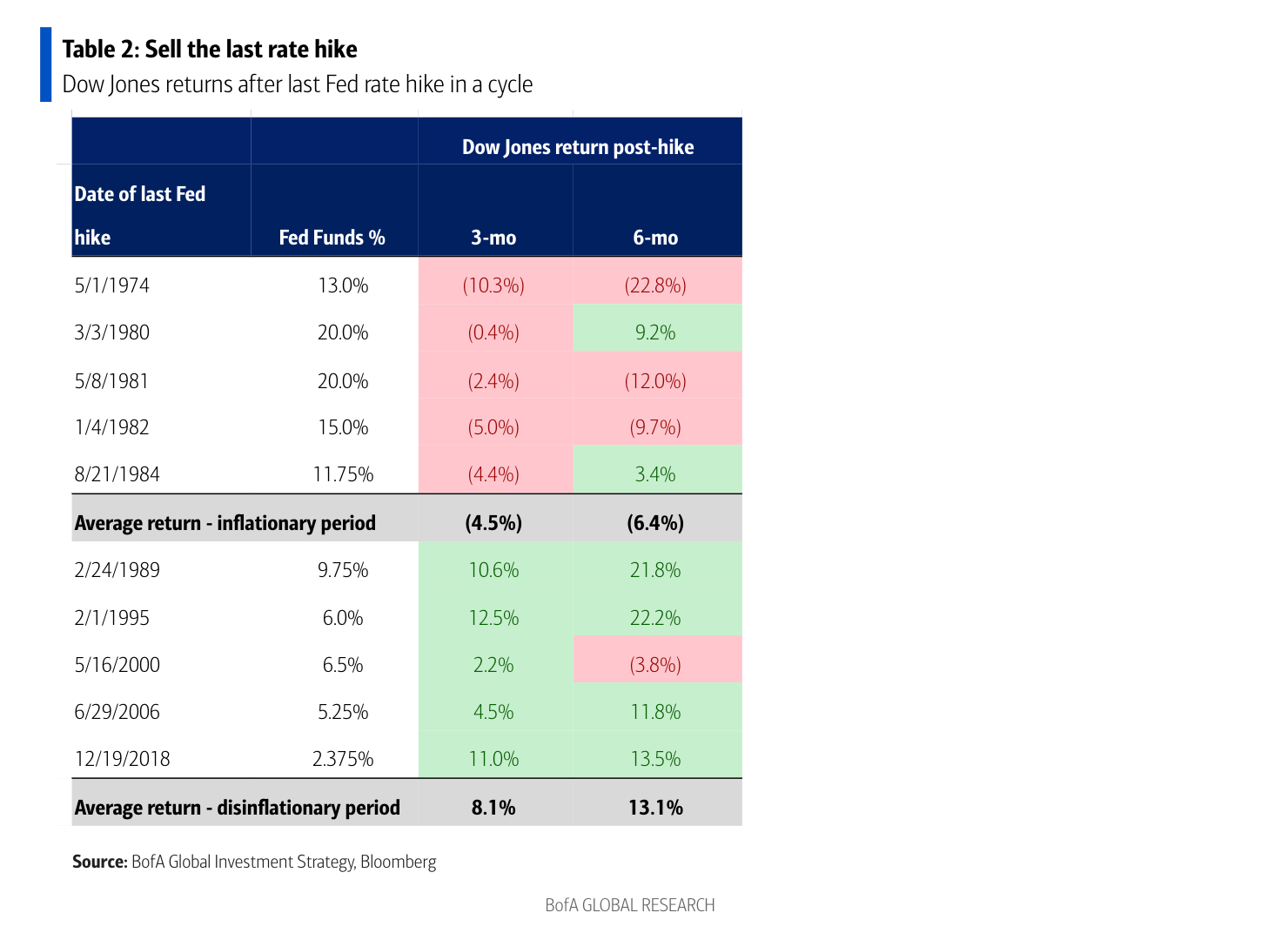 Should Investors Worry About Stretched Stock Market Valuations Bof A Weighs In
May 05, 2025
Should Investors Worry About Stretched Stock Market Valuations Bof A Weighs In
May 05, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Podcast Creation Utilizing Ai To Process Repetitive Scatological Documents
May 06, 2025
Podcast Creation Utilizing Ai To Process Repetitive Scatological Documents
May 06, 2025 -
 Ai Digest Transforming Repetitive Scatological Data Into Engaging Podcast Content
May 06, 2025
Ai Digest Transforming Repetitive Scatological Data Into Engaging Podcast Content
May 06, 2025 -
 Turning Trash To Treasure An Ai Powered Podcast From Scatological Documents
May 06, 2025
Turning Trash To Treasure An Ai Powered Podcast From Scatological Documents
May 06, 2025 -
 The Ryujinx Emulator Development Stopped Due To Nintendo
May 06, 2025
The Ryujinx Emulator Development Stopped Due To Nintendo
May 06, 2025 -
 Covid 19 Pandemic Lab Owners Guilty Plea For Fake Test Results
May 06, 2025
Covid 19 Pandemic Lab Owners Guilty Plea For Fake Test Results
May 06, 2025
