COVID-19 Vaccines: A Potential Shield Against Long COVID
Table of Contents
Reduced Risk of Initial COVID-19 Infection
The Foundation of Protection:
Vaccination significantly reduces your chances of contracting COVID-19 in the first place. This is the most fundamental way vaccines combat Long COVID. By preventing infection, you eliminate the primary risk factor for developing this complex condition.
- Lower viral load: Even if a breakthrough infection occurs in a vaccinated individual, the viral load is typically much lower than in unvaccinated individuals. This reduced viral burden minimizes the potential for lasting damage to organs and systems.
- Less severe initial illness: A milder initial infection, thanks to vaccination, translates to a lower likelihood of developing long-term complications. The body's immune system is better prepared to fight off the virus, limiting the duration and severity of the illness.
- Data supporting reduced risk: Numerous studies from organizations like the CDC and WHO demonstrate a strong correlation between COVID-19 vaccination and reduced infection rates. [Insert links to relevant studies from CDC and WHO]. These studies consistently show that vaccinated individuals are less likely to contract COVID-19, and if they do, they experience a less severe illness.
Mitigating the Severity of Long COVID Symptoms
Impact on Organ Systems:
Vaccines may lessen the severity of post-COVID symptoms affecting various organ systems. While the exact mechanisms are still under investigation, emerging research suggests a protective effect.
- Brain fog and cognitive impairment: Studies are exploring the link between vaccination and reduced incidence or severity of brain fog, a common Long COVID symptom. [Insert links to relevant studies]. Early findings are promising, suggesting that vaccination might offer some protection against these cognitive challenges.
- Cardiovascular complications: Research indicates that vaccination may reduce the risk of developing heart problems associated with Long COVID, such as myocarditis or pericarditis. [Insert links to relevant studies]. This protection stems from the vaccine's ability to modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation.
- Respiratory issues: Studies are examining the vaccine's role in preventing persistent breathing problems, such as shortness of breath and chronic cough, characteristic of Long COVID. [Insert links to relevant studies]. Vaccination may help mitigate the severity of lung damage caused by the virus.
- Fatigue and other systemic symptoms: Vaccination might also lessen the intensity and duration of general fatigue and other widespread symptoms like muscle pain, headaches, and digestive issues often associated with Long COVID. [Insert links to relevant studies].
Mechanisms of Protection:
Vaccines achieve these protective effects through several key mechanisms:
- Immune response enhancement: Vaccines stimulate the body's immune system to produce antibodies and T cells that recognize and target the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This enhanced immune response better equips the body to fight off the virus and reduce the likelihood of long-term complications.
- Reduced inflammation: Inflammation plays a significant role in the development of Long COVID. Vaccines may help minimize this inflammatory response, lessening the damage to organs and tissues.
Vaccine Types and Effectiveness Against Long COVID
mRNA Vaccines:
mRNA vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) have demonstrated high efficacy in preventing COVID-19 infection and reducing the severity of illness. Studies suggest these vaccines may also offer significant protection against Long COVID. [Insert links to relevant studies].
Viral Vector Vaccines:
Viral vector vaccines (AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson) also offer protection against COVID-19 and may contribute to mitigating Long COVID risk. However, their effectiveness might vary compared to mRNA vaccines. [Insert links to relevant studies]. Further research is needed to fully understand their role in preventing Long COVID.
Booster Shots:
Booster shots are crucial for maintaining high levels of immunity over time. Data suggests that booster doses further reduce the risk of infection and severe illness, potentially offering enhanced protection against Long COVID. [Insert links to relevant studies]. Staying up-to-date with recommended booster shots is vital.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation
Debunking Myths:
Misinformation about COVID-19 vaccines is prevalent. It is crucial to address common myths and misconceptions directly. For example, the claim that vaccines cause Long COVID is false; in fact, the opposite is more likely true. Vaccines significantly reduce the chances of getting COVID-19 in the first place, thus reducing the risk of Long COVID. [Insert links to reputable sources debunking myths].
Importance of Vaccination:
Vaccination remains a vital tool in combating Long COVID and protecting public health. The evidence strongly suggests that vaccination significantly reduces the risk of developing this debilitating condition. Getting vaccinated is a crucial step in safeguarding your well-being and protecting yourself and your community from the long-term consequences of COVID-19.
Conclusion
While more research is needed to fully elucidate the relationship between COVID-19 vaccines and Long COVID, the current body of evidence suggests a strong correlation between vaccination and a reduced risk and severity of this debilitating condition. Vaccination remains a crucial tool in our arsenal against COVID-19 and its long-term consequences. Don't delay – protecting yourself with a COVID-19 vaccine is a significant step in safeguarding your health and potentially avoiding the protracted suffering of Long COVID. Consult your healthcare provider to determine the best vaccination strategy for you and learn more about protecting yourself from Long COVID through effective COVID-19 vaccination.

Featured Posts
-
 Everything You Need To Know About The Nike Air Max Dn8 Shoe
May 29, 2025
Everything You Need To Know About The Nike Air Max Dn8 Shoe
May 29, 2025 -
 Actors Join Writers Strike Hollywood Production Grinds To A Halt
May 29, 2025
Actors Join Writers Strike Hollywood Production Grinds To A Halt
May 29, 2025 -
 Bandung Hujan Hingga Sore Prakiraan Cuaca Besok 23 4 Jawa Barat
May 29, 2025
Bandung Hujan Hingga Sore Prakiraan Cuaca Besok 23 4 Jawa Barat
May 29, 2025 -
 Prakiraan Cuaca Jawa Timur 24 Maret 2024 Hujan Di Beberapa Daerah
May 29, 2025
Prakiraan Cuaca Jawa Timur 24 Maret 2024 Hujan Di Beberapa Daerah
May 29, 2025 -
 Morgan Wallens Snl Incident His Explanation And Aftermath
May 29, 2025
Morgan Wallens Snl Incident His Explanation And Aftermath
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 5 Actions To Secure A Position In The Booming Private Credit Sector
May 31, 2025
5 Actions To Secure A Position In The Booming Private Credit Sector
May 31, 2025 -
 The Private Credit Job Hunt 5 Dos And Don Ts For Success
May 31, 2025
The Private Credit Job Hunt 5 Dos And Don Ts For Success
May 31, 2025 -
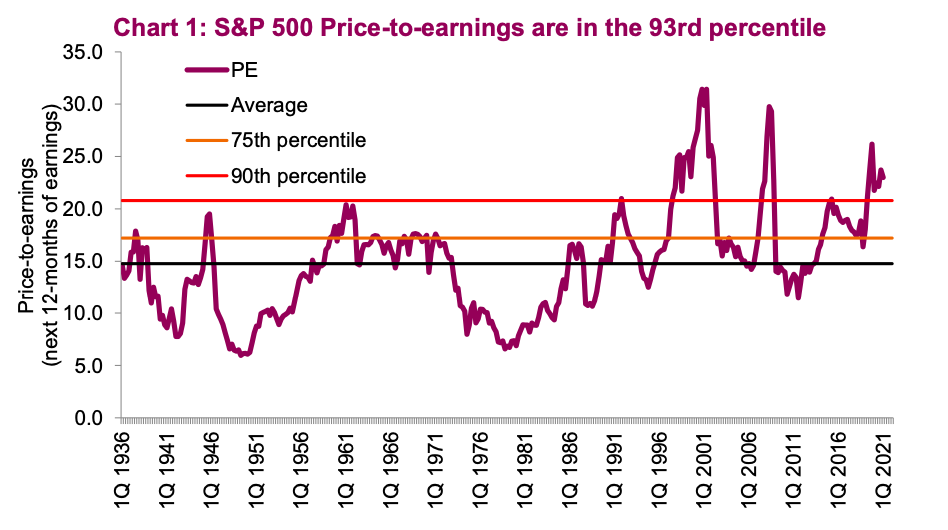 Are High Stock Market Valuations Justified Bof As Analysis
May 31, 2025
Are High Stock Market Valuations Justified Bof As Analysis
May 31, 2025 -
 Successfully Navigating The Private Credit Job Search 5 Key Strategies
May 31, 2025
Successfully Navigating The Private Credit Job Search 5 Key Strategies
May 31, 2025 -
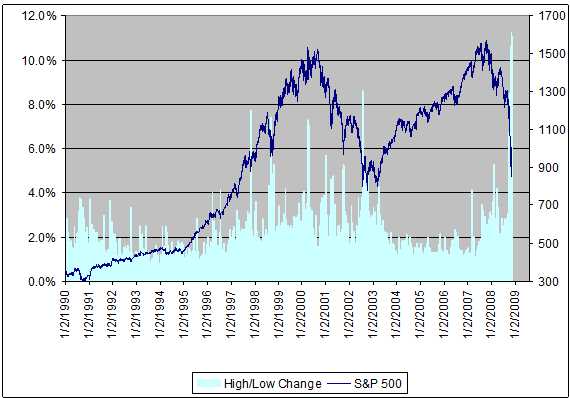 Bof As View Why Elevated Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Cause For Alarm
May 31, 2025
Bof As View Why Elevated Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Cause For Alarm
May 31, 2025
