Saskatchewan And Western Separation: A Political Panel Analysis

Table of Contents
Recent polls showing a significant rise in support for Western Canadian separatism have ignited a fiery debate across the prairies. This surge in sentiment underscores the growing concern over Western alienation and has brought the topic of "Saskatchewan and Western Separation" to the forefront of Canadian political discourse. While Western alienation has been a simmering issue for decades, fueled by perceptions of economic and political marginalization, recent events have intensified the conversation, prompting serious consideration of the potential consequences of a separated West. This article analyzes the arguments for and against Western separation, focusing specifically on Saskatchewan's pivotal role, as revealed through a recent political panel discussion.
H2: Economic Arguments for and Against Western Separation
H3: The Economic Case for Separation:
Proponents of Western separation often point to the substantial resource wealth concentrated in Saskatchewan and other Western provinces as a primary justification for independence. The argument centers on the perceived unfair distribution of tax revenue, where Western provinces contribute significantly to the national economy but receive disproportionately less in federal funding. This perceived inequity fuels the desire for greater economic autonomy and control over resource development.
- Resource Industries: Saskatchewan's economy relies heavily on resource extraction, notably potash, uranium, and agriculture. These industries generate significant wealth, contributing substantially to the Canadian GDP. Similar resource-rich provinces like Alberta (oil and gas) further strengthen the economic argument for separation.
- Funding Inequities: Critics point to the federal equalization program as a prime example of unfair distribution. They argue that the formula disadvantages resource-rich provinces, leading to a net outflow of wealth to less prosperous regions.
H3: The Economic Case Against Separation:
Conversely, opponents highlight the significant economic disruption that separation would likely cause. The transition to independence would be costly, requiring the establishment of new institutions, including a central bank, regulatory bodies, and trade agreements. This process would undoubtedly disrupt economic activity and potentially damage investor confidence.
- Trade Disruption: Separation could severely impact trade relationships with the rest of Canada and international markets, leading to economic instability and potentially higher costs for consumers. Existing trade agreements would need to be renegotiated, a process that is both complex and time-consuming.
- Institutional Costs: Establishing a new central bank, legal framework, and other essential governmental structures would demand substantial financial resources, diverting funds from other crucial areas. The potential for increased national debt adds further weight to this argument.
H2: Political and Social Arguments for and Against Western Separation
H3: The Political Case for Separation:
Many supporters of Western separation emphasize a deep-seated feeling of political marginalization within the Canadian federation. They believe that the interests of Western provinces are consistently overlooked in federal decision-making, leading to a sense of powerlessness and resentment. Moreover, a strong regional identity and distinct cultural values underpin the desire for self-determination.
- Political Grievances: Specific policy decisions, such as federal environmental regulations perceived as detrimental to the energy sector, often fuel the argument for separation.
- Regional Identity: The unique cultural and historical experiences of Western Canada, distinct from those in Central and Eastern Canada, reinforce the desire for greater political autonomy.
H3: The Political Case Against Separation:
The counterargument emphasizes the potential for political instability and conflict arising from separation. The benefits of remaining within a unified Canadian federation, including access to shared resources and a stable political framework, are often highlighted. Furthermore, establishing new political institutions and navigating the complexities of international relations after separation represent significant challenges.
- Political Instability: Separation could lead to border disputes and other forms of inter-provincial conflict, creating a volatile political landscape.
- Institutional Challenges: Creating new political and legal systems would require considerable time, effort, and resources.
H2: Saskatchewan's Unique Position in the Debate
Saskatchewan occupies a unique position in the Western separation debate. Its economy is heavily reliant on resource extraction, making it particularly susceptible to the economic consequences of separation. However, diverse opinions exist within the province regarding the merits of independence. Some advocate for separation to gain greater control over resources and political decision-making, while others emphasize the benefits of remaining within a unified Canada.
- Economic Vulnerability: Saskatchewan's dependence on resource-based industries makes its economy particularly vulnerable to shifts in global markets and changes to trade policies.
- Diversity of Opinion: While some advocate for separation, many Saskatchewan residents prioritize the stability and economic benefits offered by remaining within the Canadian federation.
Conclusion: Assessing the Future of Saskatchewan and Western Separation
The political panel discussion highlighted a complex interplay of economic, political, and social factors driving the debate surrounding Saskatchewan and Western separation. While the economic advantages of greater control over resources are undeniable for some, the potential economic disruptions and political instability resulting from separation are significant concerns. Saskatchewan's unique economic and political landscape makes its role in this debate particularly critical. The likelihood of actual separation remains uncertain, dependent on evolving economic conditions, political shifts, and the prevailing public opinion. Understanding the nuances of this complex issue is crucial. We encourage you to delve deeper into the topic of "Saskatchewan and Western Separation," exploring relevant government websites, academic research, and political commentary to stay informed on this crucial issue shaping the future of Western Canada.

Featured Posts
-
 Vodacoms Vod Improved Earnings Drive Higher Than Expected Payout
May 21, 2025
Vodacoms Vod Improved Earnings Drive Higher Than Expected Payout
May 21, 2025 -
 Premier League 2024 25 Champions Photo Celebration
May 21, 2025
Premier League 2024 25 Champions Photo Celebration
May 21, 2025 -
 Beenie Mans It A Stream Event A New Era In New York Concerts
May 21, 2025
Beenie Mans It A Stream Event A New Era In New York Concerts
May 21, 2025 -
 Tory Wifes Jail Sentence Stands After Southport Migrant Remarks
May 21, 2025
Tory Wifes Jail Sentence Stands After Southport Migrant Remarks
May 21, 2025 -
 Ea Sports Fc 24 Fut Birthday Ultimate Team Player Tier List Guide
May 21, 2025
Ea Sports Fc 24 Fut Birthday Ultimate Team Player Tier List Guide
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Brexits Toll Uk Luxury Exports Struggle In The Eu Market
May 21, 2025
Brexits Toll Uk Luxury Exports Struggle In The Eu Market
May 21, 2025 -
 Are Bmw And Porsche Losing Their Grip On The Chinese Market
May 21, 2025
Are Bmw And Porsche Losing Their Grip On The Chinese Market
May 21, 2025 -
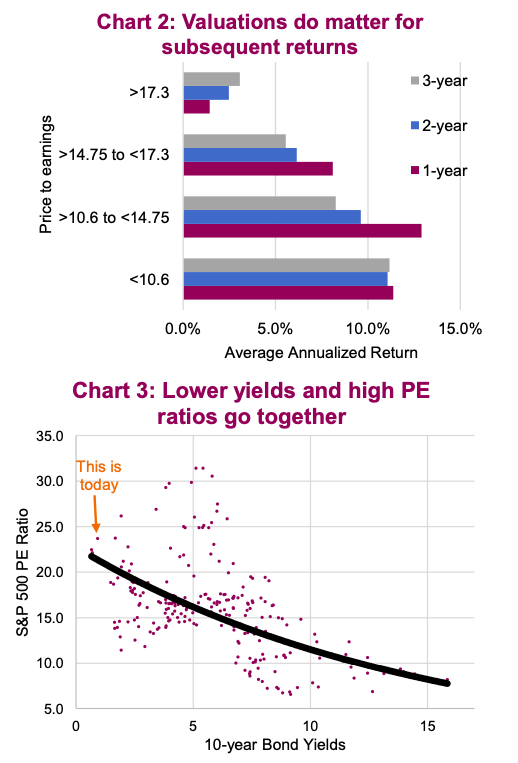 Understanding High Stock Market Valuations Bof As Take And Investor Implications
May 21, 2025
Understanding High Stock Market Valuations Bof As Take And Investor Implications
May 21, 2025 -
 Uk Luxury Sector Brexits Contribution To Export Lag In The Eu
May 21, 2025
Uk Luxury Sector Brexits Contribution To Export Lag In The Eu
May 21, 2025 -
 The China Factor Why Bmw And Porsche Are Facing Headwinds
May 21, 2025
The China Factor Why Bmw And Porsche Are Facing Headwinds
May 21, 2025
